Summary
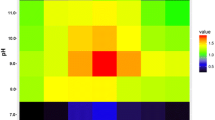
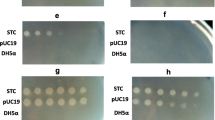
A highly glyphosate-tolerant bacterium strain HTG7 was isolated from glyphosate-polluted soil in north China, and identified as Halomonas variabilis. It was a Gram-negative motile rod giving convex colony. The strain HTG7 could tolerate up to 900 mM glyphosate in minimal medium. The 16S rDNA sequence was amplified by PCR using universal primers. The region essential for glyphosate tolerance was localized to a 3.5-kb fragment from a cosmid library of HTG7. The DNA fragment consisted of one complete open reading frame (ORF) and one partial ORF. The partial ORF was homologous to prephenate dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. The complete ORF contained the tyrA and aroA genes. Only the 1.35-kb aroA encoding EPSP synthase conferred glyphosate tolerance, and complemented with E. coli aroA mutant ER2799. E. coli JM109 harboring aroA grew well in Mops supplemented with 80 mM glyphosate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S.F., Madden T.L., Schaffer A.A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., Lipman D.J., 1997 Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programsNucleic Acids Research 25:3389–3402
Boocock M.R., Coggins J.R., 1983 Kinetics of inhibition of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase by glyphosateFEBS Letters154: 127–133
Bradshaw L.D., Padgette S.R., Kimball S.L., Wells B.H., 1997 Perspectives on glyphosate resistanceWeed Technology 11: 189–198
Chen L., Pradhan S., Evans T.C. Jr., 2001 Herbicide resistance from a divided EPSPs protein: the split Synechocystis DnaE intein as an in vivo affinity domainGene 263:39–48
Dobxon S.J., Franzmann P.D., 1996 Unification of the genera, and Halomonas Halovibrio and the species Paracoccus halodenitrificans into a single genus, Halomonas, and placement of the genus Zymobacter, in the family Halomonadaceae International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 46: 550–558
Dorsch M., Stackebrandt E., 1992 Some modifications in the procedure of direct sequencing of PCR amplified 16S rDNAJournal of Microbiological Methods 16:271–279
Dotson S.B., Smith C.E., Ling C.S., Barry G.F., Kishore G.M., 1996 Identification, characterization, and cloning of a phosphonate monoester hydrolase from Burlholderia caryophilli PG2982Journal of Biological Chemistry 271:25754–25761
Duncan K., Lewendon A., Coggins J.R., 1984 The complete amino acid sequence of Escherichia coli 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthaseFEBS Letters 170: 59–63
Dyer W.E., 1994, Resistance to glyphosate in Powles S.B., Holtum J.A.M., (Eds.) Herbicide Resistance in plants, Biology and Biochemistry Lewis Publishers Boca-Raton, FL, USA 229–241ISBN 0873717139
Fitzgibbon J.E., Braymer H.D., 1990 Cloning of a gene from Pseudomonas sp. Strain PG2982 conferring increased glyphosate resistanceApplied and Environmental Microbiology 56: 3382–3388
Garbe T., Jones C., Charles I., Dougan G., Young D., 1990 Cloning and characterization of the aroA gene from Mycoloacterium tuberculosisJournal of Bacteriology 172:6774–6782
Gasser C.S., Klee H.J., 1990 A Brassica napus gene encoding 5-enolpyruvyshikimate-3-phosphate synthaseNucleic Acids Research 18: 2821
Gasser C.S., Winter T.A., Hironaka C.M., Shan D.H., 1988 Structure, expression, and evolution of the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase genes of petunia and tomatoJournal of Biological Chemistry 263: 4280–4289
Gressel J., 1996 Fewer constrains than proclaimed to the evolution of glyphosate-resistant weedsResistant Pest Management 8: 2–5
Gruys K.J., Marzabadi M.R., Pansegrau P.D., Sikorski J.A., 1993 Steady state kinetic evaluation of the reverse reaction for Escherichia coli 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthaseArchives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 304:345–351
Gruys K.J., Walker J.A., 1992 Substrate synergism and the steadystate kinetic reation mechanism for EPEP synthase from E. coliBiochemistry 31:5534–5544
Henner D.J., Band L., Flaggs G., Chen E., 1986 The organization and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis his H, tyr A and aro E genesGene 49:247–252
Holt J.S., Lebaron H.M., 1990 Significance and distribution of herbicide resistance Weed Technology 4:141–149
Jacob G.S., Garbow J.R., Hallas L.E., Kimack N.M., Kishore G.M., Schaefer J., 1988 Metabolism of glyphosate in Pseudomonas sp. Strain LBrApplied and Environmental Microbiology 54:2953–2958
Klee H.J., Muskopf Y.M., Gasser C.S., 1987 Cloning of an Arabidopsis thaliana gene encoding 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase: sequence analysis and manipulation to obtain glyphosate-tolerant plantsMolecular and General Genetics 210: 434–442
Maidak B.L., Cole J.R., Parker C.T., 1999 A new version of the RDP (Ribosomal Database Project)Nucleic Acids Research 27:171–173
Maskell D.J., Morrissey P., Dougan G., 1988 Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the aroA gene of Bordetella epitasis Journal of Bacteriology 169: 2467–2471
Moore J.K., Braymer H.D., Larson A.D., 1983 Isolation of a Pseudomonas sp. which utilizes the phosphonate herbicide glyphosateApplied and Environmental Microbiology 46: 316–320
Neidhardt F.C., Bloch P.L., Smith D.F., 1974 Culture media for enterobacteriaJournal of Bacteriology 119:736–747
Pace N.R., Stahl D.A., Lane D.T., Olsen G.J., 1986 The analysis of natural microbial populations by ribosomal RNA sequencesAdvances in Microbial Ecology 9:1–55
Pittard, A.J. 1996 Biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. In Escherichia coli and Salmonella, Cellular and Molecular Biology, ed. Neidhardt, F., 2nd edn., Vol. 1, pp. 458–484. Washington, DC: ASM Press. ISBN 1555810845
Sambrook J., Russell D.W., 2001 Molecular Cloning: a laboratory manual Cold Sping Harbor Laboratory Cold Sping Harbor, NY ISBN 0879695773
Schylz A., Sost D., Amrhein N., 1984 Insensitivity of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase to glyphosate confers resistance to this herbicide in a strain of Aerobacter aerogenesArchives of Microbiology 137: 121–123
Shinabarger D.L., Braymer H.D., Larson A.D., 1986 Isolation of a Pseudomonas sp. Strain PG2982Journal of Bacteriology 168: 702–707
Stalker D.M., Hiatt W.R., Comai L., 1985 A single amino acid substitution in the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase confers resistance to the herbicide glyphosateJournal of Biological Chemistry 260: 4724–4728
Vaughan L.M., Smith P.R., Foster T.J., 1993 An aromatic dependent mutant of the fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida is attenuated in fish and is effective as a live vaccine against the salmonid disease furunculousInjection and Immunity 61: 2172–2181
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by High-technology Research and Development Program of China, and in part financial support from Program on Special Problems and Specific Project for Gene-transferring of China .We thank Shuzhen Ping, Wei Zhang, Yuquan Xu, Li Zou, Rui Zhao and Zhiwei Pan for generously supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Lu, W., Chen, M. et al. Genetic analysis of glyphosate tolerance in Halomonas variabilis strain HTG7 . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 681–686 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9090-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9090-4