Abstract
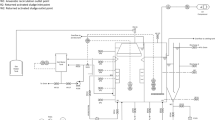
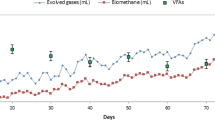
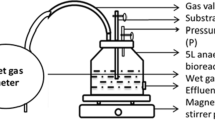
Performance of a laboratory-scale integrated baffled reactor for the treatment of raw palm oil mill effluent (POME) was investigated. Initially, the reactor was fed with diluted POME (COD = 1,830 mg/L and OLR = 0.46 g COD/L day) which was then increased gradually to actual concentration (COD = 45,500 mg/L and OLR = 11.38 g COD/L day). Reactor operation was studied in two different hydraulic retention times (HRTs) (4 and 6 days) using POME with no effluent-recycled feed and after alkalinity supplementation. Chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal of 79 and 83 % at an HRT of 4 and 6 days were attained at the highest organic loading rate (OLR = 11.38 g COD/L day). The presence of Arcella-like and Metopus-like species and pH profile in the bioreactor’s compartments imply that anaerobic system is active in the reactor throughout the study. Use of methanogen-enriched inocula, smooth OLR augmentation, and appropriate separation of acidogens and methanogens in the reactor were the reasons for satisfactory performances of the system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antony, A., Bassendeh, M., Richardson, D., Aquilina, S., Hodgkinson, A., Law, I., & Leslie, G. (2012). Diagnosis of dissolved organic matter removal by GAC treatment in biologically treated papermill effluents using advanced organic characterisation techniques. Chemosphere, 86, 829–836.
APHA, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (1992). American Public Health Association, NW, Washington, DC.
Borja, R., & Banks, C. J. (1994). Anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent using an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Biomass and Bioenergy, 6, 381–389.
Cheng, F., O-Thong, S., Boe, K., & Angelidaki, I. (2011). Comparison of UASB and EGSB reactors performance, for treatment of raw and deoiled palm oil mill effluent (POME). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189, 229–234.
Feng, H., Hu, L., Mahmood, Q., Fang, C., Qiu, C., & Shen, D. (2009). Effects of temperature and feed strength on a carrier anaerobic baffled reactor treating dilute wastewater. Desalination, 239, 111–121.
Feng, H., Hu, L., Mahmood, Q., Qiu, C., Fang, C., & Shen, D. (2008). Anaerobic domestic wastewater treatment with bamboo carrier anaerobic baffled reactor. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 62, 232–238.
González, J. S., Rivera, A., Borja, R., & Sánchez, E. (1998). Influence of organic volumetric loading rate, nutrient balance and alkalinity: COD ratio on the anaerobic sludge granulation of an UASB reactor treating sugar cane molasses. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 41, 127–131.
Huang, J. S., Wu, C. S., & Chen, C. M. (2005). Microbial activity in a combined UASB-activated sludge reactor system. Chemosphere, 61, 1032–1041.
Malakahmad, A., Ahmad Basri, N. E., & Zain, S. M. (2011a). Study on performance of a modified anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) to treat high strength wastewater. Journal of Applied Sciences, 11, 1449–1452.
Malakahmad, A., Hasani, A., Eisakhani, M., & Isa, M. H. (2011b). Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) for the removal of Hg2+ and Cd2+ from synthetic petrochemical factory wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 191, 118–125.
Mengchun, G., Zonglian, S., & Chunji, J. (2007). Performance evaluation of a mesophilic (37 °C) upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor in treating distiller’s grains wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 808–813.
Metcalf and Eddy Inc, (2003). Wastewater engineering treatment and reuse, fourth ed., McGraw Hill.
Najafpour, G. D., Zinatizadeh, A. A. L., Mohamed, A. R., Isa, M. H., & Nasrollahzadeh, H. (2005). High-rate anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent in an up-flow sludge-fixed film bioreactor. Process Biochemistry, 41, 370–379.
Priya, M., Haridas, A., & Manilal, V. B. (2008). Anaerobic protozoa and their growth in biomethanation systems. Biodegradation, 19, 179–185.
Saritpongteeraka, K., & Chaiprapat, S. (2008). Effects of pH adjustment by parawood ash and effluent recycle ratio on the performance of anaerobic baffled reactors treating high sulfate wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 99, 8987–8994.
Setiadi T., Faisal. (1994). Palm oil mill effluent treatment by anaerobic baffled reactors, In Proceeding of Aquatech Asia’94, Singapore, 22–24 November, 134–141.
Setiadi, T., & Djajadiningrat, H. A. (1996). Palm oil mill effluent treatment by anaerobic baffled reactors: recycle effects and biokinetic parameters. Water Science and Technology, 34, 59–66.
Siddique, T., Gupta, R., Fedorak, P. M., MacKinnon, M. D., & Foght, J. M. (2008). A first approximation kinetic model to predict methane generation from an oil sands tailings settling basin. Chemosphere, 72, 1573–1580.
Singh, S., Haberl, R., Moog, O., Shrestha, R., & Shrestha, P. (2009). Performance of an anaerobic baffled reactor and hybrid constructed wetland treating high-strength wastewater in Nepal—a model for DEWATS. Ecological Engineering, 35, 654–660.
Sponza, D. T., & Demirden, P. (2010). Relationships between chemical oxygen demand (COD) components and toxicity in a sequential anaerobic baffled reactor/aerobic completely stirred reactor system treating Kemicetine. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176, 64–75.
Tomasini Ortiz, A.C., Moeller Chávez, G.E., Garzón-Zuñiga, M., Hornelas Orozco, Y. (2007). The testate lobose amoeba in the wastewater treatment, In Proceedings of the II International Conference on Environmental, Industrial and Applied Microbiology (BioMicroWorld2007), Spain, 347–351.
Yacob, S., Hassan, M. A., Yoshihito, S., Minato, W., & Subash, S. (2005). Baseline study of methane emission from open digesting tanks of palm oil mill effluent treatment. Chemosphere, 59, 1575–1581.
Yangguo, Z., Nanqi, R., & Aijie, W. (2008). Contributions of fermentative acidogenic bacteria and sulfate-reducing bacteria to lactate degradation and sulfate reduction. Chemosphere, 72, 233–242.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Mr. Zaaba Mohamad for his support and efforts throughout this research. An honorable mention also goes to Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS (UTP) for the financial assistance and Nasaruddin Palm Oil Mill for allowing the collection of raw POME.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malakahmad, A., Lahin, F.A. & Yee, W. Biodegradation of High-Strength Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) through Anaerobes Partitioning in an Integrated Baffled Reactor Inoculated with Anaerobic Pond Sludge. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1883 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1883-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1883-3