Abstract
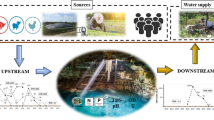
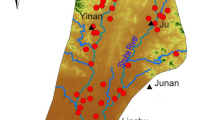
Escherichia coli (E. coli) contamination of groundwater (GW) and surface water (SW) occurs significantly through the subsurface from onsite wastewater treatment systems (OWTSs). However, E. coli transport in the subsurface remains inadequately characterized at the field scale, especially within the vadose zone. Therefore, the aim of this research is to investigate the impact of groundwater fluctuations (e.g., recharging, discharging conditions) and variable conditions in the vadose zone (e.g., pulses of E. coli flux) by characterizing E. coli fate and transport in a linked surface water-soil water-groundwater system (SW-SoW-GW). In particular, this study characterizes the impact of flow regimes on E. coli transport in the subsurface and evaluates the sensitivity of parameters that control the transport of E. coli in the SW-SoW-GW system. This study was conducted in Lake Granbury, which is an important water supply in north-central Texas providing water for over 250,000 people. Results showed that there was less removal of E. coli during groundwater recharge events as compared to GW discharge events. Also, groundwater and surface water systems largely control E. coli transport in the subsurface; however, temporal variability of E. coli can be explained by linking the SW-SoW-GW system. Moreover, sensitivity analysis revealed that saturated water content of the soil, total retention rate coefficient, and hydraulic conductivity are important parameters for E. coli transport in the subsurface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. M. (1991). The effects of climate change on decomposition processes in grassland and coniferous forests. Ecological Applications, 1, 326–347.
Anderson, M. P., & Munter, J. A. (1981). Seasonal reversals of groundwater flow around lakes and the relevance to stagnation points and lake budgets. Water Resources Research, 17, 1139.
Arora, B., Mohanty, B.P., and McGuire, J.T. (2012). Uncertainty in dual permeability model parameters for structured soils. Water Resources Research, 48.
Bergendahl, J., & Grasso, D. (2000). Prediction of colloid detachment in a model porous media: hydrodynamics. Chemical Engineering Science, 55(9), 1523–1532. Available at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009250999004224 (verified 23 December 2014).
Bethune, D. N., Farvolden, R. N., Ryan, M. C., & Guzman, A. L. (1996). Industrial contamination of a municipal water-supply lake by induced reversal of ground-water flow, Managua, Nicaragua. Ground Water, 34, 699–708. Available at <Go to ISI>://WOS:A1996UV86600020.
Bhattacharjee, S., Ryan, J. N., & Elimelech, M. (2002). Virus transport in physically and geochemically heterogeneous subsurface porous media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 57, 161–187.
Bouwer, H., Lange, J. C., & Riggs, M. S. (1974). High-rate land treatment I: infiltration and hydraulic aspects of the Flushing Meadows project. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 46, 834–843. Available at http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/25038728?sid=21105777816983&uid=3739256&uid=4&uid=3739560&uid=2 (verified 3 February 2015).
Bradford, S. A., & Bettahar, M. (2005). Straining, attachment, and detachment of oocysts in saturated porous media. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34(2), 469. Available at https://dl.sciencesocieties.org/publications/jeq/abstracts/34/2/0469 (verified 4 January 2015).
Bradford, S. A., Simunek, J., Bettahar, M., Van Genuchten, M. T., & Yates, S. R. (2003). Modeling colloid attachment, straining, and exclusion in saturated porous media. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 2242–2250.
Bradford, S.A., Simunek, J., and Walker, S.L. (2006). Transport and straining of E. coli O157:H7 in saturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 42.
Butler, R. G., Orlob, G. T., & McGauhey, P. H. (1954). Underground movement of bacterial and chemical pollutants. Journal of American Water Works Association, 46, 97–111.
Cunningham, A., Characklis, W.G., Abedeen, F., Crawford, D. (1991). Influence of biofilm accumulation on porous media hydrodynamics. Environmental Science & Technology, 25, 1305–1311. Available at http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/es00019a013.
Davis, R. O. E., & Bennett, H. H. (1927). Grouping of soils on the basis of mechanical analysis. Washington: U.S. Department of Agriculture.
