Abstract
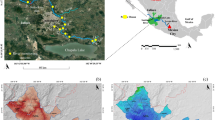
We investigated the effects of Fe-mining tailings of the Fundão dam on water quality, concerning physical and chemical parameters, aiming to infer the recovery process of the affected areas, and prospects of water quality in the coming years. Water quality data from the Gualaxo do Norte and Carmo rivers were evaluated in three moments: (i) before the dam rupture (1999–2000), (ii) 1 year after the rupture of the Fundão dam (2016), and (iii) after the implementation of recover mitigation activities (2017–2019). Concerning the variables evaluated, the mean concentrations of Fe and Mn were higher in the dry period, and increasing turbidity was detected in the rainy season. The turbidity, even after the recovery measures, peaked at 300 and 400 NTU in 2017 and 2019, respectively. The concentrations of dissolved Fe, Mn, and Cr, closely related to the tailings, decreased with rainfall by a dilution mechanism. Conversely, the concentrations of Cd, Al, Zn, and Cu increased in the rainy season, probably by greater erosion. The implementation of the recovery actions at the Gualaxo do Norte headwaters are helping to reduce the Mn and Fe concentrations and turbidity downriver, all associated with the Fe-mining tailings.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abowei, J. F. N. (2010). Salinity, dissolved oxygen, pH and surface water temperature conditions in Nkoro river, Niger delta, Nigeria. Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2(1), 36–40. https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=DJ2012046329
ANM, A. N. de M (2019). Sumário mineral 2017 (ano base 2016). Agência Nacional de Mineração, 37, 201 p. http://www.anm.gov.br/dnpm/publicacoes/serie-estatisticas-e-economia-mineral/sumario-mineral/sumario-brasileiro-mineral-2017/aco_sm_2017
APHA, A. P. H. A. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. (L. S. Clesceri, A. E. Greenberg, & A. D. Eaton, Eds.) (21st ed.). Washington, DC
Appiah-Effah, E., Nyarko, K. B., Antwi, E. O., & Awuah, E. (2015). Heavy metals and microbial loads in raw fecal sludge from low income areas of Ashanti Region of Ghana. Water Practice and Technology, 10(1), 124–132. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2015.014.
Azis, A., Yusuf, H., Faisal, Z., & Suradi, M. (2015). Water Turbidity impact on discharge decrease of groundwater recharge in recharge reservoir. Procedia Engineering, 125, 199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.11.029.
Barceló, J., Poschenrieder, C., Andreu, I., & Gunsé, B. (1986). Cadmium-induced decrease of water stress resistance in bush bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Contender) I. Effects of Cd on water potential, relative water content, and cell wall elasticity. Journal of Plant Physiology, 125(1–2), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(86)80239-5.
Brasil (2017). Resolução RDC no 166, de 25 de julho de 2017
Carvalho, A. R., Schlittler, F. H. M., & Tornisielo, V. L. (2000). Relações da atividade agropecuária com parâmetros físicos químicos da água. Química Nova, 23(5), 618–622. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-40422000000500009.
Coimbra, K. T. O., Alcântara, E., & de Souza Filho, C. R. (2019). An assessment of natural and manmade hazard effects on the underwater light field of the Doce River continental shelf. Science of the Total Environment, 685, 1087–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.127.
CONAMA (2005). Resolução n° 357, 18 de março de 2005
Correll, D. L., Goff, N. M., & Peterjohn, W. T. (1982). Ion balances between precipitation inputs and Rhode river watershed discharges. In Geological aspects of acis deposition (7th ed., pp. 77–111). Las Vegas, NV
Costa, A. T. (2001). Geoquímica das águas e dos sedimentos da bacia do rio Gualaxo, Leste-Sudeste do Quadrilátero Ferrífero (MG): Estudo de uma área afetada por atividades de extração mineral. Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto.
DNPM, D. N. de P. M. (2019). Anuário Mineral Brasileiro: Principais Substâncias Metálicas - 2018. Anuário Mineral Brasileiro http://www.anm.gov.br/dnpm/publicacoes/serie-estatisticas-e-economia-mineral/anuario-mineral/anuario-mineral-brasileiro/amb_2018.pdf.
Dornfeld, C. B. (2002). Utilização de análises limnológicas, bioensaios de toxicidade e macroinvertebrados bentônicos para o diagnóstico ambiental do reservatório de Salto Grande (Americana, SP). USP
EPA. (1992). Method 3005A - Acid digestion of waters for total recoverable or dissolved metals for analysis by FLAA or ICP spetroscopy
Fernandes, K. N. (2017). Qualidade das águas nos rios Gualaxo do Norte, Gualaxo do Sul e do Carmo, afluentes do alto rio Doce (Watu). Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto.
