Abstract
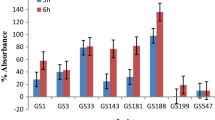
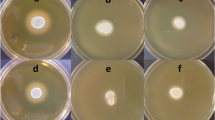
The aim of this work was to select strains with proteolytic activity on wheat gliadin, among lactic acid bacteria, previously isolated from Tunisian fermented wheat dough. Hydrolysis of gliadin, as sole nitrogen source, in an agar medium was visualized by a clear zone surrounding colonies. The increase in absorbance due to gliadin breakdown was measured spectrophotometrically using O-phthaldialdehyde (OPA) on Gliadin Glucose Broth medium. Fermented liquid dough inoculated with individual selected Enterococcus faecalis, showed a decrease of the gliadin concentration from 45 g/kg to 18 g/kg determined by sandwich ELISA test (R-7001). Only the enterococci strains show an hydrolysis of gliadin proteins. Strains showing proteolytic activity are gaining more and more importance in cereal based fermented foods and may help to reduce gliadin involved in coeliac disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Centeno JA, Menéndez S, Rodriguez-Otero JL (1996) Main microbial flora present as natural starters in Cebreiro raw cow’s-milk cheese (Northwest spain). Int J Food Microbiol 33:307–313. doi:10.1016/0168-1605(96)01165-8
Chae HJ, Joo H, In MJ (2001) Utilisation of brewer’s yeast cells for the production of food-grade yeast extract. Part 1: effects of different enzymatic treatments on solid and protein recovery and flavour characteristics. Bioresour Technol 76:253–258. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00102-4
Charalampopoulos D, Pandiella SS, Webb C (2002) Growth studies of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria in cereal-based substartes. J Appl Microbiol 92:851–859. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.2002.01592.x
Church FC, Swaisgood HE, Porter DH, Catignani GL (1983) Spectrophotometric assay using O-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J Dairy Sci 66:1219–1227
Collin P, Thorell L, Kaukinen K, Mäki M (2004) The safe threshold for gluten contamination in gluten-free products. Can trace amounts be accepted in the treatment of oeliac disease? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19:1277–1283. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.01961.x
Corsetti A, Settani L (2007) Lactobacilli in sourdough fermentation: a review. Food Res Int 40:539–558. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2006.11.001
Corsetti A, Settani L, Valmorri S, Mastrangelo M, Suzzi G (2007) Identification of subdominant sourdough lactic acid bacteria and their evolution during laboratory-scale fermentations. Food Microbiol 24:592–600. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2007.01.002
De Vuyst D, Neysens P (2005) The sourdough microflora: biodiversity and metabolic interactions. Trends Food Sci Technol 16:43–56. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2004.02.012
Di Cagno R, De Angelis M, Lavermicocca P, De Vincenzi M, Giovannini C, Faccia M, Gobbetti M (2002) Proteolysis by sourdough lactic acid bacteria: effects on wheat flour protein fractions and gliadin peptides involved in human cereal intolerance. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:623–633. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.2.623-633.2002
Foulquié Moreno MR, Sarantinopoulos P, Tsakalidou E, De Vuyst L (2006) The role and application of enterococci in food and health. Int J Food Microbiol 106:1–24. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.06.026
Giraffa G (2003) Functionality of enterococci in dairy products. Int J Food Microbiol 88:215–222. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00183-1
Gobbetti M, Smacchi E, Corsetti A (1996) The proteolytic system of Lactobacillus sanfrancisco CB1: purification and characterization of a proteinase, a dipeptidase, and an aminopeptidase. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3220–3226
ICC (1986) International association for cereal chemistry standard methods. Verlay Moritz Shafer, Detmold
Kawamura Y, Yonezawa D (1982) Wheat flour proteases and their action on gluten proteins in dilute acetic acid. Agric Biol Chem 46:767–773
Khedid K, Faid M, Mokhtari A, Soulaymani A, Zinedine A (2008) Characterisation of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the one humped camel milk produced in Morocco. Microbiol Res (in press)
