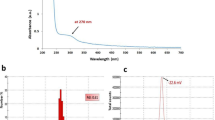
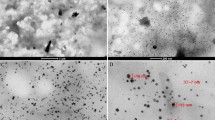
Abstract
A novel cerium-loaded cellulose nanocomposite bead (CCNB) is synthesized and tested for fluoride adsorption. The optimization of the process under the cooperative influence of different experimental variables was made employing response surface methodology (RSM). It is found from fractional factorial design (FFD) that among the different experimental variables, only adsorbent dose, temperature, and pH are significant. At the optimum condition (adsorbent dose 1 g L−1, temperature 313 K, pH 3.0), a maximum fluoride adsorption of 94 % was observed for an initial fluoride concentration of 2.5 mg L−1. A quadratic polynomial model equation based on central composite design (CCD) was built to predict the extent of adsorption. The result of the analysis of variance (ANOVA) shows high coefficients of determination (correlation coefficient; R 2 = 0.9772, adjusted R 2 = 0.9545, and adequate precision = 18.1045) and low probability value (Prob > F, 0.001) which signifies the validity of the model. The equilibrium adsorption data conformed to the Tempkin isotherm, having higher R 2 and lower SE value, among the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Tempkin equations at different temperatures. The adsorption data was found to fit well the second-order rate equation with film diffusion governing the overall rate. The activation energy value was calculated to be 16.74 kJ mol−1. Fluoride can be eluted from fluoride-loaded CCNB using alkali. CCNB can be reused at least for five successive operations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-aad, E., Bechara, R., Grimblot, J., & Aboukais, A. (1993). Preparation and characterization of CeO2 under an oxidizing atmosphere. Thermal analysis XPS and EPR Study. Chemistry of Materials, 5(6), 793–797.
Aksu, Z., & Gonen, F. (2006). Binary biosorption of phenol and chromium (VI) onto immobilized activated sludge in a packed bed: prediction of kinetic parameters and breakthrough curves. Separation and Purification Technology, 49(3), 205–216.
Alagumuthu, G., & Ranjan, M. (2010). Kinetic and equilibrium studies on fluoride removal by zirconium (IV) impregnated ground nut shell carbon. Hemijska Industrija, 64(4), 295–304.
Allen, S. J., Mckay, G., & Porter, J. F. (2004). Adsorption isotherm models for basic dye adsorption by peat in single and binary component systems. Journal of Colloid Interface Science., 280, 322–333.
Behbahani, M., Moghaddam, M. R. A., & Arami, M. (2011). Techno-economical evaluation of fluoride removal by electrocoagulation process: optimization through response surface methodology. Desalination, 271(1/3), 209–218.
Boyd, G. E., Adamson, L. S., & Meyers, L. S. (1947). The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solution by organic zeolites; kinetics. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 69(11), 2836–2848.
Brereton, R. G. (2003). Chemometrics: data analysis for the laboratory and chemical plant. West Sussex: Wiley.
Camacho, L. M., Torres, A., Saha, D., & Deng, S. (2010). Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of fluoride on sol-gel-derived activated alumina adsorbents. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 349(1), 307–313.
Castel, C., Schweizer, M., Simonnot, M. O., & Sardin, M. (2000). Selective removal of fluoride ions by a two-way ion-exchange cyclic process. Chemical Engineering Science, 55(17), 3341–3352.
Chand, D. (1999). Fluoride and human health—causes for concern. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 19(2), 81–89.
Chiou, M. S., & Li, H. Y. (2003). Adsorption behavior of reactive dye in aqueous solution on chemical cross-linked chitosan beads. Chemosphere, 50(8), 1095–1105.
Crank, J. (1956). The mathematics of diffusion. Oxford: Clarendon.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 57(1906), 385–471.
Ghiaci, M., Abbaspur, A., Kia, R., & Seyedeyn-Azad, F. (2004). Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of benzene, toluene, and phenol onto organo-zeolites and as-synthesized MCM-41. Separation and Purification Technology, 40(3), 217–229.
Goksungur, Y., Uren, S., & Guvenc, U. (2005). Biosorption of cadmium and lead ions by ethanol treated waste baker’s yeast biomass. Bioresource Technology, 96(1), 103–109.
Gupta, V. K., Sriastava, S. K., & Mohan, D. (1997). Equilibrium uptake, sorption dynamics, process optimization and column operation for the removal and recovery of malachite green from wastewater using activated carbon and activated slag. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 36(6), 2207–2218.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second-order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34(5), 451–465.
Hu, C. Y., Lo, S. L., & Kuan, W. H. (2005). Effects of the molar ratio of hydroxide and fluoride to Al(III) on fluoride removal by coagulation and electro coagulation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 283(2), 472–476.
Jagtap, S., Thakre, D., Wanjari, S., Kamble, S., Labhsetwar, N., & Rayalu, S. (2009). New modified chitosan-based adsorbent for defluoridation of water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 332(2), 280–290.
Jagtap, S., Yenkie, M. K., Labhsetwar, N., & Rayalu, S. (2012). Fluoride in drinking water and defluoridation of water. Chemical Review, 112(4), 2454–2466.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Journal of American Chemical Society, 38(11), 2221–2295.
Larsen, M. J., & Pearce, E. I. F. (2002). Defluoridation of drinking water by boiling with brushite and calcite. Caries Research, 36(5), 341–346.
