Summary
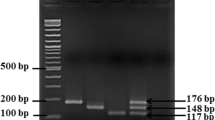
A combination of immunomagnetic separation and polymerase chain reaction (IMS-PCR) was used to detect Salmonella typhi in food and water samples. IMS was found to be an effective method for specific capture of S. typhi from artificially inoculated meat rinse samples. The bacteria could be detected within 6 h by IMS-PCR with a sensitivity of 105 cells. However, when tested in milk samples, the method was less effective. In comparison to conventional culture method, IMS-PCR is a rapid and specific method for detection of S. typhi and could be useful in outbreak situations for tracing the source of infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Chaudhry B.V. Laxmi N. Nisar K. Ray D. Kumar (1997) ArticleTitleStandardisation of polymerase chain reaction for detection of Salmonella typhi in typhoid fever Journal of Clinical Pathology 50 437–439 Occurrence Handle9215131
T.R. Cote H. Convery D. Robinson A. Ries T. Barrett L. Frank Furlong W. Horan J. D. Dwyer (1995) ArticleTitleTyphoid fever in the park: epidemiology of an outbreak at a cultural interface Journal of Community Health 20 451–458 Occurrence Handle8568020
S.K. Hoiseth (2000) Vaccines Bacterial J. Lederberg (Eds) Encyclopedia of Microbiology. EditionNumber2nd edn Academic Press New York 767–778
J.A. Hudson R.J. Lake M.G. Savill P. Scholes R.E. McCormick (2001) ArticleTitleRapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes in ham samples using immunomagnetic separation followed by polymerase chain reaction Journal of Applied Microbiology 90 614–621 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01287.x Occurrence Handle11309074
G.F. Ibrahim G.H. Fleet M.J. Lyons R.A. Walker (1985) ArticleTitleMethod for isolation of highly purified Salmonella flagellins Journal of Clinical Microbiology 22 1040–1044 Occurrence Handle4066915
P. Kerr D. Finlay F. Thomson-Carter H.J. Ball (2001) ArticleTitleA comparison of monoclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA and immunomagnetic bead selective enrichment for the detection of Escherichia coli O157 from bovine faeces Journal of Applied Microbiology 91 1–4 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01459.x
S. Kumar K. Balakrishna U. Tuteja H.V. Batra (2003) ArticleTitleApplication of monoclonal antibodies to flagellin of Salmonella typhi for its detection in foods Indian Journal of Microbiology 43 193–197
P.G. Lantz B. Hahn-Hagerdal P. Radstrom (1994) ArticleTitleSample preparation methods in PCR detection of Food pathogens Trends in Food Science and Technology 5 384–389 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0924-2244(94)90166-X
J.H. Mermin R. Villar J. Carpenter L. Roberts A. Samaridden L. Gasanova S. Lomakina C. Bopp L. Hutwagner P. Mead B. Ross E.D. Mintz (1999) ArticleTitleA massive epidemic of multidrug-resistant typhoid fever in Tajikistan associated with consumption of municipal water Journal of Infectious Diseases 179 1416–1422 Occurrence Handle10.1086/314766 Occurrence Handle10228063
T. Nishina K. Shiozawa M. Hayashi M. Akiyama K. Sahara N. Miwa S. Nakatsugawa M. Murakami A. Nakamura (1989) ArticleTitleSupply system in Fuji city Kansenshogaku Zasshi 63 240–247 Occurrence Handle2504837
Pang T. (998)) ArticleTitleGenetic dynamics of Salmonella typhi– diversity in clonality Trends in Microbiology 6 339–342 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0966-842X(98)01341-9
A. Ramesh B.P. Padmapriya A. Chandrashekar M.C. Varadaraj (2002) ArticleTitleApplication of convenient DNA extraction method and mutiplex PCR for the direct detection of Staphylococcus aureus and Yersinia enterocolitica in milk samples Molecular and Cellular Probes 16 307–314 Occurrence Handle10.1006/mcpr.2002.0428 Occurrence Handle12270272
M.A. Usera A. Aladuena A. Echeita E. Amor J.L. Gomez-Garces C. Ibanez I. Mendez J.C. Sanz M. Lopez-Brea (1993) ArticleTitleInvestigation of an outbreak of Salmonella typhi in a public school in Madrid European Journal of Epidemiology 9 251–54 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00146259 Occurrence Handle8405309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Balakrishna, K., Singh, G. et al. Rapid detection of Salmonella typhi in foods by combination of immunomagnetic separation and polymerase chain reaction. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21, 625–628 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-004-3553-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-004-3553-x