Abstract
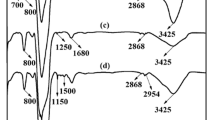
Surface modification of the silica nanoparticles was performed using trithiocyanuric acid (TCA-SNPs) so as to enhance the adsorption of Ag+ from aqueous solutions. The surface modification to the adsorbent was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmission electron microscope, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The Ag+ adsorption capacity was found to increase with increase in the solution pH, with the optimal pH being 5.0. The Ag+ adsorption isotherm was generated at 25 °C at the optimal solution pH and the maximum adsorption capacity was found to be 80 mg/g, significantly higher than the adsorption capacity reported for other adsorbents in literature. The increase in adsorption capacity was attributed to the presence of thiol groups on the surface of the modified adsorbents. Additionally, the adsorption kinetics was estimated at 25 °C, which indicated very high rates of adsorption initially, with rapid reduction in rate of adsorption with time. Both adsorption isotherms as well as the adsorption kinetics were modeled with popular models. The adsorption isotherm was found to match with the Langmuir model while the adsorption kinetics was found to match with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The adsorption-desorption cycles indicate the TCA-SNPs to be stable adsorption performance and retain high adsorption efficiency ensuring commercial adoption. A relatively low adsorption of other ions such as Mn2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Co3+ as compared to Ag+ was ensured.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abinashi, S., Jeongwon, P., Hyoeun, K., & Pyung-Kyu, P. (2016). Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto hydrous iron oxide-impregnated alginate beads. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 35, 277–286.
Ali, L. I. A., Ibrahim, W. A. W., Sulaiman, A., Kamboh, M. A., & Sanagi, M. M. (2016). New chrysin-functionalized silica-core shell magnetic nanoparticles for the magnetic solid phase extraction of copper ions from water samples. Talanta, 148, 191–199.
Bootharaju, M. S., & Pradeep, T. (2011). Investigation into the reactivity of unsupported and supported Ag7 and Ag8 clusters with toxic metal ions. Langmuir, 27, 8134–8143.
Bose, P., Bose, M. A., & Kumar, S. (2002). Critical evaluation of treatment strategies involving adsorption and chelation for wastewater containing copper, zinc and cyanide. Advances in Environmental Research, 7, 179–195.
Cecen, F., Semerci, N., & Geyik, A. G. (2010). Inhibition of respiration and distribution of Cd, Pb, Hg, Ag and Cr species in a nitrifying sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 178, 619–627.
Chang, Y. C., Chang, S. W., & Chen, D. H. (2006). Magnetic chitosan nanoparticles: studies on chitosan binding and adsorption of Co(II) ions. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 66, 335–341.
Coruh, S., Senel, G., & Ergun, O. N. (2010). A comparison of the properties of natural clinoptilolites and their ion-exchange capacities for silver removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180, 486–492.
Eckelman, M. J., & Graedel, T. E. (2007). Silver emissions and their environmental impacts: a multilevel assessment. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 6283–6289.
EI-Shahawi, M. S., Bashammakh, A. S., & Bahaffi, S. O. (2007). Chemical speciation and recovery of gold(I, III) from wastewater and silver by liquid-liquid extraction with the ion-pair reagent amiloride mono hydrochloride and AAS determination. Talanta, 72, 1494–1499.
Ghaedi, M., Shokrollahi, A., Niknam, K., Niknam, E., Najibi, A., & Soylak, M. (2009). Cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of cadmium(II), lead(II), palladium(II) and silver(I) in environmental samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 1022–1027.
Hassan, M. L., & El-Wakil, N. A. (2003). Heavy metal ion removal by amidoximated bagasse. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 87, 666–670.
He, C., Ren, L., Zhu, W., Xu, Y., & Qian, X. (2015). Removal of mercury from aqueous solution using mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with polyamide receptor. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 458, 229–234.
Hou, H., Yu, D., & Hu, G. (2015). Preparation and properties of ion-imprinted hollow particles for the selective adsorption of silver ions. Langmuir, 31, 1376–1384.
Kirci, S., GÜlfen, M., & Aydin, A. O. (2009). Separation and recovery of silver(I) ions from base metal ions by thioureaor urea-formaldehyde chelating resin. Separation Science and Technology, 44, 1869–1883.
Li, X., Wang, Z., Li, Q., Ma, J., & Zhu, M. (2015). Preparation, characterization, and application of mesoporous silica-grafted graphene oxide for highly selective lead adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 273, 630–637.
Lihareva, N., Dimova, L., Petrov, O., & Tzvetanova, Y. (2010). Ag+ sorption on natural and Na-exchanged clinoptilolite from Eastern Rhodopes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 130, 32–37.
Liu, P., Borrell, P. F., Bozic, M., Kokol, V., Oksman, K., & Mathew, A. P. (2015). Nano-celluloses and their phosphorylated derivatives for selective adsorption of Ag+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ from industrial effluents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 294, 177–185.
Lu, X., Yin, Q., Xin, Z., & Zhang, Z. (2010). Powerful adsorption of silver(I) onto thiol-functionalized polysilsesquioxane microspheres. Chemical Engineering Science, 65, 6471–6477.
Manzoori, J. L., Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, H., & Amjadi, M. (2007). Ultra-trace determination of silver in water samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry after preconcentration with a ligand-less cloud point extraction methodology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 144, 458–463.
Manzoori, J. L., Amjadi, M., & Hallaj, T. (2009). Preconcentration of trace cadmium and manganese using 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol-modified TiO2 nanoparticles and their determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 89, 749–758.
Monier, M., Ayad, D. M., & Sarhan, A. A. (2010). Adsorption of Cu(II), Hg(II) and Ni(II) ions by modified natural wool chelating fibers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176, 348–355.
