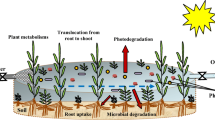
Abstract
Heavy metals and metalloids (HMMs) pose a serious threat to both environmental and human health. The unique characteristics and environmental toxicity of HMMs make their removal from the environment a major challenge. Constructed wetlands (CWs) are increasingly being used as an eco-friendly system for the removal of HMMs from aqueous environments. In this review, bibliometric analysis was performed using the Scopus database using VOSviewer software to assess the developing use of CWs in recent years. Heavy metal and metalloid (HMM) removal pathways were reviewed (such as precipitation, co-precipitation, adsorption and ion exchange, plant action and microbial action) along with the impact of key factors (pH, chemical oxygen demand, dissolved oxygen, HMM concentration, and temperature). This review aimed to establish the connections between published results, to help effectively optimize the use of CWs for the removal of HMMs and identify the most critical factors for their effective removal. Important aspects that require further research include assessing the synergistic toxicity between different pollutants and combining the use of CWs with other technologies to optimize pollutant remediation efficiency.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Ali S, Abbas Z, Rizwan M, Zaheer IE, Yavaş İ, Ünay A, Abdel-DAIM MM, Bin-Jumah M, Hasanuzzaman M, Kalderis D (2020) Application of floating aquatic plants in phytoremediation of heavy metals polluted water: a review. Sustainability 12:1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051927
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetr 11:959–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Batool A, Saleh TA (2020) Removal of toxic metals from wastewater in constructed wetlands as a green technology; catalyst role of substrates and chelators. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:109924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109924
Bowman N, Patel D, Sanchez A, Xu W, Alsaffar A, Tiquia-Arashiro SM (2018) Lead-resistant bacteria from Saint Clair River sediments and Pb removal in aqueous solutions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:2391–2398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8772-4
Bradl HB (2004) Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J Colloid Interface Sci 277:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.04.005
Chen J, Li X, Jia W, Shen S, Deng S, Ji B, Chang J (2021) Promotion of bioremediation performance in constructed wetland microcosms for acid mine drainage treatment by using organic substrates and supplementing domestic wastewater and plant litter broth. J Hazard Mater 404:124125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124125
Chimney MJ, Pietro KC (2006) Decomposition of macrophyte litter in a subtropical constructed wetland in south Florida (USA). Ecol Eng 27:301–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2006.05.016
Cohen RRH (2006) Use of microbes for cost reduction of metal removal from metals and mining industry waste streams. J Clean Prod 14:1146–1157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.10.009
de Groot NS, Ventura S (2006) Effect of temperature on protein quality in bacterial inclusion bodies. FEBS Lett 580:6471–6476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.10.071
Deng J, Guo P, Zhang X, Su H, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Li Y (2020) Microplastics and accumulated heavy metals in restored mangrove wetland surface sediments at Jinjiang Estuary (Fujian, China). Mar Pollut Bull 159:111482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111482
Dey P, Malik A, Mishra A, Singh DK, von Bergen M, Jehmlich N (2020) Mechanistic insight to mycoremediation potential of a metal resistant fungal strain for removal of hazardous metals from multimetal pesticide matrix. Environ Pollut 262:114255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114255
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
Gandy CJ, Davis JE, Orme PHA, Potter HAB, Jarvis AP (2016) Metal removal mechanisms in a short hydraulic residence time subsurface flow compost wetland for mine drainage treatment. Ecol Eng 97:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.09.011
Gomes HI, Mayes WM, Whitby P, Rogerson M (2019) Constructed wetlands for steel slag leachate management: partitioning of arsenic, chromium, and vanadium in waters, sediments, and plants. J Environ Manag 243:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.127
Guo X, Cui X, Li H, Xiong B (2021) Purifying effect of biochar-zeolite constructed wetlands on arsenic-containing biogas slurry in large-scale pig farms. J Clean Prod 279:123579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123579
Hua T, Haynes RJ (2016) Constructed wetlands: fundamental processes and mechanisms for heavy metal removal from wastewater streams. Int J Environ Eng 8:148–178. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEE.2016.10003208
Hua T, Haynes RJ, Zhou YF (2018) Potential use of two filter media in constructed wetlands for simultaneous removal of As, V and Mo from alkaline wastewater - Batch adsorption and column studies. J Environ Manag 218:190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.038
Hua T, Haynes RJ, Zhou YF, Boullemant A, Chandrawana I (2015) Potential for use of industrial waste materials as filter media for removal of Al, Mo, As, V and Ga from alkaline drainage in constructed wetlands—adsorption studies. Water Res 71:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.12.036
Huang J, Cai W, Zhong Q, Wang S (2013) Influence of temperature on micro-environment, plant eco-physiology and nitrogen removal effect in subsurface flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 60:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.07.023