Ferreira, F. F., de Freitas, M. B. D., Szinwelski, N., Vicente, N., Medeiros, L. C. C., Schaefer, C. E. G. R., et al. (2020). Impacts of the Samarco tailing dam collapse on metals and arsenic concentration in freshwater fish muscle from Doce River, Southeastern Brazil. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 16(5), 622–630. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.4289.
Foesch, M. D. S., Francelino, M. R., Rocha, P. A., & Gomes, A. R. L. (2020). River water contamination resulting from the Mariana disaster, Brazil. Floresta e Ambiente, 27(4), 2–10. https://doi.org/10.1590/2179-8087.013218.
Fritzsons, E., Mantovani, L. E., Chaves Neto, A., & Hindi, E. C. (2009). A influência das atividades mineradoras na alteração do pH e da alcalinidade em águas fluviais: o exemplo do rio Capivari, região do carste paranaense. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental, 14(3), 381–390. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1413-41522009000300012.
Gensemer, R. W., & Playle, R. C. (1999). The bioavailability and toxicity of aluminum in aquatic environments. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 29(4), 315–450. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389991259245.
Ghose, M. K., & Sen, P. K. (2001). Characteristics of iron ore tailing slime in India and. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 68, 51–61.
Girardi, R., Pinheiro, A., Garbossa, L. H. P., & Torres, É. (2016). Water quality change of rivers during rainy events in a watershed with different land uses in Southern Brazil. RBRH, 21(3), 514–524. https://doi.org/10.1590/2318-0331.011615179.
Golder Associates. (2017). Programa de Monitoramento Quali-Quantitativo Sistema de Água e Sedimentos
Gong, Y., Liang, X., Li, X., Li, J., Fang, X., & Song, R. (2016). Influence of rainfall characteristics on total suspended solids in urban runoff: A case study in Beijing, China. Water (Switzerland), 8(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/w8070278.
González, A. G., & Herrador, M. Á. (2007). A practical guide to analytical method validation, including measurement uncertainty and accuracy profiles. TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 26(3), 227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2007.01.009.
Guedes, C. D., Pereira, J. G., de Lena, J. C., de Paiva, J. F., & Lima, R. M. F. (2004). Coagulação/floculação de suspensões ricas em óxidos de ferro por sulfato de alumínio. Química Nova, 27(5), 715–719. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-40422004000500007.
Hatje, V., Pedreira, R. M. A., De Rezende, C. E., Schettini, C. A. F., De Souza, G. C., Marin, D. C., & Hackspacher, P. C. (2017). The environmental impacts of one of the largest tailing dam failures worldwide. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11143-x.
Kaczynski, S. E., & Kieber, R. J. (1993). Aqueous trivalent chromium photoproduction in natural waters. Environmental Science & Technology, 27(8), 1572–1576. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00045a011.
Maia, L. C., & Pereira, A. R. (2017). Impactos no abastecimento de água decorrentes do rompimento da barragem de fundão: estudo de caso de Governador Valadares. In Congresso ABES (pp. 1–6). https://www.tratamentodeagua.com.br/artigo/impactos-no-abastecimento-rompimento-barragem/
Marques, M. M., & Barbosa, F. (2001). Biological quality of waters from an impacted tropical watershed (middle Rio Doce basin, southeast Brazil), using benthic macroinvertebrate communities as an indicator. Hydrobiologia, 457(1997), 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012297915323.
Marta-Almeida, M., Mendes, R., Amorim, F. N., Cirano, M., & Dias, J. M. (2016). Fundão dam collapse: Oceanic dispersion of River Doce after the greatest Brazilian environmental accident. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 112(1–2), 359–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.07.039.
Mechi, A., & Sanches, D. L. (2010). Impactos ambientais da mineração no estado de são Paulo. Estudos Avançados, 24(68), 209–220.
Milanez, B., & Losekann, C. (2016). Desastre no Vale do Rio Doce: Antecedentes, impactos e ações sobre a destruição. Folio Digital
Moruzzi, R. B., & Reali, M. A. P. (2012). Oxidação E Remoção De Ferro E Manganês Em Águas Para Fins De Abastecimento Público Ou Industrial– Uma Abordagem Geral. Revista De Engenharia E Tecnologia, 4(1), 29–43.
Nordberg, G. F. (1996). Current issues in low-dose cadmium toxicology: Nephrotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Environ. Sci, 4, 133–147.
Nordstrom, D. K. A., Jenne, E. W., & Ball, J. (2009). Redox equilibria of iron in acid mine waters (pp. 51–79). In: ACS Symposium Series. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1979-0093.ch003.
Oliveira, A. R. M., Borges, A. C., Matos, A. T., & Nascimento, M. (2018). Estimation on the concentration of suspended solids from turbidity in the water of two sub-basins in the Doce river basin. Engenharia Agrícola, 38(5), 751–759.
