Abstract
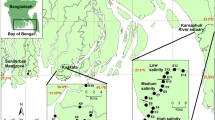
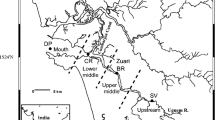
Wetland dynamics are probably linked to cholera endemicity in South Asia. We focus on links between Vibrio cholerae abundance, chitin content and suspended particle load in size fractions of suspended particulate matter (SPM) along the salinity gradient of Sunderban mangrove waters. SPM decreased downstream, while salinity increased from 0.2 to 4. Particulate organic carbon (90 ± 25 μM) and nitrogen (9.1 ± 3.3 μM) highly correlated with SPM and turbidity, suggesting a significant contribution of fine particles to organic matter. Total chitin ranged 1–2 mg/l and decreased downstream. The distribution among size fractions of SPM, chitin and V. cholerae O1 (the bacterial serogroup mainly associated with cholera epidemics) was similar, with ~98% of the total in the fraction <20 μm. In comparison, the number of V. cholerae O1 attached to zooplankton and microplankton size classes >20 μm was almost negligible, in contrast to usual assumptions. Thus, microdetritus, nanoplankton and fungal cells in size classes <20 μm represent a chitinaceous substrate on which V. cholerae can grow and survive. Total bacteria, cultivable vibrios and V. cholera O1 increased 5–10 times downstream, together with salinity and nitrite concentration. Overall, nitrate and silicate concentrations were relatively constant (>22 μM N and 100 μM Si). However, nitrite increased ~9 times in the outer sector, reaching ~1.2 μM N, probably as a result of increased abundance of nitrate-reducing vibrios. A characterization of Vibrio habitats that takes account of the presence of nitrate-reducing bacteria could improve the understanding of both mangrove nitrogen cycling and cholera seasonality.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adel MM (2005) Background state leading to arsenic accumulation in the Bengal basin groundwater. J Water Health 3:435–452
Anonymous (2008) Sunderbans. http://westbengalforest.gov.in/urls_all/forest_wild_life_terrain.htm
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) & Water Environment Federation (WEF), Washington, DC
Bhowmick R, Ghosal A, Chatterjee NS (2007) Effect of environmental factors on expression and activity of chitinase genes of vibrios with special reference to Vibrio cholerae. J Appl Microbiol 103:97–108
Biswas H, Dey M, Ganguly D, De TK, Ghosh S, Jana TK (2010) Comparative analysis of phytoplankton composition and abundance over a two-decade period at the land–ocean boundary of a tropical mangrove ecosystem. Estuaries Coasts 33:384–394
Brandhorst W (1959) Nitrification and denitrification in the eastern tropical North Pacific. J Cons Int Explor Mer 25:3–20
Colwell RR, Huq A, Islam MS, Aziz KM, Yunus M, Khan NH, Mahmud A, Sack RB, Nair GB, Chakraborty J, Sack DA, Russek-Cohen E (2003) Reduction of cholera in Bangladeshi villages by simple filtration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1051–1055
Dham VV, Menezes Heredia A, Wafar S, Wafar M (2002) Seasonal variations in uptake and in situ regeneration of nitrogen in mangrove waters. Limnol Oceanogr 47:241–254
Dittmar T, Lara RJ (2001) Driving forces behind nutrient and organic matter dynamics in a mangrove tidal creek in North Brazil. Est Coast Shelf Sci 52:249–259
Faruque SM, Sack DA, Sack RB, Colwell RR, Takeda Y, Nair GB (2003) Emergence and evolution of Vibrio cholerae O139. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1304–1309
Gallagher JT, Morris A, Dexter TM (1985) Identification of two binding sites for wheat-germ agglutinin on polylactosamine-type oligosaccharides. Biochem J 231:115–122
Gebauer M (2007) Bangladesh: Wo der Klimawandel nach Salz schmeckt. Spiegel on-line 26. April 2007
Gismervik I (1997) Implications of zooplankton stoichiometry on distribution of N and P among planktonic size fractions. J Plankton Res 19:343–356
Huq A, Colwell RR (1995) Vibrios in marine and estuarine environment. J Mar Biotechnol 3:60–63
Ishimaru K, Akagawa-Matsushita M, Muroga K (1996) Vibrio ichthyoenteri sp. nov., a pathogen of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) larvae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:155–159
Islam MS, Drasar BS, Bradley DJ (1990) Long-term persistence of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 in the mucilaginous sheath of a blue-green alga, Anabaena variabilis. J Trop Med Hyg 93:133–139
Islam MS, Alam MJ, Khan SI, Huq A (1994a) Fecal pollution of freshwater environments in Bangladesh. Int J Environ Stud 46:161–165
Islam MS, Drasar BS, Sack RB (1994b) The aquatic flora and fauna as reservoirs of Vibrio cholerae: a review. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res 12:87–96
Islam MS, Drasar BS, Sack RB (1994c) Probable role of blue-green algae in maintaining endemicity and seasonality of cholera in Bangladesh: a hypothesis. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res 12:245–256
Islam MS, Siddika A, Khan MNH, Goldar MM, Sadique MA, Kabir A (2001) Microbiological analysis of tube-well water in a rural area of Bangladesh. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3328–3330
Islam MS, Brooks A, Kabir MS, Jahid IK, Shafiqul Islam M, Goswami D, Nair GB, Larson C, Yukiko W, Luby S (2007) Faecal contamination of drinking water sources of Dhaka city during the 2004 flood in Bangladesh and use of disinfectants for water treatment. J Appl Microbiol 103:80–87
