Abstract
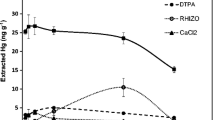
This article evaluates various extraction techniques’ suitability for soil mercury phytoavailable fraction assessment, including DGT method and extraction with microscopic filamentous fungi metabolites, MgCl2, rainwater, and EDTA. After mercury extraction from contaminated soils by these techniques, the obtained data were compared to mercury accumulation by shoots of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Comparison of these values showed that DGT method is able to separate soil mercury with the best agreement to total mercury concentration in shoots of barley. However, comparing mercury extraction efficiency of selected techniques to extraction efficiency of barley, statistical significance at 0.05 significance level was proved for fungal Cladosporium sp. and Alternaria alternata metabolites. Our results indicate that these extraction techniques are suitable for risk assessment of mercury phytoavailability in contaminated areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, P., Lynch, J. M., & De Leij, F. A. A. M. (2007). Desorption of zinc by extracellularly produced metabolites of Trichoderma harzianum, Trichoderma reesei and Coriolus versicolor. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 103, 2240–2247.
Biester, H., & Scholz, C. (1997). Determination of mercury binding forms in contaminated soils: mercury pyrolysis versus sequential extractions. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 233–239.
Cavallini, A., Natali, L., Durante, M., & Maserti, B. (1999). Mercury uptake, distribution and DNA affinity in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) plants. Science of the Total Environment, 243–244, 119–127.
Diviš, P., Dočekalová, H., & Smetková, V. (2003). In situ measurement of depth profiles of labile metal species in sediments by technique of diffusive gradients in thin films. Chemicke Listy, 97, 1184–1189.
Diviš, P., Dočekalová, H., & Řezáčová, V. (2005). Gel techniques for in situ measurement in natural waters, soils and sediments. Chemicke Listy, 99, 640–646.
Dočekal, B., Smetková, V., & Dočekalová, H. (2003). Characterization of Czech soils by diffusive gradients in thin films technique. Chemical Papers, 57, 161–166.
Dočekalová, H., Kovařková, V., & Dočekal, B. (2012). Mobility and bioaccessibility of trace metals in soils assessed by conventional extraction procedures and passive diffusive samplers. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 24, 261–265.
FAO. (2006). Guidelines for Soil description (4th ed.). Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Fiala, K., Kobza, J., Matúšková, Ľ., Brečková, V., Makovníková, J., Barančíková, G., et al. (1999). Záväzné metódy rozborov pôd: ciastkový monitorovací systém – pôda. Bratislava: Výskumný ústav pôdoznalectva a ochrany pôdy.
Fomina, M., Hillier, S., Charnock, J. M., Melville, K., Alexander, I. J., & Gadd, G. M. (2005). Role of oxalic acid overexcretion in transformations of toxic metal minerals by Beauveria caledonica. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 371–381.
Gregušová, M., Dočekal, B., & Dočekalová, H. (2008). Characterization of resin gels for diffusive gradient in thin films technique. Chemicke Listy, 102, 213–217.
Hiller, E., Jurkovič, L., & Šutriepka, M. (2010). Metals in the surface sediments of selected water reservoirs, Slovakia. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 84, 635–640.
Hiller, E., Petrák, M., Tóth, R., Lalinská-Voleková, B., Jurkovič, Ľ., Kučerová, G., et al. (2013). Geochemical and mineralogical characterization of a neutral, low-sulfide/high-carbonate tailings impoundment, Markušovce, eastern Slovakia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 7627–7642.
Hlodák, M., Matúš, P., & Urík, M. (2014). Mercury geochemistry and analytical methods of determination and fractionation of mercury in soils and plants. Chemicke Listy, 108, 1119–1124.
Hlodák, M., Matúš, P., Urík, M., Kořenková, L. & Mikušová, P. (2015). Biogeochemistry of Hg in soil-plant system in anthropogenically contaminated area. Chemicke Listy, 109, 385–389.
Issaro, N., Abi-Ghanem, C., & Bermond, A. (2009). Fractionation studies of mercury in soils and sediments: a review of the chemical reagents used for mercury extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 631, 1–12.
