Abstract
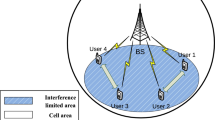
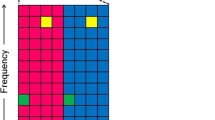
In this paper, we consider the problem of distributed scheduling for overlay inband device-to-device (D2D) communication systems that employ an orthogonal frequency division multiple access physical layer technology. To improve the spatial reuse gain, we propose a multi-channel-based scheduling algorithm that divides the overall radio resource dedicated to D2D communication into multiple data channels and schedules the links allocated to each channel based on a signal-to-interference-aware priority-based scheduling method. Further, we develop a cross-layer queueing model to analyze the medium-access-control layer performance of the proposed scheduling algorithm and compare the analytic results with the simulation results. We demonstrate that the proposed scheduling algorithm outperforms the existing single one-channel-based algorithm to provide lower packet dropping probability, higher spectral efficiency, and lower packet delay.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corson, M. S., Laroia, R., Li, J., Par, V., Richardson, T., & Tsirtsis, G. (2010). Toward proximity-aware internetworking. IEEE Wireless Communications Magazines, 17(6), 26–33.
Lei, L., Zhong, Z., Lin, C., & Shen, X. (2012). Operator controlled device-to-device communications in LTE-advanced networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Magazines, 19(3), 96–104.
Asadi, M., Wang, Q., & Mancuso, V. (2014). A survey on device-to-device communication in cellular networks. In IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 16(4), 1801–1819. 4th Quater.
Lin, X., Andrews, J. G., Ghosh, A., & Ratasuk, R. (2014). An overview of 3GPP device-to-device proximity services. IEEE Wireless Communications Magazine, 52(4), 40–48.
Liu, J., Sheng, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Sun, H., & Shi, Y. (2013). A distributed opportunistic scheduling protocol for device-to-device communications. In 2013 IEEE 24th International Symposium on Personal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), pp. 1715–1719.
IEEE Std 802.11-2012. (2012). In Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications, IEEE.
Xu, K., Gerla, M., & Bae, S. (2002). How effective is the IEEE 802.11 RTS/CTS handshake in ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM, Taipei, pp. 72–76.
Kuang, T., & Williamson, C. (2004). A bidirectional multi-channel MAC protocol for improving TCP performance on multihop wireless ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the ACM MSWiM, Venice, pp. 301–310.
Zhai, H., Wang, J., & Fang, Y. (2006). DUCHA: A new dual-channel MAC protocol for multihop ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(11), 3224–3233.
Su, H., & Zhang, X. (2008). Cross-layer based opportunistic MAC protocols for QoS provisionings over cognitive radio wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas Communications, 26(1), 118–129.
Bui, L., Eryilmaz, A., Srikant, R., & Wu, X. (2008). Asynchronous congestion control in multi-hop wireless networks with maximal matching-based scheduling. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 16(4), 826–839.
Bui, L., Sanghavi, S., & Srikant, R. (2009). Distributed link scheduling with constant overhead. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 17(5), 1467–1480.
Wu, X., Tavildar, S., Shakkottai, S., Richardson, T., Li, J., & Laroia, R. (2013). FlashLinQ: A synchronous distributed scheduler for peer-to-peer ad hoc Networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 21(4), 1215–1228.
Lin, X., Andrews, J. G., & Ghosh, A. (2014). Spectrum sharing for device-to-device communication in cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communication, 13(12), 6727–6740.
Naderializadeh, N., & Avestimehr, A. S. (2014). ITLinQ: A new approach for spectrum sharing in device-to-device communication systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas Communications, 32(6), 1139–1151.
Liu, Q., Zhou, S., & Giannakis, G. B. (2005). Queuing with adaptive modulation and coding over wireless links: Cross-layer analysis and design. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 4(3), 1142–1153.
Huang, W. L., & Letaief, K. B. (2007). Cross-layer scheduling and power control combined with adaptive modulation for wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 55(4), 728–739.
Rashid, M. M., Hossain, M. J., Hossain, E., & Bhargava, V. K. (2009). Opportunistic spectrum scheduling for multiuser cognitive radio: A queueing analysis. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(10), 5259–5269.
Lei, L., Zhang, Y., Shen, X., Lin, C., & Zhong, Z. (2013). Performance analysis of device-to-device communications with dynamic interference using stochastic Petri Nets. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(12), 6121–6141.
Weber, S. P., Andrews, J. G., & Veciana, G. (2005). Transmission capacity of wireless ad hoc networks with outage constraints. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(12), 4091–4102.
Haenggi, M., Andrews, J. G., Baccelli, F., Dousse, O., & Franceschetti, M. (2009). Stochastic geometry and random graphs for the analysis and design of wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas Communications, 27(7), 1029–1049.
Neuts, M. F. (1981). Matrix geometric solutions in stochastic modelsan algorithmic approach. Baltimore, MD: John Hopkins Univ. Press.
Bertsekas, Dimitri P., & Gallager, R. (2006). Data networks. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
ITU-R Rec. P.1411-6. (2012). In Propagation data and prediction methods for the planning of short-range outdoor radiocommunication systems and radio local area networks in the frequency range 300 MHz to 100 GHz, ITU-R.
ETSI TR 36.942 LTE. (2011). Evolved universal terrestrial radio access (E-UTRA); radio frequency (RF) system scenarios (Release 10) V10.2.0.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2013R1A1A2011098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DH., Oh, SJ. & Lim, J. Multi-channel-based scheduling for overlay inband device-to-device communications. Wireless Netw 23, 2587–2600 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1306-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1306-z