Abstract
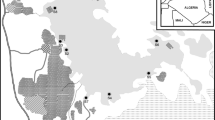
Spatial and seasonal mobilization trends of metals in surface water were evaluated in the US–Mexico San Pedro River (SPR). Water samples were collected at five sampling stations for the analysis of dissolved oxygen, pH, electric conductivity, sulfates, and metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, and Zn). Quality of the water was characterized through Ecological Criteria of Water Quality (ECWQ) established in Mexico and Water Quality Criteria (Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)). High total metal concentrations were detected as follows: Fe > Cu > Mn > Zn > Pb > Cd. Metal concentrations were slightly higher in dry season than in rainy season: Cd (below detection limit (BDL)–0.21 mg L−1), Cu (BDL–13 mg L−1), Fe (0.16–345 mg L−1), Mn (0.12–52 mg L−1), Pb (BDL–0.48 mg L−1), and Zn (0.03–17.8 mg L−1). Low pH and dissolved oxygen values as well as high sulfate content were detected in both seasons. High values of metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, Zn) were detected at station E1 representing pollution source, as well as at stations E2 (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn), E3 (Fe, Mn, Pb), and E4 and E5 (Fe, Mn). Detected concentrations exceeded maximum permissible established in ECWQ and Water Quality Criteria (EPA). Efflorescence salts on sediments in the dry season could increase levels of metals in water column. This study provides valuable information on the potential mobility of metals in surface water of SPR located in an arid environment where transport processes are strongly linked to climate. The information derived from this study should help the regional and national authorities to address present environmental regulations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias, H. M. (2000). International groundwaters. The upper San Pedro River basin case. Natural Resources Journal, 40, 199–221.
Bigham, J.M., & Nordstrom, D.K. (2000). Iron and aluminium hidroxysulfates from acid sulfate waters. P. 351–403. In: Alpers, C.N., Jambor J.L. & Nordstrom D.K. (eds.) Sulfate Minerals-Crystallography, Geochemistry and Environmental Significance. Mineralogical Society of America and Geochemical Society, Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, (40), 351–403.
Chapman, B. M., Jones, D. R., & Jung, R. F. (1983). Processes controlling metal ion attenuation in acid mine drainage streams. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 47, 1957–1973.
Cidu, R., Frau, F., & Da Pelo, S. (2011). Drainage at abandoned mine sites: natural attenuation of contaminants in different seasons. Mine Water Environment, 30, 113–126.
Concas, A., Ardau, C., Cristini, A., Zuddas, P., & Cao, G. (2006). Mobility of heavy metals from tailings to stream waters in a mining activity contaminated site. Chemosphere, 63, 244–253.
Connell, W. D., & Miller, J. G. (1984). Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Pollution. New York, U.S.A.: John Willey & Sons.
De Aguinaga, R. E. (2002). Modelación geohidrológica del acuífero del Río San Pedro. México: Tesis de licenciatura. Universidad de Sonora.
EPA. (1996). Method 6010B. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry. (Environmental Protection Agency) Las Vegas, Nevada. Revision 2.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). (1982). Handbook for sampling and sample preservation of water and wastewater (Report No. EPA-600/4-82-029), U.S.A.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). (1986). Gold Book of Quality Criteria for Water. (Environmental Protection Agency) EPA 440/5-86-001. U.S.A.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). (1999). Methods and guidance for analysis of water, version 2.0. United States Environment Protection Agency. U.S.A.
Förstner, U. (1979). Metal transfer between solid and aqueous phases. In: U. Förstner Environmental Geology G. T. W. Wittman (Eds.), Metal pollution in the aquatic environment (pp. 192–270). Verlag, Berlin: Springer
Garbarino, J.R., Hayes, H.C., Roth, D.A., Antweiler, R.C., Brinton, T.I. & Taylor, H.E. (1995). Heavy metals in the Mississippi River. In: R.H., Meade (Ed.), Contaminants in the Mississippi River (1987–92). U.S. Virginia: Geological Survey Circular 1133
Gómez-Alvarez, A. (2008). Estudio de Caracterización y Biodisponibilidad de Metales Pesados (Agua y Sedimento) del Río San Pedro, localizado en una Región Semi-Árida del Noroeste de México. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California, México.