Jacob JM, Karthik C, Saratale RG, Kumar SS, Prabakar D, Kadirvelu K, Pugazhendhi A (2018) Biological approaches to tackle heavy metal pollution: a survey of literature. J Environ Manag 217:56–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.077
Kataki S, Chatterjee S, Vairale MG, Dwivedi SK, Gupta DK (2021) Constructed wetland, an eco-technology for wastewater treatment: a review on types of wastewater treated and components of the technology (macrophyte, biolfilm and substrate). J Environ Manag 283:111986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.111986
Kosolapov DB, Kuschk P, Vainshtein MB, Vatsourina AV, Wießner A, Kästner M, Müller RA (2004) Microbial processes of heavy metal removal from carbon-deficient effluents in constructed wetlands. Eng Life Sci 4:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200420048
Li Q, Liu J, Gadd GM (2020) Fungal bioremediation of soil co-contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons and toxic metals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:8999–9008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10854-y
Li S, Zhao B, Jin M, Hu L, Zhong H, He Z (2020) A comprehensive survey on the horizontal and vertical distribution of heavy metals and microorganisms in soils of a Pb/Zn smelter. J Hazard Mater 400:123255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123255
Lizama-Allende K, Ayala J, Jaque I, Echeverría P (2021) The removal of arsenic and metals from highly acidic water in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands with alternative supporting media. J Hazard Mater 408:124832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124832
Lizama AK, Fletcher TD, Sun G (2011) Removal processes for arsenic in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 84:1032–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.022
Lizama Allende K, Fletcher TD, Sun G (2012) The effect of substrate media on the removal of arsenic, boron and iron from an acidic wastewater in planted column reactors. Chem Eng J 179:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.10.069
Ma N, Wang W, Gao J, Chen J (2017) Removal of cadmium in subsurface vertical flow constructed wetlands planted with Iris sibirica in the low-temperature season. Ecol Eng 109:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.09.008
Marchand L, Mench M, Jacob DL, Otte ML (2010) Metal and metalloid removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of plants and standardized measurements: a review. Environ Pollut 158:3447–3461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.08.018
Matagi SV, Swai D, Mugabe R (1998) A review of heavy metal removal mechanisms in wetlands. Afr J Trop Hydrobiol Fish 8:23–35
Mayes WM, Batty LC, Younger PL, Jarvis AP, Kõiv M, Vohla C, Mander U (2009) Wetland treatment at extremes of pH: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:3944–3957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.045
Mufarrege MDLM, Di Luca GA, Hadad HR, Maine MA (2021) Exposure of Typha domingensis to high concentrations of multi-metal and nutrient solutions: study of tolerance and removal efficiency. Ecol Eng 159:106118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.106118
Oyuela Leguizamo MA, Fernández Gómez WD, Sarmiento MCG (2017) Native herbaceous plant species with potential use in phytoremediation of heavy metals, spotlight on wetlands—a review. Chemosphere 168:1230–1247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.075
Rahman KZ, Wiessner A, Kuschk P, van Afferden M, Mattusch J, Müller RA (2014) Removal and fate of arsenic in the rhizosphere of Juncus effusus treating artificial wastewater in laboratory-scale constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 69:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.03.050
Ren G, Jin Y, Zhang C, Gu H, Qu J (2015) Characteristics of Bacillus sp. PZ-1 and its biosorption to Pb(II). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 117:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.03.033
Salama E-S, Roh H-S, Dev S, Khan MA, Abou-Shanab RAI, Chang SW, Jeon B-H (2019) Algae as a green technology for heavy metals removal from various wastewater. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2648-3
Schwindaman JP, Castle JW, Rodgers JH Jr (2014) Fate and distribution of arsenic in a process-designed pilot-scale constructed wetland treatment system. Ecol Eng 68:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.03.049
Seo DC, Yu K, DeLaune RD (2008) Comparison of monometal and multimetal adsorption in Mississippi River alluvial wetland sediment: batch and column experiments. Chemosphere 73:1757–1764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.09.003
Shelef O, Gross A, Rachmilevitch S (2013) Role of plants in a constructed wetland: current and new perspectives. Water 5:405–419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020405
Sheoran AS, Sheoran V (2006) Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: a critical review. Miner Eng 19:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2005.08.006
Stein OR, Borden-Stewart DJ, Hook PB, Jones WL (2007) Seasonal influence on sulfate reduction and zinc sequestration in subsurface treatment wetlands. Water Res 41:3440–3448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.04.023
Thomson B, Hepburn CD, Lamare M, Baltar F (2017) Temperature and UV light affect the activity of marine cell-free enzymes. Biogeosciences 14:3971–3977. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-14-3971-2017
Truu M, Juhanson J, Truu J (2009) Microbial biomass, activity and community composition in constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 407:3958–3971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.11.036