Kattner G (1999) Storage of dissolved inorganic nutrients in seawater: poisoning with mercuric chloride. Mar Chem 67:61–66
Kattner G, Becker H (1991) Nutrients and organic nitrogenous compounds in the marginal ice zone of the Fram Strait. J Mar Syst 2:385–394
Keyhani NO, Roseman S (1999) Physiological aspects of chitin catabolism in marine bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1473:108–122
Koch R (1884) An address on cholera and its bacillus. Br Med J 6:453–459
Lara RJ, Neogi SB, Islam S, Mahmud ZH, Yamasaki S, Nair GB (2009) Influence of estuarine dynamics and catastrophic climatic events on Vibrio distribution in the Karnaphuli estuary, Bangladesh. EcoHealth 6:279–286
Lara RJ, Islam MS, Yamasaki S, Neogi SB, Nair GB (in press) Aquatic ecosystems, human health and ecohydrology. In: E. Wolanski, D. McLusky (eds) Treatise on estuarine and coastal science.“Ecohydrology and restoration”,Vol. 10 (L. Chícharo, M. Zalewski (eds.)). Elsevier, Amsterdam
Laws EA, Popp B.N, Bidigare RR, Riebesell U, Burkhardt S, Wakeham SG (2001) Controls on the molecular distribution and carbon isotopic composition of alkenones in certain haptophyte algae. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 2. doi:10.1029/2000GC000057
Lio-Po GD, Leaño EM, Peñaranda MMD, Villa-Franco AU, Sombito CD, Guanzon NG Jr (2005) Anti-luminous Vibrio factors associated with the ‘green water’ grow-out culture of the tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 250:1–7
Lobitz B, Beck L, Huq A, Wood B, Fuchs G, Faruque ASG, Colwell RR (2000) Climate and infectious disease: use of remote sensing for detection of Vibrio cholerae by indirect measurement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1438–1443
MacFarlane GT, Herbert RA (1982) Nitrate dissimilation by Vibrio spp. isolated from estuarine sediments. J Gen Microbiol 128:2463–2468
Meibom KL, Blokesch M, Dolganov NA, Wu CY, Schoolnik GK (2005) Chitin induces natural competence in Vibrio cholerae. Science 310:1824–1827
Miller CJ, Drasar BS, Feachem RG (1982) Cholera and estuarine salinity in Calcutta and London. Lancet 29:1216–1218
Mirza MMQ (1998) Diversion of the Ganges water at Farakka and its effects on salinity in Bangladesh. Environ Manag 22:711–722
Moloney CL, Field JG (1991) The size-based dynamics of plankton food webs. I. a simulation model of carbon and nitrogen flows. J Plankton Res 13:1003–1038
Montgomery MT, Welschmeyer NA, Kirchman DL (1990) A simple assay for chitin: application to sediment trap samples from the subarctic Pacific. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 64:301–308
OCHA (2007) Bangladesh Cyclone Sidr. United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. http://ochaonline.un.org/News/Emergencies/Bangladesh/tabid/2707/Default.aspx. Accessed on December 3, 2007
Rameshkumar N, Sproer C, Lang E, Nair S (2010) Vibrio mangrovi sp.nov., a diazotrophic bacterium isolated from mangrove-associated wild rice (Poteresia coarctata Tateoka). FEMS Microbiol Lett 307:35–40
Svitil AL, Ni Chadhain SM, Moore JA, Kirchman DL (1997) Chitin degradation proteins produced by the marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi growing on different forms of chitin. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:408–413
Tamplin ML, Gauzens AL, Huq A, Sack DA, Colwell RR (1990) Attachment of Vibrio cholerae serogroup O1 to zooplankton and phytoplankton of Bangladesh waters. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1977–1980
Udden SM, Zahid MS, Biswas K, Ahmad QS, Cravioto A, Nair GB, Mekalanos JJ, Faruque SM (2008) Acquisition of classical CTX prophage from Vibrio cholerae O141 by El Tor strains aided by lytic phages and chitin-induced competence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11951–11956
UNEP (2007) Fast melting glaciers from rising temperatures expose millions in himalaya to devastating floods and water shortages. UNEP-ROAP News Release 07/10.http://www.unep.org/Documents.Multilingual/Default.asp?DocumentID=512&ArticleID=5600&l=en
Watkins WD, Cabelli VJ (1985) Effect of fecal pollution on Vibrio parahaemolyticus densities in an estuarine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1307-1313
West PA, Colwell RR (1984) Identification and classification of Vibrionaceae: an overview. In: RR Colwell (ed) Vibrios in the environment, New York, John Wiley, pp 285–363
Wichern F (2004) Fungi vs bacteria: their different roles in decomposition of organic matter. soils are alive newsletter, Vol. 3 Nr 3. http://www.soilhealth.see.uwa.edu.au/fungi_vs_bacteriacomponents/
Wolf AT (2001) Water and human security. J Contemp Water Res Educ 118:29
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the grant LA 868/5-1 from DFG/BMZ, Germany. We thank the Environmental Microbiology Laboratory of ICDDR, B, specially Md. A. Matin, Md. H. Uddin and P. Gope for their support during sample collection and processing. Thanks are due to D. Peterke and D. Dasbach (ZMT) for their technical assistance and to K.U. Ludwichowski (AWI) for the determination of inorganic nutrients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lara, R.J., Neogi, S.B., Islam, M.S. et al. Vibrio cholerae in waters of the Sunderban mangrove: relationship with biogeochemical parameters and chitin in seston size fractions. Wetlands Ecol Manage 19, 109–119 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-010-9204-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-010-9204-0