Pedreira, G., & de Sousa, H. C. (2011). Comunidade arbórea de uma mancha florestal permanentemente alagada e de sua vegetação adjacente em Ouro Preto-MG, Brasil. Ciencia Florestal, 21(4), 663–675. https://doi.org/10.5902/198050984511.
Quaresma, L. F. (2009). Projeto de assistência técnica ao setor de energia - Perfil da Mineração de Ferro. Ministério de Minas - MME, 4–56.
Rao, G. V., Markandeya, R., & Sharma, S. K. (2016). Recovery of iron values from iron ore slimes of Donimalai tailing dam. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 69(1), 143–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0809-0.
Renova, F. (2019). Relatório Anual de Atividades. Mariana, MG
Rodrigues, A. S. L., Malafaia, G., Costa, A. T., & Nalini Júnior, H. A. (2013). Background values for chemical elements in sediments of the Gualaxo Do Norte River Basin, Mg, Brazil. Revista de Ciências Ambientais, 7(2), 15–32. https://doi.org/10.18316/1142.
Santos, J. P., Cota, G. E. M., Limoeiro, B. F., Pedras, K. C., da Costa, A. M., & Viana, J. H. M. (2017). Susceptibilidade à erosão no Rio Gualaxo do Norte-MG. Caminhos de Geografia, 18(63), 286–307. https://doi.org/10.14393/RCG186313.
Saúde, M. E. da. (2017). Portaria de Consolidação no 5 de 28 de setembro de 2017
Schaefer, C. E. G. R., dos Santos, E. E., de Souza, C. M., Neto, J. D., Filho, E. I. F., & Delpupo, C. (2015). Cenário histórico, quadro físiográfico e estratégias para recuperação ambiental de Tecnossolos nas áreas afetadas pelo rompimento da barragem do Fundão, Mariana, MG. Arquivos do Museu de História Natural e Jardim Botânico - UFMG, 24(1/2), 104–135.
Schaefer, C. E. G. R., dos Santos, E. E., Fernandes Filho, E. I., & de Assis, I. R. (2016). Paisagens de Lama: Os Tecnossolos para recuperação ambiental de áreas afetadas pelo desatre da barragem do Fundão, em Mariana. Boletim informativo da SBCS, 1(1), 18–23.
Silva, A. E. P., Angelis, C. F., Machado, L. A. T., & Waichaman, A. V. (2008). Influência da precipitação na qualidade da água do Rio Purus. Acta Amazonica, 38(4), 733–742. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0044-59672008000400017.
Silva, A. C., Cavalcante, L. C. D., Fabris, J. D., Júnior, R. F., Barral, U. M., & Farnezi, M. M. de M., et al. (2016). Chemical, mineralogical and physical characteristics of a material accumulated on the river margin from mud flowing from the collapse of the iron ore tailings dam in Bento Rodrigues, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Revista Espinhaço, 5(2), 44–53.
Silva, D. C., Bellato, C. R., de Marques Neto, J. O., & Fontes, M. P. F. (2018). Trace elements in river waters and sediments before and after a mining dam breach (Bento Rodrigues, Brazil). Quimica Nova, 41(8), 857–866. https://doi.org/10.21577/0100-4042.20170252.
Silva, S. K. D. B. da, Santos, J. A. dos, Santos, F. M. dos, & Flores, C. M. (2019). Intoxicação por metais pesados. In Jornada Científica dos Campos Gerais (p. 4). Ponta Grosa, PR
SUPRAM, S. R. de M. A. e D. S (2008). Parecer Único SUPRAM - ZM Processo(s) No: 00015/1984/066/2008, 18
Theis, T. L., Young, T. C., & DePinto, J. V. (1988). Factors affecting metal partitioning during resuspension of sediments from the Detroit River. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 14(2), 216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0380-1330(88)71550-6.
Toniolo, G. R. (2016). Identificação de constituintes opticamente ativos na água do lago Guaíba, a partir de dados de sensores orbitais e espectrorradiometria de campo. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul.
Ulmgren, L. (2000). Measures taken in smaller industries to avoid hazardous substances entering domestic wastewater systems. In Stockholm Water Company
Yabe, M. J. S., & de Oliveira, E. (1998). Metais pesados em águas superficiais como estratégia de caracterização de bacias hidrográficas. Química Nova, 21(5), 551–556. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-40421998000500003.
Acknowledgements
We thank the financial support of FAPEMIG and CAPES for developing this project (APQ03603-17) and for granting of a research for the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santana, F.C., Francelino, M.R., Schaefer, C.E.G.R. et al. Water Quality of the Gualaxo do Norte and Carmo Rivers After the Fundão Dam Collapse, Mariana, MG. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05113-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05113-3