Abstract
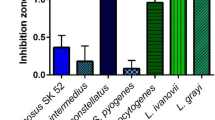
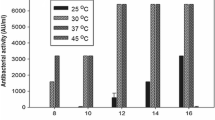
The influence of growth parameters on the production of bacteriocins (aureocins) by five strains of Staphylococcus aureus was investigated. These aureocins have a broad spectrum of activity and can inhibit important human and animal pathogens. All strains produced large inhibition zones upon the indicator strain when they were grown in rich media such as brain-heart infusion (BHI), N2GT and 2 × YT. Bacteriocin production was not influenced by the initial pH of the medium (6.0–8.0). At lower temperature (28 °C), there was a marked reduction in bacteriocin production. Incubation of the producers under anaerobiosis affected profoundly the production of two related bacteriocins, aureocins MB92 and 146L, and slightly increased the production of aureocins A53 and 215FN. Production of aureocins MB92 and 215FN was apparently abolished in media containing ≥ 2.5 g and ≥ 3.5 g Nacl/100 ml, respectively. Although production of the remaining aureocins was observed in all NaCl concentrations tested (0.5–7.5 g/100 ml), the larger inhibition zones were detected in media containing up to either 1.5 g (for aureocins A70 and 146L) or 2.5 g NaCl/100 ml (for aureocin A53). Aureocin 215FN could not be detected in the culture supernatant. For the remaining aureocins tested, the highest levels of bacteriocin production occurred in either the late-log or early stationary growth phase of cultures grown in BHI medium at 37 °C. Changes in environmental conditions can, therefore, have detrimental effects on the production of active aureocins. Such factors are relevant when considering the potential biotechnological applications of these substances and when testing new S. aureus isolates for bacteriocin production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.M. Aasen T. Moretro L. Axelsson I. Storro (2000) ArticleTitleInfluence of complex nutrients, temperature and pH on bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus sakei CCUG 42687 Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 53 159–166
S.R. Biswas P. Ray M.C. Johnson B. Ray (1991) ArticleTitleInfluence of growth conditions on the production of a bacteriocin, pediocin AcH, by Pediococcus acidilatici H Applied and Environmental Microbiology 57 1265–1267
S.M. Ennahar T. Sashihara K. Sonomoto A. Ishizaki (2000) ArticleTitleClass IIa bacteriocins: biosynthesis, structure and activity FEMS Microbiology Reviews 24 85–106
M.R. Gamon E.C. Moreira S.S. Oliveira L.M. Teixeira M.C.F. Bastos (1999) ArticleTitleCharacterization of a novel bacteriocin-encoding plasmid found in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 75 233–243
M. Giambiagi-deMarval M.A. Mafra E.G.C. Pendio M.C.F. Bastos (1990) ArticleTitleDistinct groups of plasmids correlated with bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus Journal of General Microbiology 136 1591–1599
Y. Héchard B. Dérijard F. Letellier Y. Cenatiempo (1992) ArticleTitleCharacterization and purification of mesentericin Y105, an anti-Listeria bacteriocin from Leuconostoc mesenteroides Journal of General Microbiology 138 2725–2731
R.W. Jack J.R. Tagg B. Ray (1995) ArticleTitleBacteriocins of Gram-postive bacteria Microbiological Reviews 59 171–200
M.C. Joerger T.R. Klaenhammer (1986) ArticleTitleCharacterization and purification of helveticin J and evidence for a chromosomally determined bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 481 Journal of Bacteriology 167 439–446
A.L. Kaiser T.J. Montville (1993) ArticleTitleThe influence of pH and growth rate on production of the bacteriocin, bavaricin MN, in the batch and continuous fermentations Journal of Applied Bacteriology 75 536–540
A.G. Larsen F.K. Vogensen J. Josephsen (1993) ArticleTitleAntimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from sour doughs: purification and characterization of bavaricin A, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus bavaricus MI401 Journal of Applied Bacteriology 75 113–122
M.V. Leal-Sánchez R. Jiménez-Díza A. Maldonado-Barragán A. Garrido-Fernández J.L. Ruiz-Barba (2002) ArticleTitleOptimization of bacteriocin production by batch fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum LPCO10 Applied and Environmental Microbiology 68 4465–4471
O. McAuliffe R.P. Ross C. Hill (2001) ArticleTitleLantibiotics: structure, biosynthesis and mode of action FEMS Microbiological Reviews 25 285–308
J. Meghrous E. Huot M. Quittelier H. Petitdemande (1992) ArticleTitleRegulation of nisin biosynthesis by continuous cultures and resting cells of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Research in Microbiology 143 879–890
C.I. Mørtvedt-Abildgaard J. Nissen-Meyer B. Jelle B. Grenov M. Skaugen I.F. Nes (1995) ArticleTitleProduction and pH-dependent bactericidal activity of lactocin S, a lantibiotic from Lactobacillus sake L45 Applied and Environmental Microbiology 61 175–179
M.A.D.B. Navaratna H.-G. Sahl J.R. Tagg (1998) ArticleTitleTwo-component anti-Staphylococcus aureus lantibiotic activity produced by Staphylococcus aureus C55 Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64 4803–4808
D.J.A. Netz R. Pohl A.G. Beck-Sickinger T. Selmer A.J. Pierik M.C.F. Bastos H.-G. Sahl (2002) ArticleTitleBiochemical characterisation and genetic analysis of aureocin A53, a new, atypical bacteriocin from Staphylococcus aureus Journal of Molecular Biology 319 745–756
S.S. Oliveira D.C. Póvoa J.S. Nascimento M.S.V. Pereira J.P. Siqueira Jr M.C.F. Bastos (1998a) ArticleTitleAntimicrobial substances produced by Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from cattle in Brazil Letters in Applied Microbiology 27 229–234
S.S. Oliveira J. Abrantes M. Cardoso D. Sordelli M.C.F. Bastos (1998b) ArticleTitleStaphylococcal strains involved in bovine mastitis are inhibited by Staphylococcus aureus antimicrobial peptides Letters in Applied Microbiology 27 287–291
B. Ray (1993) ArticleTitleSublethal injury, bacteriocins and food microbiology ASM News 59 285–291
H.-G. Sahl G. Bierbaum (1998) ArticleTitleLantibiotics: biological activities of uniquely modified peptides from Gram-positive bacteria Annual Review of Microbiology 52 41–79
T. Toba S.K. Samant E. Yoshioka T. Itoh (1991) ArticleTitleReutericin 6, a new bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus reuteri LA 6 Letters in Applied Microbiology 13 281–286
E.E. Vaughan C. Daly G.F. Fitzgerald (1992) ArticleTitleIdentification and characterization of helveticin V-1829, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 1829 Journal of Applied Microbiology 73 299–308
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nascimento, J.d.S., Abrantes, J., Giambiagi-deMarval, M. et al. Growth conditions required for bacteriocin production by strains of Staphylococcus aureus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20, 941–947 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-004-3626-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-004-3626-x