Türker OC, Türe C, Yakar A, Saz Ç (2017) Engineered wetland reactors with different media types to treat drinking water contaminated by boron (B). J Clean Prod 168:823–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.067
Valipour A, Ahn Y-H (2016) Constructed wetlands as sustainable ecotechnologies in decentralization practices: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5713-y
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84:523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Wang X, Li D, Gao P, Gu W, He X, Yang W, Tang W (2020) Analysis of biosorption and biotransformation mechanism of Pseudomonas chengduensis strain MBR under Cd(II) stress from genomic perspective. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 198:110655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110655
Woulds C, Ngwenya BT (2004) Geochemical processes governing the performance of a constructed wetland treating acid mine drainage, Central Scotland. Appl Geochem 19:1773–1783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.04.002
Wu S, Wallace S, Brix H, Kuschk P, Kirui WK, Masi F, Dong R (2015) Treatment of industrial effluents in constructed wetlands: challenges, operational strategies and overall performance. Environ Pollut 201:107–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.03.006
Xu X, Yang Y, Wang G, Zhang S, Cheng Z, Li T, Yang Z, Xian J, Yang Y, Zhou W (2020) Removal of heavy metals from industrial sludge with new plant–based washing agents. Chemosphere 246:125816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125816
Yıldırım K, Kasım GÇ (2018) Phytoremediation potential of poplar and willow species in small scale constructed wetland for boron removal. Chemosphere 194:722–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.036
Yin K, Lv M, Wang Q, Wu Y, Liao C, Zhang W, Chen L (2016) Simultaneous bioremediation and biodetection of mercury ion through surface display of carboxylesterase E2 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA1. Water Res 103:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.053
Yin K, Wang Q, Lv M, Chen L (2019) Microorganism remediation strategies towards heavy metals. Chem Eng J 360:1553–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.226
Yu G, Peng H, Fu Y, Yan X, Du C, Chen H (2019) Enhanced nitrogen removal of low C/N wastewater in constructed wetlands with co-immobilizing solid carbon source and denitrifying bacteria. Bioresour Technol 280:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.043
Yu G, Wang G, Li J, Chi T, Wang S, Peng H, Chen H, Du C, Jiang C, Liu Y, Zhou L, Wu H (2020) Enhanced Cd2+ and Zn2+ removal from heavy metal wastewater in constructed wetlands with resistant microorganisms. Bioresour Technol 316:123898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123898
Zazo JA, Paull JS, Jaffe PR (2008) Influence of plants on the reduction of hexavalent chromium in wetland sediments. Environ Pollut 156:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.01.006
Zhang W, Chen L, Liu D (2012) Characterization of a marine-isolated mercury-resistant Pseudomonas putida strain SP1 and its potential application in marine mercury reduction. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1305–1314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3454-5
Zhang W, Yin K, Li B, Chen L (2013) A glutathione S-transferase from Proteus mirabilis involved in heavy metal resistance and its potential application in removal of Hg2+. J Hazard Mater 261:646–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.023
Zhang X, Wang T, Xu Z, Zhang L, Dai Y, Tang X, Tao R, Li R, Yang Y, Tai Y (2020) Effect of heavy metals in mixed domestic-industrial wastewater on performance of recirculating standing hybrid constructed wetlands (RSHCWs) and their removal. Chem Eng J 379:122363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122363
Zhao M, Wang S, Wang H, Qin P, Yang D, Sun Y, Kong F (2019) Application of sodium titanate nanofibers as constructed wetland fillers for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Environ Pollut 248:938–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.040
Zhao Q, Huang J-C, He S, Zhou W (2020) Enhancement of a constructed wetland water treatment system for selenium removal. Sci Total Environ 714:136741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136741
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51308069), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (No. 2021JJ30728), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department [Project Contract No. 19A032], and the Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province [Project Contract No. XSKJ2019081-41].
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51308069), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (No. 2021JJ30728), the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department [Project Contract No. 19A032], and the Water Conservancy Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province [Project Contract No. XSKJ2019081-41].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft. PL: Writing—original draft. GW: Writing—original draft. JW: Formal analysis. YZ: Formal analysis, Visualization. SW: Formal analysis, Visualization. KY: Visualization. CD: Visualization. HC: Supervision, Validation, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no confict of interest.
Informed consent
If the article is accepted for publication, the transfer of copyright from the author to this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, G., Li, P., Wang, G. et al. A review on the removal of heavy metals and metalloids by constructed wetlands: bibliometric, removal pathways, and key factors. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37, 157 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03123-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03123-1