Abstract
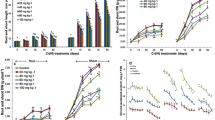
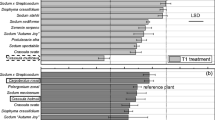
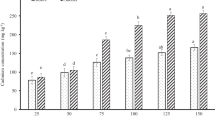
Seedlings of Cosmos bipinnatus were cultured in vitro for 30 days on modified Murashige–Skoog medium supplemented with four different concentrations of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI); 0.0–2.0 mM). Seed germination occurred after 7 days of culture, but was significantly lower when cultured in 2.0 mM Cr(VI) than when cultured without Cr(VI) in the medium. Seedlings were able to survive heavy metal stress condition, irrespectively of the Cr(VI) concentration used. The seedlings showed two metal tolerance mechanisms that were dependent on chromium concentration: (1) metal exclusion at 0.0–0.5 mM and (2) metal accumulation at 1.0–2.0 mM. Regarding the latter mechanism, seedlings showed metal accumulation values considered as characteristic of hyperaccumulator species. The highest bioaccumulation in dry tissue was of 5443 mg Cr kg−1 in shoot and 4767 mg Cr kg−1 in root for seedlings cultured with 2.0 mM of Cr(VI). These results indicated that substantial Cr translocation from the roots unto shoots took place (translocation factor > 1.14) associated to a bioaccumulation factor for Cr(VI) greater than 98.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bah, A. M., Dai, H., Zhao, J., Sun, H., Cao, F., Zhang, G., & Wu, F. (2011). Effects of cadmium, chromium and lead on growth, metal uptake and antioxidative capacity in Typha angustifolia. Biological Trace Element Research, 142(1), 77–92. Springer 1.307.
Baker, H. G. (1974). The evolution of weeds. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 5, 1–24.
Baker, A. J. M. (1981). Accumulators and excluders-strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 3(1–4), 643–654.
Baker, A. J. M. (1987). Metal tolerance. New Phytologist, 106(1), 93–111.
Barceló, J., Poschenrieder, C., & Gunse, B. (1986). Water relations of chromium VI treated bush bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Contender) under both normal and water stress conditions. Journal of Experimental Botany, 37(2), 178–187.
Bautista, Z. F. (1999). Introducción al estudio de la contaminación del suelo por metales pesados. Yucatán: México. Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán.
Buendía-González, L., Orozco-Villafuerte, J., Cruz-Sosa, F., Barrera-Díaz, C. E., & Vernon-Carter, E. J. (2010). Prosopis laevigata a potential chromium (VI) and cadmium (II) hyperaccumulator desert plant. Bioresource Technology, 101(5), 5862–5867.
Carrillo-Castañeda, G., Juárez Muños, J., Peralta-Videa, J. R., Gómez, E., Tiemannb, K. J., Duarte-Gardea, M., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2002). Alfalfa growth promotion by bacteria grown under iron limiting conditions. Advances in Environmental Research, 6(3), 391–399.
Chaney, R. L., Li, Y. M., Brown, S. L., Homer, F. A., Malik, M., Angle, J. S., Baker, A. J. M., Reeves, R. D., & Chin, M. (2000). Improving metal hyperaccumulator wild plants to develop commercial phytoextraction systems: approaches and progress. In N. Terry & G. Bañuelos (Eds.), Phytoremediation of contaminated soil and water (pp. 129–123). Florida: Lewis.
Chatterjee, J., & Chatterjee, C. (2000). Phytotoxicity of cobalt, chromium and copper in cauliflower. Environmental Pollution, 109(1), 69–74.
Chen, F., Wu, F. B., Dong, J., Vincze, E., Zhang, G., Wang, F., Huang, Y., & Wei, K. (2007). Cadmium translocation and accumulation in developing barley grains. Planta, 227(1), 223–232.
Espinosa, G. F. J., & Sarukhán, J. (1997). Manual de malezas del Valle de México. Mexico, D. F.: UNAM - Fondo de Cultura Económica.
Henson, I. E., Mahalakshmi, V., Bidinger, F. R., & Alagars-Wamy, G. (1981). Genotypic variation in pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum L.) Leeke in the ability to accumulate abscisic acid in response on water stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 32(130), 899–910.
Lasat, M. M. (2002). Phytoextraction of toxic metals: a review of biological mechanisms. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31(1), 109–120.
Lefevre, I., Marchal, G., Correal, E., Zanuzzi, A., & Lutts, S. (2009). Variation in response to heavy metals during vegetative growth in Dorycnium pentaphyllum Scop. Plant Growth Regulator, 59(1), 1–11.
