Abstract
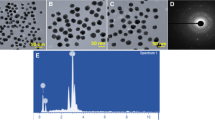
Saponins are glycosides, which destabilize the membrane by altering the membrane permeability. Thus, the present study was aimed to fabricate the silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using fenugreek derived saponin (SN) against multi-drug resistant bacteria. This study has optimized the concentration of SN (240 mg/mL) for the synthesis of an effective AgNPs against the test organism Escherichia coli. The SN reduced AgNPs produced a reddish-brown colour and displayed UV absorption at 416 nm. The bio-reducing efficiency of SN (62.76%) was calculated from the HPLC quantitation of free SN in the colloidal solution of AgNPs. The FESEM-EDAX analysis of SN-AgNPs revealed a spherical shape and showed signals for elemental silver along with carbon and oxygen. The spherical morphology of SN-AgNPs was also confirmed from its TEM and AFM micrographs and their sizes were found in between 2–15 nm. The hydrodynamic size, zeta potential and crystalline nature of SN-AgNPs were studied by DLS and XRD analyses and were found to be 9–30 nm, −18 mV and fcc crystallinity respectively. The FT-IR analysis of SN-AgNPs revealed that the functional groups such as C–O, C=C, C=O and O–H of SN are involved in the reduction and stability of AgNPs. The SN-AgNPs have depicted a notable in vitro structural stability and showed a remarkable antibacterial activity against the bacterial species, related to severe burn wound infections. In conclusion, the findings of our study clearly demonstrate that the SN-AgNPs conjugate would be a novel effective antibacterial agent for the prevention/eradication of multi-drug resistant bacterial infections in severe burn wounds.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S (2016) A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res 7:17–28. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
Amin M, Anwar F, Janjua MRSA, Iqbal MA, Rashid U (2012) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through reduction with Solanum xanthocarpum L. berry extract: characterization, antimicrobial and urease inhibitory activities against Helicobacter pylori. Int J Mol Sci 13:9923–9941. doi:10.3390/ijms13089923
Ankanna S, Prasad TNVKV, Elumalai EK, Savithramma N (2010) Production of biogenic silver nanoparticles using Boswellia Ovalifoliolata stem bark. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 5:369–372
Arabski M, Wȩgierek-Ciuk A, Czerwonka G, Lankoff A, Kaca W (2012) Effects of saponins against clinical E. coli strains and eukaryotic cell line. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:1–6. doi:10.1155/2012/286216
AshaRani PV, Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S (2009) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 3:279–290. doi:10.1021/nn800596w
Banerjee P, Nath D (2015) A phytochemical approach to synthesize silver nanoparticles for non-toxic biomedical application and study on their antibacterial efficacy. Nanosci Technol 2:1–14
Bankura KP, Maity D, Mollick MMR, Mondal D, Bhowmick B, Bain MK, Chakraborty A, Sarkar J, Acharya K, Chattopadhyay D (2012) Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of dextran stabilized silver nanoparticles in aqueous medium. Carbohydr Polym 89:1159–1165. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.089
Baumann E, Stoya G, Völkner A, Richter W, Lemke C, Lins W (2000) Hemolysis of human erythrocytes with saponin affects the membrane structure. Acta Histochem 102:21–35. doi:10.1078/0065-1281-00534
Chitra M, Dhamodar P, Chandru R, Vijaya Kumara Swamy HV (2014) Antimicrobial and phytochemical analysis of acetone extract of Trigonella foenumgrecum seeds. Int J Res Sci Innov 1:44–48
Francis G, Kerem Z, Makkar HP, Becker K (2002) The biological action of saponins in animal systems: a review. Br J Nutr 88:587–605. doi:10.1079/BJN2002725
Geethalakshmi R, Sarada DVL (2013) Characterization and antimicrobial activity of gold and silver nanoparticles synthesized using saponin isolated from Trianthema decandra L. Ind Crops Prod 51:107–115. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.08.055
Gengan RM, Anand K, Phulukdaree A, Chuturgoon A (2013) A549 lung cell line activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Albizia adianthifolia leaf. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 105:87–91. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.12.044
Ibrahim HMM (2015) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J Radiat Res App Sci 8:265–275. doi:10.1016/j.jrras.2015.01.007
Jacob MC, Favre M, Bensa JC (1991) Membrane cell permeabilisation with saponin and multiparametric analysis by flow cytometry. Cytometry 12:550–558. doi:10.1002/cyto.990120612