DeFlaun, M. F., Murray, C. J., Holben, W., Scheibe, T., Mills, A., Ginn, T., Griffin, T., Majer, E., & Wilson, J. L. (1997). Preliminary observations on bacterial transport in a coastal plain aquifer. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 20, 473–487.
Dwivedi, D., and Mohanty, B.P. (2016). Hot spots and persistence of nitrate in aquifers across scales. Entropy, 18(1).
Dwivedi, D., Mohanty, B.P., and Lesikar, B.J. (2008). E. coli fate and transport below subsurface septic tanks in Lake Granbury area. In ASA-CSSA-SSSA International Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, 5–9 Oct.
Dwivedi, D., Mohanty, B. P., & Lesikar, B. J. (2013). Estimating Escherichia coli loads in streams based on various physical, chemical, and biological factors. Water Resources Research, 49, 2896–2906.
Eaton, A. D., Clesceri, L. S., Greenberg, A. E., & Franson, M. A. H. (1988). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington: American Public Health Association.
Federle, T. W., Dobbins, D. C., Thorntonmanning, J. R., & Jones, D. D. (1986). Microbial biomass, activity, and community structure in subsurface soils. Ground Water, 24, 365–374.
Foppen, J. W. A., & Schijven, J. F. (2006). Evaluation of data from the literature on the transport and survival of Escherichia coli and thermotolerant coliforms in aquifers under saturated conditions. Water Research, 40(3), 401–426. Available at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16434075 (verified 9 December 2014).
Foppen, J. W. A., Mporokoso, A., & Schijven, J. F. (2005). Determining straining of Escherichia coli from breakthrough curves. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 76(3–4), 191–210. Available at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169772204001512 (verified 23 December 2014).
Foppen, J. W., van Herwerden, M., & Schijven, J. (2007). Measuring and modelling straining of Escherichia coli in saturated porous media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 93, 236–254.
Gagliardi, J. V., & Karns, J. S. (2000). Leaching of Escherichia coli O157 :H7 in diverse soils under various agricultural management practices. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 877–883. Available at ISI:000085604800001.
Gelhar, L. W., Welty, C., & Rehfeldt, K. R. (1992). A critical review of data on field-scale dispersion in aquifers. Water Resources Research, 28, 1955–1974.
Harmel, R. D., King, K. W., Richardson, C. W., & Williams, J. R. (2003). Long-term precipitation analyses for the central Texas Blackland Prairie. Transactions of ASAE, 46(5), 1381.
Harvey, R., & Garabedian, S. (1991). Use of colloid filtration theory in modeling movement of bacteria through a contaminated sandy aquifer. Environmental Science & Technology, 25, 178–185. doi:10.1021/es00013a021.
Haznedaroglu, B. Z., Bolster, C. H., & Walker, S. L. (2008). The role of starvation on Escherichia coli adhesion and transport in saturated porous media. Water Research, 42, 1547–1554.
Hendry, M. J., Lawrence, J. R., & Maloszewski, P. (1999). Effects of velocity on the transport of two bacteria through saturated sand. Ground Water, 37, 103–112. Available at <Go to ISI>://000078117900017.
Jamieson, R. C., Gordon, R. J., Tattrie, S. C., & Stratton, G. W. (2003). Sources and persistence of fecal coliform bacteria in a rural watershed. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 38, 33–47.
Jiang, G., Noonan, M. J., Buchan, G. D., & Smith, N. (2007). Transport of Escherichia coli through variably saturated sand columns and modeling approaches. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 93, 2–20.
Johnson, P. R., & Elimelech, M. (1995). Dynamics of colloid deposition in porous media: blocking based on random sequential adsorption. Langmuir, 11, 801–812. doi:10.1021/la00003a023.
Klute, A., & Dirksen, C. (1986). Hydraulic conductivity and diffusivity. Laboratory methods. p. 687–734. In Methods of soil analysis—part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods.
Lesikar, B., Hallmark, C., Melton, R., & Harris, B. (2005). On-site wastewater treatment systems: soil particle analysis procedure. Texas Cooperative Extension, Texas A&M University System (p. 21).
Lindqvist, R., & Bengtsson, G. (1991). Dispersal dynamics of groundwater bacteria. Microbial Ecology, 21, 49–72.