Llamas, A., Ulrich, C. I., & Sanz, A. (2008). Ni2+ toxicity in rice: effect on membrane functionality and plant water content. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 46(10), 905–910.
Mazhoudi, S., Chaoudi, A., Ghorbal, M. H., & Elferjani, E. (1997). Response of antioxidant enzymes to excess copper in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum, Mill.). Plant Science, 127(2), 129–137.
Mellen, J. J. (2008). Phytoremediation of heavy metals using Amaranthus dubius. Durban: Durban University of Technology. Dissertation.
Morikawa, H., & Takahashi, M. (2000). Remediation of soil, water and air by naturally occurring and transgenic plants. Gamma Field Symposia, 39, 81–104.
Niu, Z. X., Sun, L. N., Sun, T. H., Li, Y. S., & Wang, H. (2007). Evaluation of phytoextracting cadmium and lead by sunflower, ricinus, alfalfa and mustard in hydroponic culture. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(8), 961–967.
Peer, W. A., Baxter, I. R., Richards, E. L., Freeman, J. L., & Murphy, A. S. (2005). Phytoremediation and hyperaccumulator plants. In M. J. Tamás & E. Martinoia (Eds.), Molecular biology of metal homeostasis and detoxification: topics in current genetics (Vol. 14, pp. 299–340). Berlin: Springer.
Peralta, J. R., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., Tiemann, K. J., Gómez, E., Arteaga, S., Rascon, E., & Parsons, J. G. (2001). Uptake and effects of five heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 66(6), 727–734.
Pilon-Smits, E. (2005). Phytoremediation. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 56(1), 15–39.
Poschenrieder, C., Cabot, C., Martos, S., Gallego, B., & Barceló, J. (2013). Do toxic ions induce hormesis in plants? Plant Science, 212, 15–25.
Reynoso-Cuevas, L., Gallegos-Martínez, M. E., Cruz-Sosa, F., & Gutiérrez-Rojas, M. (2008). In vitro evaluation of germination and growth of five plant species on medium supplemented with hydrocarbons associated with contaminated soils. Bioresource Technology, 99(14), 6379–6385.
Rodríguez-Elizalde, M. A., Delgado-Alvarado, A., González-Chávez, M. C., Carrillo-González, R., Mejía-Muñoz, J. M., & Vargas-Hernández, M. (2010). Emergence and growth of ornamental plants on substrates polluted with mine residues. Interciencia, 35(1), 26–32.
Salt, D. E. (2001). Nickel hyperaccumulation in Thlaspi goesigense: a scientific travelogue. In Vitro Cellular and Developmental Biology – Plant, 37(3), 326–329.
Scoccianti, V., Crinelli, R., Tirillini, B., Mancinelli, V., & Speranza, A. (2006). Uptake and toxicity of Cr(III) in celery seedlings. Chemosphere, 64(10), 1695–1703.
Shanker, A. K., Cervantes, C., Loza-Tavera, H., & Avudainayagam, S. (2005). Chromium toxicity in plants. Environment International, 31(5), 739–753.
Skeffington, R. A., Shewry, P. R., & Peterson, P. J. (1976). Chromium uptake and transport in barley seedlings (Hordeum vulgare L.). Planta, 132(3), 209–214.
Wang, P. F., Zhang, S. H., Wang, C., & Han, N. N. (2012). Cr bioaccumulation and its effects on nutrient elements uptake and oxidative response in Corbicula fluminea exposed to hexavalent chromium. Advanced Materials Research, 343–344, 975–980.
Wu, F. B., Dong, J., Qian, Q. Q., & Zhang, G. P. (2005). Subcellular distribution and chemical form of Cd and Cd–Zn interaction in different barley genotypes. Chemosphere, 60(10), 1437–1446.
Zhang, X., Liu, J., Wang, D., Zhu, Y., Hu, C., & Sun, J. (2009). Bioaccumulation and chemical form of chromium in Leersia hexandra Swartz. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 82(3), 358–362.
Zhao, F. J., Lombi, E., & McGrath, S. P. (2003). Assessing the potential for zinc and cadmium phytoremediation with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant and Soil, 249(1), 37–43.
Acknowledgements
Author Buendía-González wishes to thank the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) for the partial financing of this work through project grant “Biorremediación para la conservación de la biodiversidad,” and also LB-G thanks the Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México for the partial financing of this project through grant 3422/2013CHT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santiago-Cruz, M.A., Villagrán-Vargas, E., Velázquez-Rodríguez, A.S. et al. Exploring the Cr(VI) Phytoremediation Potential of Cosmos bipinnatus . Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 2166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2166-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2166-8