Abstract
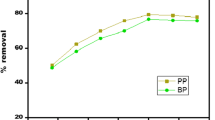
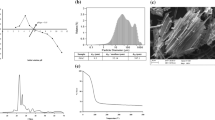
In this study, red oak (Quercus rubra) acorns were used as precursor for preparing activated carbon by thermal activation. Red oak activated carbon (RAC) was evaluated for the removal of methyl blue (MB), using batch adsorption experiments. SEM images taken before and after adsorption experiments showed difference of surface morphology. A 26 full factorial design approach was used to determine the main and interaction effect of independent factors on dye removal rate. The six independent factors used for this study were sorbent dosage, initial dye concentration, pH, temperature, mixing rate (rpm), and mixing time. The response of this factorial design was percentage of dye removal (R%) from an aqueous solution. All independent factors showed significant influence. Initial dye concentration and adsorbent dose exhibited largest negative and positive influence on removal rate, respectively. The factorial experiments also demonstrated significant synergistic/ antagonistic interaction between all these factors. Optimum conditions for adsorption were adsorbent dosage = 0.25 g/50 ml, initial dye concentration = 10.0 mg L 1, pH = 10, temperature = 45 °C, mixing rate = 175 rpm, and mixing time = 2.0 h. Under these conditions, response, dye removal rate R, was maximized, with a value of 97.18%. The findings of this study could be useful for industrial wastewater treatment systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbas, M., & Trari, M. (2015). Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study on the removal of Congo red from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto apricot stone. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 98, 424–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.09.015.
Abdel-Ghani, N. T., El-Chaghaby, G. A., Elgammal, M. H., & El, S. A. R. (2016). Optimizing the preparation conditions of activated carbons from olive cake using KOH activation. Xinxing Tan Cailiao/New Carbon Materials, 31(5), 492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(16)60027-6.
Aljeboree, A. M., Alshirifi, A. N., & Alkaim, A. F. (2017). Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, S3381–S3393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.01.020.
Andas, J., Rahman, M. L. A., & Yahya, M. S. M. (2017). Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from palm kernel shell. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 226(1), 54–61. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/226/1/012156.
Arenas, C. N., Vasco, A., Betancur, M., & Martínez, J. D. (2017). Removal of indigo carmine (IC) from aqueous solution by adsorption through abrasive spherical materials made of rice husk ash (RHA). Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 106(Ic), 224–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.01.013.
Bingol, D., Tekin, N., & Alkan, M. (2010). Brilliant yellow dye adsorption onto sepiolite using a full factorial design. Applied Clay Science, 50(3), 315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.08.015.
Bulut, Y., & Aydin, H. (2006). A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination, 194(1–3), 259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.10.032.
Cechinel, M. A. P., De Souza, S. M. A. G. U., & Souza, A. A. U. (2014). Study of lead (II) adsorption onto activated carbon originating from cow bone. Journal of Cleaner Production, 65(15), 342–349.
Chaari, I., Moussi, B., & Jamoussi, F. (2015). Interactions of the dye, C.I. direct orange 34 with natural clay. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 647, 720–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.06.142.
Cheng, C., Liu, H., Dai, P., Shen, X., Zhang, J., Zhao, T., & Zhu, Z. (2016). Microwave-assisted preparation and characterization of mesoporous activated carbon from mushroom roots by phytic acid (C6H18O24P6) activation. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 67, 532–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.08.032.
Danish, M., Ahmad, T., Majeed, S., Ahmad, M., Ziyang, L., Pin, Z., & Shakeel Iqubal, S. M. (2018). Use of banana trunk waste as activated carbon in scavenging methylene blue dye: Kinetic, thermodynamic, and isotherm studies. Bioresource Technology Reports, 3(July), 127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.07.007.
Deng, Y. (2020). Low-cost adsorbents for urban stormwater pollution control. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 14(5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1262-9.
Elmoubarki, R., Mahjoubi, F. Z., Tounsadi, H., Moustadraf, J., Abdennouri, M., Zouhri, A., El Albani, A., & Barka, N. (2015). Adsorption of textile dyes on raw and decanted moroccan clays: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Water Resources and Industry, 9, 16–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2014.11.001.