Li, Z., Deng, S., Zhang, X., Zhou, W., Huang, J., & YU, G. (2010). Removal of fluoride from water using titanium-based adsorbents. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China, 4(4), 414–420.
Mckay, G., Allen, J. S., McConvey, I. F., & Otterbeurn, M. S. (1981). Transport process in the sorption of ions by peat particles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 80(2), 323–339.
Medellin-Castillo, N. A., Leyva-Ramos, R., Ocampo-Perez, R., Garcia de la Cruz, R. F., Aragon-Pina, A., Martinez-Rosales, J. M., Guerrero-Coronado, R. M., & Fuentes-Rubio, L. (2007). Adsorption of fluoride from water solution on bone char. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 46(26), 9205–9212.
Montgomery, D. C. (2009). Design and analysis of experiments (7th ed.). Hoboken: Wiley.
Reichenberg, D. (1953). Properties of ion exchange resins in relation to their structures. III. Kinetics of exchange. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 75(3), 589–597.
Rengaraj, S. J., Yeon, W., Kim, Y., Jung, Y., Ha, Y. K., & Kim, W. H. (2007). Adsorption characteristics of Cu(II) onto ion exchange resins 252H and 1500H: kinetics, isotherms and error analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 143(1/2), 469–477.
Rocha, R. A., & Muccillo, E. N. S. (2003). Physical and chemical properties of nanosized powders of gadolinia-doped ceria prepared by the cation complexation technique. Materials Research Bulletin, 38(15), 1979–1986.
Rudzinski, W., & Panczyk, T. (2002). Remarks on the current state of adsorption kinetic theories for heterogeneous solid surfaces: a comparison of the ART and the SRT approaches. Langmuir, 18(2), 439–449.
Santra, D., Joarder, R., & Sarkar, M. (2014). Taguchi design and equilibrium modeling for fluoride adsorption on cerium loaded cellulose nanocomposite bead. Carbohydrate Polymers, 111, 813–821.
Sarici-Özdemir, Ç., & Önal, Y. (2014). Error analysis studies of dye adsorption onto activated carbon from aqueous solutions. Particulate Science and Technology, 32(1), 20–27.
Sarkar, M., & Majumdar, P. (2011). Application of response surface methodology for optimization of heavy metal biosorption using surfactant modified chitosan bead. Chemical Engineering Journal, 175, 376–387.
Sarkar, M., Acharya, P., & Bhattacharya, B. (2003). Modeling the adsorption kinetics of some priority organic pollutants in water from diffusion and activation energy parameters. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 266(1), 28–32.
Sarkar, M., Banerjee, A., & Pramanick, P. P. (2006a). Kinetics and mechanism of fluoride removal using laterite. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 45(17), 5920–5927.
Sarkar, M., Banerjee, A., Pramanik, P. P., & Sarkar, A. R. (2006b). Use of laterite for the removal of fluoride from contaminated drinking water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 302(2), 432–441.
Sarkar, M., Manna, S., & Pramanik, P. P. (2008). Evaluation of the efficiency of fly ash from thermal power plant in controlling aquatic pollution. Journal of Indian Chemical Society, 85(11), 1130–1133.
Sehn, P. (2008). Fluoride removal with extra low energy reverse osmosis membranes: three years of large scale field experience in Finland. Desalination, 223(1/3), 73–84.
Sereshti, H., Karimi, M., & Samadi, S. (2009). Application of response surface method for optimization of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of water-soluble components of Rosa damascena Mill. essential oil. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(2), 198–204.
Temkin, M. I., & Pyzhev, V. (1940). Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochimica URSS, 12(3), 217–222.
Teutli-Sequeira, A., Solache-Ríos, M., & Balderas-Hernández, P. (2012). Modification effects of hematite with aluminum hydroxide on the removal of fluoride ions from water. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223(1), 319–327.
Veressinina, Y., Trapido, M., Ahelik, V., & Munter, R. (2001). Proceedings of the Estonian Academy of Sciences. Chemistry, 50(2), 81–88.
Viswanathan, N., Sundaram, C. S., & Meenakshi, S. (2009). Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution using protonated chitosan beads. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(1), 423–430.
Wang, D. M., Hao, G., Shi, Q. H., & Sun, Y. (2007). Fabrication and characterization of superporous cellulose bead for high-speed protein chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 1146(1), 32–40.
Weber, T. W., & Chakravorti, R. K. (1974). Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed‐bed adsorbers. American Institute of Chemical Engineers Journal, 20(2), 228–238.
Yadav, A. K., Abbassi, R., Gupta, A., & Dadashzadeh, M. (2013). Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution and groundwater by wheat straw, sawdust and activated bagasse carbon of sugarcane. Ecological Engineering, 52, 211–218.
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (D.S) is grateful to the University of Kalyani for providing research fellowship. The assistances and the instrumental facilities available under UGC-SAP, DST-FIST, and DST-PURSE programs are duly acknowledged. Thanks are due to IACS and SNBNCBS, Kolkata, for SEM and EDS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, M., Santra, D. Modeling Fluoride Adsorption on Cerium-Loaded Cellulose Bead—Response Surface Methodology, Equilibrium, and Kinetic Studies. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 30 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2307-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2307-8