Gómez-Álvarez, A., Valenzuela-García, J. L., Aguayo-Salinas, S., Meza-Figueroa, D. M., Ramírez-Hernández, J., & Ochoa-Ortega, G. (2007). Chemical partitioning of sediment contamination by heavy metals in the San Pedro River, Sonora, México. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 9, 25–35.
Gómez-Álvarez, A., Meza-Figueroa, D. M., Villalba-Atondo, A. I., Valenzuela-García, J. L., Ramírez-Hernández, J., & Almendariz-Tapia, F. J. (2009). Estimation of potential pollution from mine tailings in the San Pedro River (1993–2005), México-U.S. border. Environmental Geology, 57, 1469–1479.
Gómez-Álvarez, A., Valenzuela-García, J. L., Meza-Figueroa, D., De la O-Villanueva, M., Ramírez-Hernández, J., & Almendariz-Tapia, F. J. (2011). Impact of mining activities on sediments in a semi-arid environment: San Pedro River. Applied Geochemistry, 12, 2101–2112.
Herrera-Carbajal, S. (2005). Estudio hidrológico de la Cuenca del Río San Pedro, Sonora, utilizando el Modflow. Tesis de Maestría. Universidad de Sonora, México.
Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Macklin, M. G., & Taylor, M. P. (1999a). 2000 years of sediment-borne heavy metal storage in the Yorkshire Ouse Basin, NE England, U.K. Hydrological Processes, 13, 1087–1102.
Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Schell, C., & Macklin, M. G. (1999b). Mineralogy and geochemistry of alluvium contaminated by metal mining in the Rio Tinto area, southwest Spain. Applied Geochemistry, 14, 1015–1030.
Hun-Bok, J., Seong-Taek, Y., Mayer, B., Soon-Oh, K., Seong-Sook, P., & Pyeong-Koo, L. (2005). Transport and sediment-water partitioning of trace metals in acid mine drainage: Na example from the abandoned Kwangyang Au-Ag mine área, South Korea. Environmental Geology, 48, 437–449.
I.N.E.G.I. (Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografia e Informática). (1982). Cartas topográficas H12B32, H12B33, H12B34, H12B42, H12B43, H12B44, H12B52, H12B53 Y H12B54. Escala 1:50,000. México.
I.N.E.G.I. (Instituto Nacional de Estadística Geografia e Informática). (1993). Estudio hidrológico del Estado de Sonora. México: Gobierno del Estado de Sonora.
Kimball, B. A., Callender, E., & Axtmann, E. V. (1995). Effects of colloids on metal transport in a river receiving acid mine drainage, upper Arkansas River, Colorado, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 10, 285–306.
Lobban, S. C., Harrison, J. P., & Duncan, J. M. (1985). The physicological ecology of seaweeds. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Longjiang, M., Qiang, E., Duowen, M., Ke, H., & Jinghong, Y. (2011). Contamination assessment of heavy metal in surface sediments of the Wuding River, northern China. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 290, 409–414.
Lu, L., Wang, R., Chen, F., Xue, J., Zhang, P., & Lu, J. (2005). Element mobility during pyrite weathering: implications for acid and heavy metal pollution at mining-impacted sites. Environmental Geology, 49, 82–89.
Meza-Figueroa, D., Maier, R. M., De la O-Villanueva, M., Gómez, A. A., Moreno, Z. A., Rivera, J., Campillo, A., Grandlic, C., Anaya, R., & Palafox, R. J. (2009). The impact of unconfined mine tailings in residential areas from a mining town in a semi-arid environment: Nacozari, Sonora, México. Chemosphere, 77, 140–147.