Fadhil, D. H., Al-Hussin, A., & Yousif, E. (2019). Removal of methylene blue dye from water using ecofriendly waste product (Eggshell) as an adsorbent and using the optimum adsorption conditions with real water sample from Tigris river. Al-Nahrain Journal of Science, 22(1), 9–14. https://doi.org/10.22401/anjs.22.1.02.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2012a). Mesoporous activated carbon from wood sawdust by K 2CO 3 activation using microwave heating. Bioresource Technology, 111, 425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.141.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2012b). Potential of jackfruit peel as precursor for activated carbon prepared by microwave induced NaOH activation. Bioresource Technology, 111, 143–150.
Giraldo, L., & Moreno-Pirajan, J. C. (2014). Study of adsorption of phenol on activated _ carbons obtained from eggshells. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 106, 41–47.
Güzel, F., Aksoy, Ö., & Akkaya, G. (2014). Evaluation of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) pulps for the removal of copper(II) ions: Kinetic, equilibrium, and desorption studies. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 35(4), 482–493. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2013.796481.
Hines, W. W., Montgomery, D. C., Goldsman, D. M., & Borror, C. M. (2003). Probability and Statistics in Engineering (4th ed.). Hoboken: Wiley.
Hoslett, J., Ghazal, H., Mohamad, N., & Jouhara, H. (2020). Science of the total environment removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by biochar prepared from the pyrolysis of mixed municipal discarded material. Science of the Total Environment, 714, 136832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136832.
Krishnan, R., Radhika, R., Jayalatha, T., Jacob, S., Rajeev, R., George, B. K., & Anjali, R. (2017). Removal of perchlorate from drinking water using granular activated carbon modified by acidic functional group: adsorption kinetics and. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 109, 158–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.03.014.
Li, G., Li, J., Tan, W., Jin, H., Yang, H., Peng, J., Barrow, C. J., Yang, M., Wang, H., & Yang, W. (2016). Preparation and characterization of the hydrogen storage activated carbon from coffee shell by microwave irradiation and KOH activation. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 113, 386–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.05.003.
Mashkoor, F., & Nasar, A. (2020). Magsorbents: Potential candidates in wastewater treatment technology – A review on the removal of methylene blue dye. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 500(January), 166408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166408.
Mekatel, E. H., Amokrane, S., Aid, A., Nibou, D., & Trari, M. (2015). Adsorption of methyl orange on nanoparticles of a synthetic zeolite NaA/CuO. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 18(3), 336–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2014.09.009.
Mohammed, M. R., & Abass, A. M. (2020). Preparation and characterization of low cost adsorbents for the remove of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by using adsorption technology. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 12(2), 1024–1033. https://doi.org/10.31838/IJPR/2020.12.02.0155.
Montgomery, D. C. (2009). Design and Analysis of Experiments (7th ed.). New York: Wiley.
Mpatani, F. M., Aryee, A. A., Kani, A. N., Wen, K., Dovi, E., Lingbo, Q., Li, Z., & Han, R. (2020). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous medium by citrate modified bagasse: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Bioresource Technology Reports, 11(May), 100463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2020.100463.
Nakhli, A., Bergaoui, M., Toumi, K. H., Khalfaoui, M., Benguerba, Y., Balsamo, M., Soetaredjo, F. E., Ismadji, S., Ernst, B., & Erto, A. (2020). molecular insights through computational modeling of methylene blue adsorption onto low-cost adsorbents derived from natural materials: A multi-model’s approach. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 140, 106965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2020.106965.
Ngulube, T., Gumbo, J. R., Masindi, V., & Maity, A. (2017). An update on synthetic dyes adsorption onto clay based minerals: A state-of-art review. Journal of Environmental Management, 191, 35–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.031.
Nodehi, R., Shayesteh, H., & Kelishami, A. R. (2020). Enhanced adsorption of congo red using cationic surfactant functionalized zeolite particles. Microchemical Journal, 153(September 2019), 104281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104281.
Ong, Siew-teng, Sie-tiong Ha, Pei-sin Keng, Chnoong-kheng Lee, and Yung-tse Hung. 2012. “Removal of dyes from wastewaters by low-cost adsorbents.” In Handbook of Environment and Waste Management, 1st ed. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814327701_0021.
Ozbay, N., & Yargic, A. S. (2018). Statistical analysis of cu(ii) and co(ii) sorption by apple pulp carbon using factorial design approach. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 57, 275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.08.033.
Palma, C., Lloret, L., Puen, A., Tobar, M., & Contreras, E. (2016). Production of carbonaceous material from avocado peel for its application as alternative adsorbent for dyes removal. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 24(4), 521–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2015.11.029.
Petrides, G., and R. Peterson. 1973. A Field Guide to Trees and Shrubs.