Lindqvist, R., Cho, J. S., & Enfield, C. G. (1994). A kinetic model for cell density dependent bacterial transport in porous media. Water Resources Research, 30, 3291–3299. Available at <Go to ISI>://WOS:A1994PU14200007.
Logan, B. E., Jewett, D. G., Arnold, R. G., Bouwer, E. J., & O’Melia, C. R. (1995). Clarification of clean-bed filtration models. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 121(12), 869–873. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1995)121:12(869 (verified 4 January 2015).
Long, T., & Or, D. (2007). Microbial growth on partially saturated rough surfaces: simulations in idealized roughness networks. Water Resources Research, 43.
Lowe, K. S., & Siegrist, R. L. (2008). Controlled field experiment for performance evaluation of septic tank effluent treatment during soil infiltration. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 134, 93–101.
Mace, R.E., C.A. H., A. R., and Way, S. C. (2000). Groundwater availability of the Trinity Aquifer, Hill Country Area, Texas—numerical simulations through 2050.
Mallants, D., Mohanty, B. P., Vervoort, A., & Feyen, J. (1997). Spatial analysis of saturated hydraulic conductivity in a soil with macropores. Soil Technology, 10, 115–131.
Matthess, G., Pekdeger, A., & Schroeter, J. (1988). Persistence and transport of bacteria and viruses in groundwater—a conceptual evaluation. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2(2), 171–188. Available at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016977228890006X (verified 3 January 2015).
McCaulou, D. R., Bales, R. C., & Arnold, R. G. (1995). Effect of temperature-controlled motility on transport of bacteria and microspheres through saturated sediment. Water Resources Research, 31, 271.
McMahon, P. B., Tindall, J. A., Collins, J. A., Lull, K. J., & Nuttle, J. R. (1995). Hydrologic and geochemical effects on oxygen uptake in bottom sediments of an effluent-dominated river. Water Resources Research, 31, 2561–2569.
Milford, M. H. (1997). Introduction to soils and soil science laboratory exercises. Dubuque: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company.
Murphy, E. M., & Ginn, T. R. (2000). Modeling microbial processes in porous media. Hydrogeology Journal, 8, 142–158.
Or, D., Smets, B. F., Wraith, J. M., Dechesne, A., & Friedman, S. P. (2007). Physical constraints affecting bacterial habitats and activity in unsaturated porous media—a review. Advances in Water Resources, 30, 1505–1527.
Pachepsky, Y. A., & Shelton, D. R. (2011). Escherichia coli and fecal coliforms in freshwater and estuarine sediments. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 1067–1110.
Pachepsky, Y. A., Sadeghi, A. M., Bradford, S. A., Shelton, D. R., Guber, A. K., & Dao, T. (2006). Transport and fate of manure-borne pathogens: modeling perspective. Agricultural Water Management, 86, 81–92.
Pang, L., Close, M., Goltz, M., Sinton, L., Davies, H., Hall, C., & Stanton, G. (2004). Estimation of septic tank setback distances based on transport of E. coli and F-RNA phages. Environment International, 29, 907–921.
Pang, L., Nokes, C., Šimůnek, J., Kikkert, H., & Hector, R. (2006). Modeling the impact of clustered septic tank systems on groundwater quality. Vadose Zone Journal, 5, 599.
Personne, J. C., Poty, F., Vaute, L., & Drogue, C. (1998). Survival, transport and dissemination of Escherichia coli and enterococcci in a fissured environment. Study of a flood in a karstic aquifer. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 84(3), 431–438. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00366.x (verified 14 January 2015).
Powelson, D. K., & Mills, A. L. (2001). Transport of in sand columns with constant and changing water contents. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(1), 238. Available at https://dl.sciencesocieties.org/publications/jeq/abstracts/30/1/238 (verified 14 January 2015).
Riebschleager, K. J., Karthikeyan, R., Srinivasan, R., & McKee, K. (2012). Estimating potential E. coli sources in a watershed using spatially explicit modeling techniques. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 48(4), 745–761. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2012.00649.x (verified 2 December 2014).
Ryan, J. N., & Elimelech, M. (1996). Colloid mobilization and transport in groundwater. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 107(95), 1–56. Available at http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/092777579503384X.
Saiers, J.E. (2005). Correction to “Ionic-strength effects on colloid transport and interfacial reactions in partially saturated porous media.” Water Resources Research, 41.
