Abstract
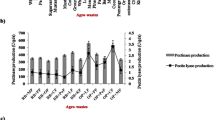
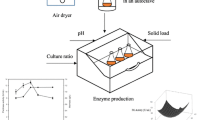
The role of bacilli in cocoa fermentation is not well known. Their potential of production of pectinolytic enzymes during this process was evaluated. Bacillus growth was monitored and pectinolytic strains were screened for their use of pectin as sole carbon source. Effects of cocoa fermentation parameters susceptible to influence on enzyme production were analysed. Among 98 strains isolated, 90 were positive for pectin degradation and 80% of them presented detectable pectinolytic activities in submerged fermentation. Forty-eight strains produced polygalacturonase (PG), 47 yielded pectin lyase (PL) and 23 strains produced both enzymes. Bacilli growth was not significantly affected during fermentation. PL production was favoured by galactose, lactose, glucose as sugars, and arginine, glutamine, cysteine and ammonium sulphate as nitrogen compounds. Pectin at low concentration (0.05%) and iron stimulated PL production. It was strongly repressed by galacturonic acid (1%), and negatively affected by nitrogen starvation, zinc and temperatures above 45°C. PL yield was very weak below pH 4.0 and in anaerobic conditions. PG production was weakened by sucrose and cation depletion. It was increased slightly by cysteine, ammonium nitrate and nitrogen starvation and significantly above 40°C. PG synthesis was not affected by acidic pH (3.0–6.0) or oxygen availability. As fermentation products, lactate and acetate lowered the production of both enzymes while ethanol had no effect. The high proportion of pectinolytic producers among the strains studied and analysis of factors influencing pectinolytic enzymes production, suggest that Bacillus sp. is liable to produce at least one enzyme during cocoa fermentation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnieszka N (2005) Binding of heavy metals to pomace fibers. Food chemistry 90(3):395–400
Albersheim P (1966) Pectin lyase from fungi. Methods Enzymol 8:628–631
Biehl B, Voigt J, Heinrichs H, Senjuk V, Bytof G (1993) pH-dependent enzymatic formation of oligopeptides and amino acids, the aroma precursors in raw cocoa beans. In: Lafforest J (ed) XIth international cocoa research conference. Cocoa Producers’ Alliance: Yamassoukro, Ivory Coast, pp 717–722
Braudeau J (1991) Le cacaoyer, techniques agricoles et productions tropicales. pp 201–210. 304 pages
De Vries RP, Visser J (2001) Aspergillus enzymes involved in degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:497–522
Freire ES, Romeu AP, Passo FJ, Mororo RC, Schwan RF, Collado AL, Chepote RE, Ferreira HI (1990) Aproveitamento de residuos e subprodutos da poscolheita do cacau. Boletim técnico, CEPLAC/Cocoa Research centre/CEPEC, Bahia, Brazil
Forsyth WGC, Quesnel VC (1963) Mechanisms of cocoa curing. Adv Enzymol 25:457–492
Gill MS, McLeod AJ, Moreau M (1985) Aroma components of cocoa beans. In: Adda J (ed) Proceedings of the 4th Weurman flavour research symposuim, Dourdan, France; Development in Food Science 10; Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Elsevier
Hugouvieux Cotte-Pattat N, Dominguez H, Robert-Baudouy J (1992) Environmental conditions affect transcription of the pectinase genes of Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937. J bacteriol 174:7807–7818
Hsu EJ, Vaughn RH (1969) Production and catabolite repression of the constitutive polygalacturonic acid trans-eliminase of Aeromonas liquefaciens. J Bacteriol 98:172–181
Jinap S. 1994. Organic acids in cocoa beans – a review. ASEAN Food J 9:3–12
Madhani HD, Galitski T, Lander ES, Fink GR (1999) Effect of a developemental mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade revealed by expression signatures of signalling mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12530–12535
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Nasser W, Chalet F, Robert-Baudouy J (1990) Purification and characterization of extracellular pectate lyase from Bacillus subtilis. Biochimie 72:689–695
Ogawa A, Sawada K, Saito K, Hakamada Y, Sumitomo N, Hatada Y, Kobayashi T, Ito S (2000) A new high-alkaline and high-molecular-weight pectate lyase from a Bacillus isolate: enzymatic properties and cloning of the gene for the enzyme. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1133–1141
Oguntoyinbo FA (2003) Molecular characterization and functional characteristics of Bacillus species isolated from okpehe a traditional fermented condiment. PhD thesis, submitted in the Department of Botany and Microbiology, University of Ibadan, Nigeria
