Abstract
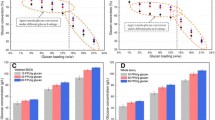
The combined effect of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation and separate hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) for ethanol production by Kluyveromyces marxianus 6556 was studied using two lignocellulosic feedstocks viz., corncob and soybean cake. The ethanologenic efficiency of K. marxianus 6556 was observed as 28% (theoretical yield) in a fermentation medium containing glucose, but, there was no ethanol production by cells grown on xylose. A maximum sugar release of 888 mg/g corncob and 552 mg/g soybean cake was achieved through acid hydrolysis pretreatment. Furthermore, corncob and soybean cake treated with commercial cellulase (100 IU for 48 h) from Trichoderma reesei yielded reducing sugars of 205 and 100 mg/g, respectively. Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation resulted in highest ethanol production of 5.68 g/l on corncob and 2.14 g/l on soybean cake after 48 h of incubation. On the contrary, the presence of inhibitors decreased the overall ethanol yield in the hydrolysates obtained through SHF of corncob and soybean cake.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SHF:
-
Separate hydrolysis and fermentation
- CBS:
-
Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures
- NREL:
-
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
- AOAC:
-
Association of Official Analytical Chemistry
References
Adrados BP, Choteborska P, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2005) Ethanol production from non-starch carbohydrates of wheat bran. Bioresour Technol 96:843–850
Balat M, Balat H, Cahide ÖZ (2008) Progress in bioethanol processing. Prog Energy Combust Sci 34:551–573
Ballesteros M, Oliva JM, Negro MJ, Manzanares P, Ballestros I (2004) Ethanol from lignocellulosic materials by a simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process (SFS) with Kluyveromyces marxianus CECT 10875. Proc Biochem 39:1843–1848
Cardona CA, Sanchez OJ (2007) Fuel ethanol production: process design trends and integration opportunities. Bioresour Technol 98:2415–2457
Chandel AK, Chan ES, Ravinder R, Lakshmi M, Venkateswar NR, Pogaku R (2007) Economics and environmental impact of bioethanol production technologies: an appraisal. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 2:14–32
Chandrakant P, Bisaria VS (1998) Simultaneous bioconversion of cellulose and hemicellulose to ethanol. Crit Rev Biotechnol 18:295–331
Chen M, Xia L, Xue P (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob and ethanol production from cellulosic hydrolysate. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59:85–89
Cooper C (1999) A renewed boost for ethanol. Chem Eng 106:35
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59(2):257–268
Gray KA, Zhao L, Emptage M (2006) Bioethanol. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10:141–146
Kádár Z, Szengyel Z, Réczey K (2004) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) of industrial wastes for the production of ethanol. Ind Crop Prod 20:103–110
Larsson S, Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Tengeborg C, Stenberg K, Zacchi G (1999) The generation of fermentation inhibitors during dilute acid hydrolysis of soft-wood. Enzym Microb Technol 24:151–159
Lee J (1997) Biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol. Biotechnology 56:1–24
Lin Y, Tanaka S (2006) Ethanol fermentation from biomass resources: current state and prospects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:629–642
Oliva JM, Ballesteros I, Negro MJ, Manzanares P, Cabanńas A, Ballesteros M (2004) Effect of binary combinations of selected toxic compounds on growth and fermentation of Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnol Prog 20:715–720
Penner MH, Liaw ET (1994) Kinetic consequences of high ratios of substrate to enzyme saccharification systems based on Trichoderma cellulase. In: Himmel ME, Baker JO, Overend RP (eds) Enzymatic conversion of biomass for fuels production. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 363–371
Rouhollah H, Iraj N, Gitil E, Sorah A (2007) Mixed sugar fermentation by Pichia stipitis, Sacharomyces cerevisiae, and an isolated xylose fermenting Kluyveromyces marxianus and their cocultures. Afr J Biotechnol 6:1110–1114
Saha BC, Iten LB, Cotta MA, Wu YV (2005) Dilute acid pretreatment, enzymatic saccharification and fermentation of wheat straw to ethanol. Proc Biochem 40:3693–3700
Sheehan J, Himmel ME (1999) Enzymes, energy, and the environment: a strategic perspective on the US Department of Energy’s research and development activities for bioethanol. Biotechnol Prog 15:817–827
Stanbuk BU, Franden MA, Singh A, Zhang M (2003) d-Xylose transport by Candida Succiphila and Kluyveroyces marxianus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 106:255–263
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Tomás-Pejó E, García-Aparicio M, Negro MJ, Oliva JM, Ballesteros M (2009) Effect of different cellulase dosages on cell viability and ethanol production by Kluyveromyces marxianus in SSF processes. Bioresour Technol 100:890–895
Varga E, Thomsen MH, Thomsen AB (2004) Bioethanol production from wet oxidized corn stover using pretreatment manure as a nutrient source. BioSystems 4:1–4
Wen ZY, Liao W, Chen SL (2004) Hydrolysis of animal manure lignocellulosics for reducing sugar production. Bioresour Technol 91:31–39
Wilkins M, Mueller M, Eichling S, Banat I (2008) Fermentation of xylose by the thermotolerant yeast strains Kluyveromyces marxianus IMB2, IMB4, and IMB5 under anaerobic conditions. Proc Biochem 43(4):346–350
Yablochkova EN, Bolotnikova OI, Mikhailova NP, Nemova N, Ginak AI (2004) The activity of key enzymes in xylose-assimilating yeasts at different rate of oxygen transfer to the fermentation medium. Appl Biochem Microbiol 72:163–168
Zafar S, Owais M (2006) Ethanol production from crude whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biochem Eng J 27:295–298
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the National Research Foundation (NRF), South Africa and the Durban University of Technology for the financial support. Dr. Pratyoosh Shukla gratefully acknowledges Birla Institute of Technology (Deemed University), Ranchi, India for providing study leave to visit Durban University of Technology, Durban, South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Shukla, P., Ayyachamy, M. et al. Improved bioethanol production through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulosic agricultural wastes by Kluyveromyces marxianus 6556. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 1041–1046 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0267-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0267-0