Šimůnek, J., van Genuchten, M. Th., & Šejna, M. (2006). The HYDRUS software package for simulating two- and three-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media (version 1.0, edited, PC Progress, Prague, Czech Republic.).
Sinton, L. W., Finlay, R. K., Pang, L., & Scott, D. M. (1997). Transport of bacteria and bacteriophages in irrigated effluent into and through an alluvial gravel aquifer. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 98(1-2), 17–42. doi:10.1023/A%3A1026492110757 (verified 12 December 2014).
Sinton, L. W., Noonan, M. J., Finlay, R. K., Pang, L., & Close, M. E. (2000). Transport and attenuation of bacteria and bacteriophages in an alluvial gravel aquifer. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 34(1), 175–186. doi:10.1080/00288330.2000.9516924 (verified 12 December 2014).
Smith, M. S., Thomas, G. W., White, R. E., & Ritonga, D. (1985). Transport of Escherichia coli through intact and disturbed soil columns. Journal of Environmental Quality, 14, 87.
Spalding, R. F., & Exner, M. E. (1993). Occurrence of nitrate in groundwater—a review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 22, 392.
Sun, N., Elimelech, M., Sun, N. Z., & Ryan, J. N. (2001). A novel two-dimensional model for colloid transport in physically and geochemically heterogeneous porous media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 49, 173–199.
Tan, Y., Gannon, J. T., Baveye, P., & Alexander, M. (1994). Transport of bacteria in an aquifer sand: experiments and model simulations. Water Resources Research, 30, 3243.
Tong, M., Camesano, T. A., & Johnson, W. P. (2005). Spatial variation in deposition rate coefficients of an adhesion-deficient bacterial strain in quartz sand. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 3679–3687.
Torkzaban, S., Hassanizadeh, S. M., Schijven, J. F., de Bruin, H. A. M., & de Roda Husman, A. M. (2006). Virus transport in saturated and unsaturated sand columns. Vadose Zone Journal, 5(3), 877. Available at https://www.soils.org/publications/vzj/abstracts/5/3/877?access=0&view=pdf (verified 13 December 2014).
Tufenkji, N. (2007). Modeling microbial transport in porous media: traditional approaches and recent developments. Advances in Water Resources, 30, 1455–1469.
Tufenkji, N., Miller, G. F., Ryan, J. N., Harvey, R. W., & Elimelech, M. (2004). Transport of cryptosporidium oocysts in porous media role of straining and physicochemical. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(22), 5932–5938.
Twarakavi, N. K. C., Šimůnek, J., & Seo, S. (2008). Evaluating interactions between groundwater and vadose zone using the HYDRUS-based flow package for MODFLOW. Vadose Zone Journal, 7, 757.
Twarakavi, N.K.C., Šimůnek, J., and Schaap, M.G. (2010). Can texture-based classification optimally classify soils with respect to soil hydraulics? Water Resources Research, 46.
USEPA. (2002). Onsite wastewater treatment systems manual. EPA/625/R–00/008.
USEPA. (2005). http://www.epa.gov/owm/septic/pubs/onsite_handbook.pdf.
van Genuchten, M. T. (1980). A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44, 892.
Wan, J., & Wilson, J. L. (1994). Visualization of the role of the gas-water interface on the fate and transport of colloids in porous media. Water Resources Research, 30, 11.
Williams, A. E., Johnson, J. A., Lund, L. J., & Kabala, Z. J. (1998). Spatial and temporal variations in nitrate contamination of a rural aquifer, California. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27, 1147.
Zhang, P., Johnson, W. P., Scheibe, T. D., Choi, K. H., Dobbs, F. C., & Mailloux, B. J. (2001). Extended tailing of bacteria following breakthrough at the Narrow Channel focus area, Oyster, Virginia. Water Resources Research, 37, 2687–2698.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by EPA 319(h) grant for TMDL in Texas streams and partly supported by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (grant 5R01ES015634), Texas Water Resources Institute, and Texas A&M support a/c 02-130003. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, D., Mohanty, B.P. & Lesikar, B.J. Impact of the Linked Surface Water-Soil Water-Groundwater System on Transport of E. coli in the Subsurface. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 351 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3053-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3053-2