Abstract
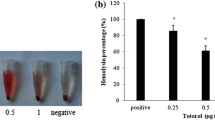
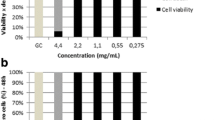
In this study, fennel oil was isolated by hydrodistillation, and the chemical composition was determined by gas chromatography/mass spectral analysis. The antimicrobial activity of fennel oil against Staphylococcus aureus was evaluated by broth microdilution. A haemolysis assay, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) release assay, western blot, and real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR were applied to investigate the influence of fennel oil on the production of S. aureus virulence-related exoproteins. The data show that fennel oil, which contains a high level of trans-anethole, was active against S. aureus, with MICs ranging from 64 to 256 μg/ml. Furthermore, fennel oil, when used at subinhibitory concentrations, could dose-dependently decrease the expression of S. aureus exotoxins, including α-toxin, Staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aprotosoaie AC, Hăncianu M, Poiată A, Tuchiluş C, Spac A, Cioană O, Gille E, Stănescu U (2008) In vitro antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of the essential oil of Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 112:832–836
Arvidson S, Tegmark K (2001) Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Food Microbiol 291:159–170
Benoit-Vical F, Grellier P, Abdoulaye A, Moussa I, Ousmane A, Berry A, Ikhiri K, Poupat C (2006) In vitro and in vivo antiplasmodial activity of Momordica balsamina alone or in a traditional mixture. Chemotherapy 52:288–292
Bernardo K, Pakulat N, Fleer S, Schnaith A, Utermöhlen O, Krut O, Müller S, Krönke M (2004) Subinhibitory concentrations of linezolid reduce Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor expression. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:546–555
Booth MC, Cheung AL, Hatter KL, Jett BD, Callegan MC, Gilmore MS (1997) Staphylococcal accessory regulator (sar) in conjunction with agr contributes to Staphylococcus aureus virulence in endophthalmitis. Infect Immun 65:1550–1556
Carson CF, Cookson BD, Farrelly HD, Riley TV (1995) Susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia. J Antimicrob Chemother 35:421–424
Chan PF, Foster SJ (1998) Role of SarA in virulence determinant production and environmental signal transduction in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 180:6232–6241
Dinges MM, Orwin PM, Schlievert PM (2000) Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Rev 13:16–34
Elgayyar M, Draughon FA, Golden DA, Mount JR (2001) Antimicrobial activity of essential oils from plants against selected pathogenic and saprophytic microorganisms. J Food Prot 64:1019–1024
Herbert S, Barry P, Novick RP (2001) Subinhibitory clindamycin differentially inhibits transcription of exoprotein genes in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 69:2996–3003
Koszczol C, Bernardo K, Krönke M, Krut O (2006) Subinhibitory quinupristin/dalfopristin attenuates virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:564–574
Lee JY, Kim YS, Shin DH (2002) Antimicrobial synergistic effect of linolenic acid and monoglyceride against Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus. J Agric Food Chem 50:2193–2199
Lowy FD (1998) Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 339:520–532
Mohsenzadeh M (2007) Evaluation of antibacterial activity of selected Iranian essential oils against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in nutrient broth medium. Pak J Biol Sci 10:3693–3697
Ohlsen K, Ziebuhr W, Koller KP, Hell W, Wichelhaus TA, Hacker J (1998) Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on alpha-toxin (hla) gene expression of methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42:2817–2823
Qiu J, Feng H, Xiang H, Wang D, Xia L, Jiang Y, Song K, Lu J, Yu L, Deng X (2010a) Influence of subinhibitory concentrations of licochalcone A on the secretion of enterotoxins A and B by Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2:135–141
Qiu J, Wang D, Xiang H, Feng H, Jiang Y, Xia L, Dong J, Lu J, Yu L, Deng X (2010b) Subinhibitory concentrations of thymol reduce enterotoxins A and B and alpha-hemolysin production in Staphylococcus aureus isolates. PLoS One 5:e9736
Senatore F, Rigano D, Formisano C, Grassia A, Basile A, Sorbo S (2007) Phytogrowth-inhibitory and antibacterial activity of Verbascum sinuatum. Fitoterapia 78:244–247
Smith-Palmer A (1999) The antimicrobial properties of plant essential oils against foodborne pathogens. PhD thesis, Queen Margaret University College, Edinburgh, UK
Smith-Palmer A, Stewart J, Fyfe L (1998) Antimicrobial properties of plant essential oils and essences against five important food-borne pathogens. Lett Appl Microbiol 26:118–122
Smith-Palmer A, Stewart J, Fyfe L (2001) The potential application of plant essential oils as natural food preservatives in soft cheese. Food Microbiol 18:463–470
Smith-Palmer A, Stewart J, Fyfe L (2004) Influence of subinhibitory concentrations of plant essential oils on the production of enterotoxins A and B and alpha-toxin by Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol 53:1023–1027
Song L, Hobaugh MR, Shustak C, Cheley S, Bayley H, Gouaux JE (1996) Structure of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore. Science 274:1859–1866
Valero M, Salmeron MC (2003) Antibacterial activity of 11 essential oils against Bacillus cereus in tyndallized carrot broth. Int J Food Microbiol 85:73–81
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 30972212) and the State Key Laboratory for molecular virology and genetic engineering (No. 2011KF02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jiazhang Qiu and Hongen Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Li, H., Su, H. et al. Chemical composition of fennel essential oil and its impact on Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 1399–1405 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0939-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0939-4