Mountouris, A., Voutsas, E., & Tassios, D. (2002). Bioconcentration of heavy metals in aquatic environments: the importance of bioavailability. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44(2002), 1136–1141.
Navarro, M. C., Pérez-Sirvent, C., Martínez-Sánchez, M. J., Vidal, J., Tovar, P. J., & Bech, J. (2008). Abandoned mine sites as a source of contamination by heavy metals: a case study in a semi-arid zone. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 96(2–3), 183–193.
Olías, M., Nieto, J. M., Sarmiento, A. M., Cerón, J. C., & Cánovas, C. R. (2004). Seasonal water quality variations in a river affected by acid mine drainage: the Odiel River (South West Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 333, 267–281.
Pagnanelli, F., Moscardini, E., Guiliano, V., & Toro, L. (2004). Sequential extraction of heavy metals in river sediments of an abandoned pyrite mining area: pollution detection and affinity series. Environmental Pollution, 132, 189–201.
Parkman, R. H., Charnock, J. M., Bryan, N. D., Livens, F. R., & Vaughan, D. J. (1999). Reaction of copper and cadmium ions in solution with goethite, lepidocrocite, mackinawite, and pyrite. American Mineralogist, 84, 407–419.
Penreath, R.J. (1994). The discharge of waters from active and abandoned mines. In: Hester, R.E. & Harrison, R.M. (eds.), Mining and its environmental impact. Issues in Environmental Science and Technology No. 1. Royal Society of Chemistry, Herts, UK. Pp. 121–132.
Saarinen, T., Mohämmädighävam, S., Marttila, H., & Klove, B. (2013). Impact of peatland forestry on runoff water quality in areas with sulphide-bearing sediments: how to prevent acid surges. Ecological Management, 293, 17–28.
Salomons, W. (1995). Environmental impact of metals derived from mining activities: processes, predictions, prevention. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 52, 5–23.
Schemel, L. E., Kimball, B. A., & Bencala, K. E. (2000). Colloid formation and metal transport through two mixing zones affected by acid mine drainage near Silverton, Colorado. Applied Geochemistry, 15, 1003–1018.
SEDUE (Secretaría de Desarrollo Urbano y Ecología) (1989). Acuerdo por el que se establecen los Criterios Ecológicos de Calidad de Agua CE- CCA-001/89, México.
Servida, D., Giovanni, G., & De Capitani, L. (2009). Geochemical hazard evaluation of sulphide-rich iron mines: the Rio Marina district (Elba Island, Italy). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 100, 75–89.
Solís-Garza, G., Villalba-Atondo, A. I., & y Nubes-Ortís, G. (2012). Calidad de agua y vegetación en el Río Santa Cruz, Sonora. España: México. Editorial Académica Española.
Taylor, M. P., & Hudson-Edwards, K. A. (2008). The dispersal and storage of sediment-asspciated metals in an arid river system: the leichhardt River, Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia. Environmental Pollution, 152, 193–204.
Villalba-Atondo, A. I., Del Castillo-Alarcón, J. M., Gómez-Álvarez, A., Pérez-Villalba, A. M., Villalba-Urquidy, S., & y Salcido-Esquer, A. (2013). Contaminación del agua y suelo en el ecosistema del Río Agua Prieta, Sonora, México. BIOtecnia, XV, 1, 3–11.
Wray, D. S. (1998). The impact of unconfined mine tailings and anthropogenic pollution on a semi-arid environment—an initial study of the Rodalquilar mining district, south east Spain. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 20, 29–38.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Department of Chemical Engineering and Metallurgy for their support for the completion of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez-Alvarez, A., Meza-Figueroa, D., Valenzuela-García, J.L. et al. Behavior of Metals Under Different Seasonal Conditions: Effects on the Quality of a Mexico–USA Border River. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 2138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2138-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2138-z