Rahman, A., Kishimoto, N., Urabe, T., & Ikeda, K. (2017). Methylene blue removal by carbonized textile sludge-based adsorbent. Water Science and Technology: a Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 76(11–12), 3126–3134. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.381.
Şahin, Ö., & Saka, C. (2013). Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from acorn shell by physical activation with h2o-co2 in two-step pretreatment. Bioresource Technology, 136, 163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.074.
Saka, C. (2012). BET, TG-DTG, FT-IR, SEM, iodine number analysis and preparation of activated carbon from acorn shell by chemical activation with ZnCl2. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 95, 21–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2011.12.020.
Santos, S. C. R., & Boaventura, R. A. R. (2016). Adsorption of cationic and anionic azo dyes on sepiolite clay: Equilibrium and kinetic studies in batch mode. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4(2), 1473–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.02.009.
Sasaki, C., Kushiki, Y., Asada, C., & Nakamura, Y. (2014). Acetone-butanol-ethanol production by separate hydrolysis and fermentation (shf) and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (ssf) methods using acorns and wood chips of Quercus acutissima as a carbon source. Industrial Crops and Products, 62, 286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.08.049.
Sayğili, H., & Güzel, F. (2016). High Surface area mesoporous activated carbon from tomato processing solid waste by zinc chloride activation: Process optimization, characterization and dyes adsorption. Journal of Cleaner Production, 113, 995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.055.
Sen, T. K., Afroze, S., & Ang, H. M. (2011). Equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto pine cone biomass of Pinus radiata. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 218(1–4), 499–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0663-y.
Senthilkumaar, S., Varadarajan, P., Porkodi, K., & Subbhuraam, C. (2005). Adsorption of methylene blue onto jute fiber carbon: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 284(1), 78–82.
Shaban, M., Abukhadra, M. R., Khan, A. A. P., & Jibali, B. M. (2018). Removal of Congo red, methylene blue and Cr(VI) ions from water using natural serpentine. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 82, 102–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.10.023.
Shoukat, S., Bhatti, H., Iqbal, M., & Noreen, S. (2017). Microporous and mesoporous materials mango stone biocomposite preparation and application for crystal violet adsorption: A mechanistic study. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 239, 180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.10.004.
Wang, Y. X., Ngo, H. H., & Guo, W. S. (2015). Preparation of a specific bamboo based activated carbon and its application for ciprofloxacin removal. Science of the Total Environment, 533, 32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.087.
Wang, J., Liu, T. L., Huang, Q. X., Ma, Z. Y., Chi, Y., & Yan, J. H. (2017). Production and characterization of high quality activated carbon from oily sludge. Fuel Processing Technology, 162, 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.03.017.
Wenzell, K., and L. Kenny. 2015. “The IUCN red list of threatened species.” 2015. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T194226A2305058.en.
Wong, Y. C., Szeto, Y. S., Cheung, W. H., & McKay, G. (2004). Adsorption of acid dyes on chitosan - equilibrium isotherm analyses. Process Biochemistry, 39(6), 695–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00152-3.
Wu, F.-C., Wu, P.-H., Tseng, R.-L., & Juang, R.-S. (2011). Preparation of novel activated carbons from h2so4-pretreated corncob hulls with koh activation for quick adsorption of dye and 4-chlorophenol. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(3), 708–713.
Yagub, M. T., Sen, T. K., Afroze, S., & Ang, H. M. (2014). Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 209, 172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002.
Yan, L. G., Li, L. Q., Hai Qin, Y., Li, S., Shan, R. R., & Bin, D. (2015). Adsorption of acid dyes from aqueous solution by ctmab modified bentonite: Kinetic and isotherm modeling. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 211, 1074–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.08.032.
Zhu, Y., Kolar, P., Shah, S. B., Cheng, J. J., & Lim, P. K. (2016). Avocado seed-derived activated carbon for mitigation of aqueous ammonium. Industrial Crops and Products, 92, 34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.07.016.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge Ms. Pat Scallion (Clean Technologies Research Institute, Dalhousie University) for providing technical supports during conducting SEM experiments. The authors also would like to acknowledge Mr. Daniel Chevalier (Mineral Resource Engineering Department, Dalhousie University) for preparation of activated carbon from acorn. The author also greatly acknowledge the anonymous reviewer for his valuable comments, criticism, and suggestion to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.S. Adsorption of Methyl Blue onto Activated Carbon Derived from Red Oak (Quercus rubra) Acorns: a 26 Factorial Design and Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04943-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04943-x