Moshhadizadeh, M. H., & Karami, Z. (2011). Solid phase extraction of trace amounts of Ag, Cd, Cu, and Zn in environmental samples using magnetic nanoparticles coated by 3-(trimethoxysilyl)-1-propantiol and modified with 2-amino-5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole and their determination by ICP-OES. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190, 1023–1029.
Nguyen-Phan, T. D., Pham, H. D., Kim, S., Oh, E. S., Kim, E. J., & Shin, E. W. (2010). Surfactant removal from mesoporous TiO2 nanocrystals by supercritical CO2 fluid extraction. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 16, 823–828.
Peng, X., Zhang, W., Gai, L., Jiang, H., Wang, Y., & Zhao, L. (2015). Dedoped Fe3O4/PPy nanocomposite with high anti-interfering ability for effective separation of Ag(I) from mixed metal-ion solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 280, 197–205.
Pourreza, N., Rastegarzadeh, S., & Larki, A. (2014). Nano-TiO2 modified with 2-mercaptobenzimidazole as an efficient adsorbent for removal of Ag(I) from aqueous solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 127–132.
Quang, D. V., Lee, J. E., Kim, J., Kim, Y. N., Shao, G. N., & Kim, H. T. (2013). A gentle method to graft thiol-functional groups onto silica gel for adsorption of silver ions and immobilization of silver nanoparticles. Powder Technology, 235, 221–227.
Reddy, S. R., Pandey, N. K., Mallika, C., & Mudali, U. K. (2016). Equilibrium and kinetics of adsorption of ruthenium on activated charcoal from nitric acid solutions. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 115, 91–97.
Saif, A. C., Zakiullah, Z., & Sharf, I. S. (2017). Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamics of arsenic adsorption onto iron-zirconium binary oxide-coated sand (IZBOCS): modelling and process optimization. Molecular Liquids, 229, 230–240.
Shin, K. Y., Hong, J. Y., & Jang, J. (2011). Heavy metal ion adsorption behavior in nitrogen-doped magnetic carbon nanoparticles: isotherms and kinetic study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190, 36–44.
Soumya, R. M., Rachna, C., Jipsi, K. A., & Savariya, D. B. (2017). Kinetics and isotherm studies for the adsorption of metal ions onto two soil types. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 7, 87–101.
Soylak, M., Cay, R. S.(2007). Separation/preconcentration of silver(I) and lead(II) in environmental samples on cellulose nitrate membrane filter prior to their flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146, 142–147
Tahmasebi, E., & Yamini, Y. (2014). Polythiophene-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a selective adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of silver(I), gold(III), copper(II) and palladium(II). Microchimica Acta, 181, 543–551.
Tang, B., Yu, G., Fang, J., & Shi, T. (2010). Recovery of high-purity silver directly from dilute effluents by an emulsion liquid membrane-crystallization process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177, 377–383.
Xie, F., Lin, X., Wu, X., & Xie, Z. (2008). Solid phase extraction of lead(II), copper(II), cadmium(II) and nickel(II) using gallic acid-modified silica gel prior to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta, 74, 836–843.
Yirikoglu, H., & GÜlfen, M. (2008). Separation and recovery of silver(I) ions from base metal ions by melamine-formaldehyde-thiourea (MFT) chelating resin. Separation Science and Technology, 43, 376–388.
Zeliyha, Ç., Gülfen, M., & Aydın, A. O. (2010). Synthesis of a novel dithiooxamide-formaldehyde resin and its application to the adsorption and separation of silver ions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174, 556–562.
Zhang, S. W., Xu, W. Q., Zeng, M. Y., Li, J., Li, J. X., Xu, J. Z., & Wang, X. K. (2013). Superior adsorption capacity of hierarchical iron oxide@magnesium silicate magnetic nanorods for fast removal of organic pollutants from aqueous solution. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1, 11691–11697.
Zhang, M., Zhang, Y., & Helleur, R. (2015). Selective adsorption of Ag+ by ion-imprinted O-carboxymethyl chitosan beads grafted with thiourea-glutaraldehyde. Chemical Engineering Journal, 264, 56–65.
Zhang, S. W., Fan, Q. H., Gao, H. H., Huang, Y. S., Liu, X., Li, J. X., Xu, X. J., & Wang, X. K. (2016). Formation of Fe3O4@MnO2 ball-in-ball hollow spheres as a high performance catalyst with enhanced catalytic performances. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 4, 1414–1422.
Zhang, L. B., Zhang, G. W., Wang, S. X., Peng, J. H., & Cui, W. (2017). Sulfoethyl functionalized silica nanoparticle as an adsorbent to selectively adsorb silver ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 71, 330–337.
Zhao, Y. G., Li, J. X., Zhang, S. W., & Wang, X. K. (2014a). Amidoxime-functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica for selective sorption of U(VI). RSC Advances, 4, 32710–32717.
Zhao, Y. G., Li, J. X., Zhao, L. P., Zhang, S. W., Huang, Y. S., Wu, X. L., & Wang, X. K. (2014b). Synthesis of amidoxime-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell magnetic microspheres for highly efficient sorption of U(VI). Chemical Engineering Journal, 235, 275–283.
Zhao, Y. G., Wang, X. X., Li, J. X., & Wang, X. K. (2015). Amidoxime functionalization of mesoporous silica and its high removal of U(VI). Polymer Chemistry, 6, 5376–5384.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 51464024 and 51664037), the Yunnan Province Young Academic Technology Leader Reserve Talents (2012HB008), and the Yunnan Province Natural Science Foundation (2013FB096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Zhang, L., Wang, S. et al. Silica Nanoparticles Modified with Trithiocyanuric Acid as a Potential Adsorbent for Removal of Ag+ from Aqueous Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 273 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3464-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3464-8