Loponen J, Mikola M, Katina K, Sontag-Strohm T, Salavaora H (2004) Degradation of HMW glutenins during wheat sourdough fermentations. Cereal Chem 81:87–93. doi:10.1094/CCHEM.2004.81.1.87
Madreau MA, Mangia NP, Murgia MA, Sanna MG, Garau G, Leccis L et al (2006) Employment of autochthonous microflora in Peccorino Sardo cheese manufacturing and evolution of physicochemical parameters during ripening. Int Dairy J 16:876–885. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2005.08.005
M’hir S, Mejri M, Hamdi M (2005) Caractérisation de la flore lactique de la farine fermentée Tunisienne. Microbiologie Hyg Alimentaire 17:25–30
Morandi S, Brasca M, Andrighetto C, Lombardi A, Lodi R (2006) Technological and moleculaar characterisation of enterococci isolated from north-west Italian dairy products. Int Dairy J 16:867–875. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2005.09.005
Osborne TB (1924) The vegetable proteins. Longmans Green and Co., London
Pepe O, Villani F, Oliviero T, Greco T, Cappola S (2002) Effect of proteolytic starter cultures as leavening agents of pizza dough. Int J Food Microbiol 2637:1–8
Prakasham RS, Subba Rao Ch, Sarma PN (2006) Green gram husk—an inexpensive substarte for alkaline protease production by Bacillus sp. in solid-state fermentation. Bioresour Technol 97:1449–1454. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.07.015
Primo-Martín C, Van de Pijpekamp A, Van Vliet T, De Jongh HHJ, Plijter JJ, Hamer RJ (2006) The role of the gluten network in the crispness of bread crust. J Cereal Sci 43:342–352. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2005.12.007
Rizzello CG, De Angelis M, Coda R, Gobbetti M (2006) Use of selected sourdough lactic acid bacteria to hydrolyse wheat and rye proteins responsible for cereal allergy. Eur Food Res Technol 223:405–411. doi:10.1007/s00217-005-0220-x
Rollán GC, De Angelis M, Gobbetti M, De Valdez GF (2005) Proteolytic activity and reduction of gliadin-like fractions by sourdough lactobacilli. J Appl Microbiol 99:1495–1502. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02730.x
Sarantinopoulous P, Kalantzopoulous G, Tsakalidou E (2002) Effect of Enterococcus faecium on microbiological, physicochemical and sensory characteristics of Greek Feta cheese. Int J Food Microbiol 76:93–105. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(02)00021-1
Thiele C (2003) Hydrolysis of gluten and the formation of flavour precursors during sourdough fermentation. Thesis, Tecnische Universität München
Thiele C, Gänzle MG, Vogel RF (2002) Contribution of sourdough lactobacilli, yeasts, and cereal enzymes to the generaton of amino acids in dough relevant for bread flavor. Cereal Chem 79:45–51. doi:10.1094/CCHEM.2002.79.1.45
Wehrle K, Crowe N, Van Boeijen I, Arendt EK (1999) Screening methods for proteolytic breakdown of gluten by lactic acid bacteria and enzyme preparations. Eur Food Res Technol 209:428–433. doi:10.1007/s002170050521
Wiese (1995) Die Mikroflora von weizenvorteigen und ihr Einfluss auf die aromabildung. Dissertation, Universität Hannover, Fachbereich Biologie
Yoon MY, Kim YJ, Hwang HJ (2007) Properties and safety aspects of Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from chungkukjang, a fermented soy product. LWT Food Sci Technol (in press)
Zotta T, Ricciardi A, Parente E (2007) Enzymatic activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Cornetto di Matera sourdougs. Int J Food Microbiol 115:165–172. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.10.026
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support for this work from the AUF cooperation (project AUF-6301PS338). We appreciated the bacteriological work accomplished by Dr. D. Janssens, BCCM/LMG, University of Gent, Belgium. We gratefully acknowledge Mrs. Muggy PETTRÉ and Pr. Claude DEROANNE for using Glutomatic and also Pr. Daniel PORTETELLE for reading ELISA test (Faculté Universitaire des Sciences Agronomiques de Gembloux, Belgium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
M’hir, S., Aldric, JM., El-Mejdoub, T. et al. Proteolytic breakdown of gliadin by Enterococcus faecalis isolated from Tunisian fermented dough. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 2775–2781 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9804-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9804-5