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim JH, Park SJ, Lee HJ, Kim YK (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3:95–101. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2006.12.001
Kumar B, Smita K, Cumbal L, Debut A (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) leaf extracts. Saudi J Biol Sci 21:605–609. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.07.004
Li Q, Zhang Z, Haque SS, Zhang M, Xia L (2010) Localized surface plasmon resonance effects by naturally occurring Chinese yam particles. J Appl Phys 108:123502. doi:10.1063/1.3520667
Marambio-Jones C, Hoek EMV (2010) A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J Nanopart Res 12:1531–1551. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-9900-y
Meena RK, Chouhan N (2015) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from plant (fenugreek seeds) reducing method and their optical properties. Res J Rec Sci 4:47–52
Mollick MMR, Rana D, Dash SK, Chattopadhyay S, Bhowmick B, Maity D, Mondal D, Pattanayak S, Roy S, Chakraborty M, Chattopadhyay D (2015) Studies on green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) pulp extract having anticancer (in vitro) and antimicrobial applications. Arab J Chem. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.04.033
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramírez JT, Yacaman MJ (2005) The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnol 16:2346–2353. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/059
Nel AE, Mädler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EMV, Somasundaran P, Klaessiq F, Castranova V, Thompson M (2009) Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat Mater 8:543–557. doi:10.1038/nmat2442
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ microbiol 73:1712–1720. doi:10.1128/AEM.02218-06
Pooloth J (2013) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum graecum and the determination of their antimicrobial activity. Int J Sci Res 2:287–290
Rhiouani H, Settaf A, Lyoussi B, Cherrah Y, Lacaille-Dubois MA, Hassar M (1998) Effects of saponins from Herniaria glabra on blood pressure and renal function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Therapie 54:735–739
Rosarin FS, Mirunalini S (2011) Nobel metallic nanoparticles with novel biomedical properties. J Bioanal Biomed 3:85–91. doi:10.4172/1948-593X.1000049
Rupasinghe HP, Jackson CJ, Poysa V, Di Berardo C, Bewley JD, Jenkinson J (2003) Soyasapogenol A and B distribution in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) in relation to seed physiology, genetic variability, and growing location. J Agric Food Chem 51:5888–5894. doi:10.1021/jf0343736
Singh RP, Magesh S, Rakkiyappan C (2011) Formation of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) extract mediated Ag nanoparticles: mechanism and applications. Int J Bio-Eng Sci Tech 2:70–80
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B (2004) Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:177–182. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012
Sparg SG, Light ME, Staden JV (2004) Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J Ethanopharmacol 94:219–243. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2004.05.016
Su HL, Chou CC, Hung DJ, Lin SH, Pao IC, Lin JH, Huang FL, Dong RX, Lin JJ (2009) The disruption of bacterial membrane integrity through ROS generation induced by nanohybrids of silver and clay. Biomaterials 30:5979–5987. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.07.030
Thakkar KN, Mhatre SS, Parikh RY (2010) Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 6:257–262. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2009.07.002
Walli RR, Al-Musrati RA, Eshtewi HM, Sherif FM (2015) Screening of antimicrobial activity of fenugreek seeds. Pharm Pharmacol Int J 2:28–31. doi:10.15406/ppij.2015.02.00028
Wijnhoven SWP, Peijnenburg WJGM, Herberts CA, Hagens WI, Oomen AG, Heugens EHW, Roszek B, Bisschops J, Gosens I, Meent DVD, Dekkers S, De Jong WH, Zijverden MV, Sips AJAM, Geertsma RE (2009) Nano-silver—a review of available data and knowledge gaps in human and environmental risk assessment. Nanotoxicol 3:109–138. doi:10.1080/17435390902725914
Zandonella C (2003) Cell nanotechnology: the tiny toolkit. Nature 423:10–12. doi:10.1038/423010a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muniyan, A., Ravi, K., Mohan, U. et al. Characterization and in vitro antibacterial activity of saponin-conjugated silver nanoparticles against bacteria that cause burn wound infection. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 147 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2309-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2309-3