Issaro, N., Besancon, S., & Bermond, A. (2010). Thermodynamic and kinetic study of the single extraction of mercury from soil using sodium-thiosulfate. Talanta, 82, 1659–1667.
Jing, Y. D., He, Z. L., & Yang, X. E. (2007). Effects of pH, organic acids, and competitive cations on mercury desorption in soils. Chemosphere, 69, 1662–1669.
John, M. (1972). Mercury uptake from soil by various plant species. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 8, 77–80.
Jones, D. (1998). Organic acids in the rhizosphere—a critical review. Plant and Soil, 205, 25–44.
Khrishna, R. R., Swapna, D., Yukselen-Aksoy, Y., & Al-Hamdan, A. Z. (2010). Sequestration of heavy metals in soils from two polluted industrial sites: implications for remediation. Land Contamination and Reclamation, 18, 13–23.
Kim, M.-K., & Zoh, K.-D. (2012). Fate and transport of mercury in environmental media and human exposure. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, 45, 335–343.
Kocman, D., Horvat, M., & Kotnik, J. (2004). Mercury fractionation in contaminated soils from the Idrija mercury mine region. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 6, 696–703.
Loredo, J., Ordóñez, A., & Álvarez, R. (2006). Environmental impact of toxic metals and metalloids from the Muñón Cimero mercury-mining area (Asturias, Spain). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136, 455–467.
Mayer, J., Buegger, F., Jensen, E. S., Schloter, M., & Heß, J. (2003). Estimating N rhizodeposition of grain legumes using a 15N in situ stem labelling method. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35, 21–28.
Medved’, J., Streško, V., Kubová, J., & Polakovičová, J. (1998). Efficiency of decomposition procedures for the determination of some elements in soils by atomic spectroscopic methods. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 360, 219–224.
Millán, R., Gamarra, R., Schmid, T., Sierra, M. J., Quejido, A. J., Sánchez, D. M., et al. (2006). Mercury content in vegetation and soils of the Almadén mining area (Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 368, 79–87.
Navarro, A., Biester, H., Mendoza, J. L., & Cardellach, E. (2006). Mercury speciation and mobilization in contaminated soils of the Valle del Azogue Hg mine (SE, Spain). Environmental Geology, 49, 1089–1101.
Öborn, I., & Linde, M. (2001). Solubility and potential mobility of heavy metals in two contaminated urban soils from Stockholm, Sweden. Water, Air and Soil Pollution: Focus, 1, 255–265.
Patra, M., & Sharma, A. (2000). Mercury toxicity in plants. Botanical Review, 66, 379–422.
Rao, C. R. M., Sahuquillo, A., & Lopez Sanchez, J. F. (2008). A review of the different methods applied in environmental geochemistry for single and sequential extraction of trace elements in soils and related materials. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 189, 291–333.
Rauret, G. (1998). Extraction procedures for the determination of heavy metals in contaminated soil and sediment. Talanta, 46, 449–455.
Reis, A. T., Lopes, C. B., Davidson, C. M., Duarte, A. C., & Pereira, E. (2014). Extraction of mercury water-soluble fraction from soils: an optimization study. Geoderma, 213, 255–260.
Renneberg, A. J., & Dudas, M. J. (2001). Transformations of elemental mercury to inorganic and organic forms in mercury and hydrocarbon co-contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 45, 1103–1109.
Rodriguez, L., Rincón, J., Asencio, I., & Rodríguez-Castellanos, L. (2007). Capability of selected crop plants for shoot mercury accumulation from polluted soils: phytoremediation perspectives. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 9, 1–13.
Sánchez, D. M., Quejido, A. J., Fernández, M., Hernández, C., Schmid, T., Millán, R., et al. (2005). Mercury and trace element fractionation in Almaden soils by application of different sequential extraction procedures. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 381, 1507–1513.
Senila, M., Levei, E. A., & Senila, L. R. (2012). Assessment of metals bioavailability to vegetables under field conditions using DGT, single extractions and multivariate statistics. Chemistry Central Journal, 6, 119.
