Abstract
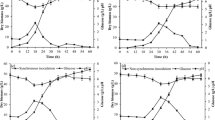
The effect of the ratio of (+) and (−) mating type of Blakeslea trispora on carotene production from deproteinized hydrolysed whey in shake flask culture was investigated. Also, the inoculum ratio of the two mating types on the morphology of the microorganism and the relationship between morphological changes of the fungus and product formation were studied. The concentration of carotenes was significantly affected by the ratio of (+) and (−) mating type of B. trispora. A ratio of 1:10 up to 1:100 of (+) and (−) type was found to achieve the highest carotene yields. The optimum ratio of the (+) and (−) mating types for the maximum pigment production (175.0 mg/g dry biomass at 8 days of fermentation) was found to be 1:10. The carotene content in B. trispora consisted of β-carotene, γ-carotene, and lycopene. At the maximum concentration of carotenes the proportion of β-carotene, γ-carotene, and lycopene (as percent of total carotenes) was 80, 12, and 8%, respectively. B.trispora growing in submerged fermentation is able to develop complex morphologies which have been classified into three major groups: freely dispersed hyphae, clumps and pellets. These parameters are strongly influence the production of carotenes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhosale P, Gadre RV (2001) Carotene production in sugarcane molasses by a Rhodotorula glutinis mutant. J Ind Microbiol Biot 26:327–332
Böhme K, Richter C, Pätz R (2006) Insights into mechanisms of growth and β-carotene production in Blakeslea trispora. Biotechnol J 1:1080–1084
Bu’Lock JD, Jones BE, Quarrie SA, Winstanley DJ (1974) Sexuality in Mucorales. The effect of plus-minus ratio on hormone production by mated cultures. Arch Microbiol 97:239–244
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Dyal SD, Narine SS (2005) Implications for the use of Mortierella fungi in the industrial production of essential fatty acids. Food Res Int 38:445–467
Dyal SD, Bouzidi L, Narine SS (2005) Maximizing the production of γ-linolenic acid in Mortierella ramanniana var. ramanniana as a function of pH, temperature and carbon source, nitrogen source, metal ions and oil supplementation. Food Res Int 38:815–829
Goksungur Y, Mantzouridou F, Roukas T (2002) Optimization of the production of β-carotene from molasses by Blakeslea trispora: a statistical approach. J Chem Technol Biot 77:933–943
Goksungur Y, Mantzouridou F, Roukas T, Kotzekidou P (2004) Production of β-carotene from beet molasses by Blakeslea trispora in stirred-tank and bubble column reactors. Appl Biochem Biotech 112:37–54
Mantzouridou F (2009) The potential of raw glycerol in the production of food grade carotenoids by fungi. In: Aggelis G (ed) Microbial conversions of raw glycerol. Nova Science Publishers, New York, pp 101–124
Mantzouridou F, Roukas T, Kotzekidou P, Liakopoulou M (2002) Optimization of β-carotene production from synthetic medium by Blakeslea trispora. Appl Biochem Biotech 101:153–175
Mantzouridou F, Tsimidou M, Roukas T (2006) Performance of crude olive pomace oil and soybean oil during carotenoid production by Blakeslea trispora in submerged fermentation. J Agr Food Chem 54:2575–2581
Mantzouridou F, Naziri E, Tsimidou M (2008) Industrial glycerol as a supplementary carbon source in the production of β-carotene by Blakeslea trispora. J Agr Food Chem 56:2668–2675
Martelli HL, Silva IM, Souza NO, Pomerou D (1990) Production of β-carotene by a Rhodotorula strain grown on sugar cane juice. Biotechnol Lett 12:207–208
Psani M, Roukas T, Kotzekidou P (2006) Evaluation of cheese whey as substrate for carotenoids production by Blakeslea trispora. Aust J Dairy Technol 61:222
Roukas T, Mantzouridou F, Boumpa TH, Vafiadou A, Goksungur Y (2007) Production of β-carotene from beet molasses and deproteinized whey by Blakeslea trispora. Food Biotechnol 21:195–196
Sutter RP, Whitaker JP (1981) Zygophore-stimulating precursors (pheromones) of trisporic acids active in (-)-phycomyces blakesleeanus. J Biol Chem 256:2334–2341
Takaichi S (2000) Characterization of carotenes in a combination of a C18HPLC column with isocratic elution and absorption spectra with a photodiode-array detector. Photosynth Res 65:93–99
Van den Ende H (1968) Relationship between sexuality and carotene synthesis in Blakeslea trispora. J Bacteriol 96:1298–1303
Zerfiridis GK (2001) Soft cheese. In: Zerfiridis GK (ed) Technology of dairy products. Giahoudi-Giapouli Publishers, Thessaloniki, pp 170–185
Acknowledgments
This paper is part of the 03ED 693 research project, implemented within the framework of the Reinforcement Programme of Human Research Manpower (PENED) and co-financed by National and Community Funds (25% from the Greek Ministry of Development-General Secretariat of Research and Technology and 75% from E.U.-European Social Fund).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varzakakou, M., Roukas, T. & Kotzekidou, P. Effect of the ratio of (+) and (−) mating type of Blakeslea trispora on carotene production from cheese whey in submerged fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 2151–2156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0398-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0398-3