Ostovar K, Keeney PG (1973) Isolation and characterization of microorganisms involved in the fermentation of Trinidad’s cocoa beans. J Food Sci 38:611–617
Ramesh MV, Lonsane BK (1991a) Regulation of alpha-amylase production in Bacillus licheniformis M27 by enzyme end-products in submerged fermentation and its overcoming in solid-state fermentation system. Biotechnol Lett 13:355–360
Ramesh MV, Lonsane BK (1991b) Ability of a solid-state fermentation technique to significantly minimize catabolite repression of alpha-amylase production by Bacillus licheniformis M27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:591–593
Rombouts JE (1952) Observation on the microflora of fermenting cocoa beans in Trinidad. Proc Soc Appl Bacteriol 15:103–111
Sanchez J, Daguenet G, Guiraud JP, Vincent JC, Galzy P (1985) A study of the yeast flora and the effect of pure culture seeding during the fermentation of cocoa beans. Lebensm Wiss Technol 18:69–76
Sauvage C, Franza T, Expert D (1991) Iron as a modulator of pathogenicity of Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937 on Saintpaulia ionantha In: Hennecke H, Verma DPS (eds) Advances in molecular genetics of plant–microbe interactions. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 94–98
Schwan RF, Rose AH (1994) Polygalacturonase production by Kluyveromyces marxianus: effect of medium composition. J Appl Bacteriol 76:62–67
Schwan RF, Rose AH, Board RG (1995) Microbial fermentation of cocoa beans, with emphasis on enzymatic degradation of the pulp. J Appl Bacteriol Symp Supp 79:96–107
Schwan RF, Cooper RM, Wheals AE (1996) Endopolygalacturonase of the yeast Kluyveromyces Marxianus is constitutive, highly active on native pectin and is the main extracellular protein. In: Visser J, Voragen AGJ (eds) Pectins and pectinases. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 861–868
Schwan RF, Cooper RM, Wheals AE (1997) Endopolygalacturonase secretion by Kluyveromyces marxianus and other cocoa pulp-degrading yeasts. Enzyme Microb Technol 21:234–244
Schwan RF (1998) cocoa fermentation conducted with a defined microbial cocktail inoculum. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1477–1483
Schwan RF, Alan EW (2004) The microbiology of cocoa fermentation and its role in chocolate quality. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 44(4):205–221
Soares MMCN, Da Silva R, Gomes E (1999) Screening of bacterial strains for pectinolytic activity: characterization of the polygalacturonase produced by Bacillus sp. Revista de Microbiologia 30:299–303
Solís-Pereira S, Favela-Torres E, Viniegra-González G, Gutiérrez-Rojas M (1993) Effects of different carbon-sources on the synthesis of pectinase by Aspergillus niger in submerged and solid-state fermentations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:36–41
Soriano M, Diaz P, Javier Pastor FI (2005) Pectinolytic systems of two aerobic sporogenous bacterial strains with high activity on pectin. Curr Microbiol 50:114–118
Soriano M, Diaz P, Javier Pastor FI (2006) Pectate lyase C from Bacillus subtilis: a novel endo-cleaving enzyme with activity on highly methylated pectin. Microbiology 152:617–625
Tamburini E, Léon AG, Perito B, Mastromei G (2003) Characterization of bacterial pectinolytic strains involved in the water retting process. Environ Microbiol 5:730–736
Timbie DJ, Sechrist L, Keeney PG (1978) Application of high pressure liquid chromatography to the study of variables affecting theobromine and caffeine concentrations in cocoa beans. J Food Sci 43:560–565
Villeneuve F, Cros E, Macheix JJ (1989) Recherche d’un indice de fermentation du cacao. III. Evolution des flavan-3-ols de la fève. Café´ Cacao The´ 33:165–170
Yamada Y, Hosono R, Lisdyanti P, Widyastuti Y, Saono S, Uchimura T, Komagata K (1999) Identification of acetic acid bacteria isolated from Indonesian sources, especially of isolates classified in the genus Gluconobacter. J Gen Appl Microbiol 45:23–28
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Ouattara and Tuo for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouattara, H.G., Koffi, B.L., Karou, G.T. et al. Implication of Bacillus sp. in the production of pectinolytic enzymes during cocoa fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24, 1753–1760 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9683-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9683-9