Senila, M., Senila, L., Urík, M., & Matúš, P. (2013). Evaluation of mercury bioavailability in soil samples using DGT and TD-AAS techniques: Case study of Baia Mare, NW Romania. Mineralia Slovaca, 45, 121–124.
Sierra, M. J., Millán, R., Esteban, E., Cardona, A. I., & Schmid, T. (2008). Evaluation of mercury uptake and distribution in Vicia sativa L. applying two different study scales: greenhouse conditions and lysimeter experiments. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 96, 203–209.
Skyllberg, U., Bloom, P. R., Qian, J., Lin, C. M., & Bleam, W. F. (2006). Complexation of mercury(II) in soil organic matter: EXAFS evidence for linear two-coordination with reduced sulfur groups. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 4174–4180.
Subirés-Muñoz, J. D., García-Rubio, A., Vereda-Alonso, C., Gómez-Lahoz, C., Rodríguez-Maroto, J. M., García-Herruzo, F., et al. (2011). Feasibility study of the use of different extractant agents in the remediation of a mercury contaminated soil from Almaden. Separation and Purification Technology, 79, 151–156.
Szkandera, R., Dočekalová, H., Kadlecová, M., Trávníčková, J., & Diviš, P. (2013). A sorption gel with titanium dioxide for mercury determination by the technique of diffusion gradient in thin film. Chemicke Listy, 107, 160–164.
Urík, M., Čerňanský, S., Ševc, J., Šimonovičová, A., & Littera, P. (2007). Biovolatilization of arsenic by different fungal strains. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 186, 337–342.
Urík, M., Hlodák, M., Mikušová, P., & Matúš, P. (2014). Potential of microscopic fungi isolated from mercury contaminated soils to accumulate and volatilize mercury(II). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 225, 2219.
Vaculík, M., Jurkovič, A., Matejkovič, P., Molnárová, M. & Lux, A. (2013). Potential risk of arsenic and antimony accumulation by medicinal plants naturally growing on old mining sites. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224.
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil O.M. and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37, 29–38.
Wang, D.-M., Lin, F.-C., Wu, T.-T., & Lai, J.-Y. (1997). Pervaporation of water-ethanol mixtures through symmetric and asymmetric TPX membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 123, 35–46.
Wang, X.-P., Shan, X.-Q., Zhang, S.-Z., & Wen, B. (2004). A model for evaluation of the phytoavailability of trace elements to vegetables under the field conditions. Chemosphere, 55, 811–822.
Wang, Y., Stauffer, C., Keller, C., & Greger, M. (2005). Changes in Hg fractionation in soil induced by willow. Plant and Soil, 275, 67–75.
Yin, Y., Allen, H. E., Huang, C. P., Sparks, D. L., & Sanders, P. F. (1997). Kinetics of mercury(II) adsorption and desorption on soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 496–503.
Zhang, X., Vu, T.-N., Volovitch, P., Leygraf, C., Ogle, K., & Wallinder, I. O. (2012). The initial release of zinc and aluminum from non-treated Galvalume and the formation of corrosion products in chloride containing media. Applied Surface Science, 258, 4351–4359.
Zornoza, P., Millán, R., Sierra, M. J., Seco, A., & Esteban, E. (2010). Efficiency of white lupin in the removal of mercury from contaminated soils: Soil and hydroponic experiments. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22, 421–427.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of Slovak Republic and the Slovak Academy of Sciences Scientific Grant Agency under VEGA contract Nos. 1/0836/15, 1/0203/14, and 1/0274/13; by the bilateral Slovak - Romanian project under contract No. SK-RO-0004-12 and by the project Materials Research Centre at FCH BUT - Sustainability and Development, REG LO1211, with financial support from the National Programme for Sustainability I (Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports). We also thank to Romanian Financing Authority CNCS –UEFISCDI, Partnership Program, BIORESOL (Contract No. 91/2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hlodák, M., Matúš, P., Urík, M. et al. Evaluation of Various Inorganic and Biological Extraction Techniques Suitability for Soil Mercury Phytoavailable Fraction Assessment. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 198 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2458-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2458-7