Abstract
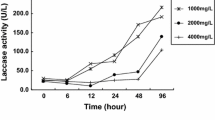
This study was performed to evaluate the ability of white-rot fungi to decolorize dye effluents. A total of 222 isolates of white-rot fungi were initially investigated to assess their ability to decolorize chemically different synthetic dyes in solid medium, resulting in selection of 25 isolates including four isolates of Berkandera adusta, five isolates of Ceriporia lacerata, three isolates of Irpex lacteus, one isolate of Perenniporia fraxinea, ten isolates of Phanerochaete spp., one isolate of Phlebia radiata, and one isolate of Porostereum spadiceum. Of the 25 isolates, B. adusta KUC9065, C. lacerata KUC8090, P. calotricha KUC8003, and P. spadiceum KUC8602 were finally selected on the basis of their ability to decolorize synthetic dyes in liquid medium, and were used to decolorize industrial effluents. B. adusta KUC9065 increased the transmittance of visible light by 71–92 %. Decolorization of wastewater by B. adusta KUC9065 was probably caused by the lignin-modifying enzymes produced by the fungus. In addition, the acute toxicity to Daphnia magna decreased from 2.5 to 2.1 and from 3.5 to 2.6 toxic units over 24 and 48 h, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banat, I. M., Nigam, P., Singh, D., & Marchant, R. (1996). Microbial decolorization of textile-dye-containing effluents: a review. Bioresource Technology, 58, 217–227.
Choi, Y.-S., Long, Y., Kim, M.-J., Kim, J.-J., & Kim, G.-H. (2013). Decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes by Irpex lacteus KUC8958. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A-Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 48, 501–508.
Diwaniyan, S., Kharb, D., Raghukumar, C., & Kuhad, R. C. (2010). Decolorization of synthetic dyes and textile effluents by basidiomycetous fungi. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 210, 409–419.
Guo, M., Lu, F. P., Liu, M. Y., Li, T. P., Pu, J., Wang, N., et al. (2008). Purification of recombinant laccase from Trametes versicolor in Pichia methanolica and its use for the decolorization of anthraquinone dye. Biotechnology Letters, 30, 2091–2096.
Heinfling, A., Martinez, M. J., Martinez, A. T., Bergbauer, M., & Szewzyk, U. (1998). Purification and characterization of peroxidases from the dye-decolorizing fungus Bjerkandera adusta. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 165, 43–50.
Jiang, H., & Murmann, J. P. (2011). Regional institutions, ownership transformation, and migration of industrial leadership in China: the case of the Chinese synthetic dye industry, 1978–2008. Australian School of Business Research Paper No. 2011 STRE 01, Australian School of Business, The University of New South Wales.
Johannes, C., & Majcherczyk, A. (2000). Laccase activity tests and laccase inhibitors. Journal of Biotechnology, 78, 193–199.
Kasinath, A., Novotný, Č., Svobodová, K., Patel, K. C., & Šašek, V. (2003). Decolorization of synthetic dyes by Irpex lacteus in liquid cultures and packed-bed bioreactor. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 32, 167–173.
Kaushik, P., & Malik, A. (2009). Fungal dye decolourization: recent advances and future potential. Environment International, 35, 127–141.
Keharia, H., & Madamwar, D. (2002). Transformation of textile dyes by white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 102, 99–108.
Kim, J.-J., Lim, Y. W., Wingfield, M. J., Breuil, C., & Kim, G.-H. (2004). Leptographium bistatum sp nov., a new species with Sporothrix synanamorph from Pinus radiata in Korea. Mycological Research, 108, 699–706.
Lee, H., Choi, Y.-S., Kim, M.-J., Huh, N., Kim, G.-H., Lim, Y.-W., et al. (2010). Degrading ability of oligocyclic aromates by Phanerochaete sordida selected via screening of white rot fungi. Folia Microbiologica, 55, 447–453.
Lee, Y. M., Lee, H., Kim, G.-H., & Kim, J.-J. (2011). Miniaturized enzyme production and development of micro-assays for cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 86, 124–127.
Lee, H., Jang, J., Kim, J.-M., Kim, G.-H., & Kim, J.-J. (2013). White rot fungus Merulius tremellosus KUC9161 identified as an effective degrader of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 53, 195–199.
Novotný, Č., Rawal, B., Bhatt, M., Patel, M., Šašek, V., & Molitoris, H. P. (2001). Capacity of Irpex lacteus and Pleurotus ostreatus for decolorization of chemically different dyes. Journal of Biotechnology, 89, 113–122.
Novotný, Č., Svobodová, K., Kasinath, A., & Erbanová, P. (2004). Biodegradation of synthetic dyes by Irpex lacteus under various growth conditions. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 54, 215–223.
Novotný, Č., Cajthaml, T., Svobodová, K., Šušla, M., & Šašek, V. (2009). Irpex lacteus, a white-rot fungus with biotechnological potential — review. Folia Microbiologica, 54, 375–390.
OECD 2004. Daphinia sp., Acute immobilization test. Guideline for testing of chemicals No. 202.
Olukanni, O. D., Osuntoki, A. A., Kalyani, D. C., Gbenle, G. O., & Govindwar, S. P. (2010). Decolorization and biodegradation of Reactive Blue 13 by Proteus mirabilis LAG. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 184, 290–298.
O'Neill, C., Hawkes, F. R., Hawkes, D. L., Lourenco, N. D., Pinheiro, H. M., & Delee, W. (1999). Colour in textile effluents — sources, measurement, discharge consents and simulation: a review. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 74, 1009–1018.
Paszczynski, A., Pasti-Grigsby, M. B., Goszczynski, S., Crawford, R. L., & Crawford, D. L. (1992). Mineralization of sulfonated azo dyes and sulfanilic acid by Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Streptomyces chromofuscus. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 3598–3604.
Rauf, M. A., & Salman Ashraf, S. (2012). Survey of recent trends in biochemically assisted degradation of dyes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 209, 520–530.
Salas-Veizaga, D. M., Morales-Belpaire, I., & Terrazas-Siles, E. (2013). Evaluation of the genotoxic potential of reactive black 5 solutions subjected to decolorizing treatments by three fungal strains. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 89, 125–129.
Sangeeta, P., Kheria, S., & Pakshirajan, K. (2011). Biodecolourization of real textile industry wastewater using white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research, 70, 982–986.
Tien, M., & Kirt, T. K. (1988). Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Methods in Enzymology, 161, 238–249.
Vilgalys, R., & Hester, R. (1990). Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. Journal of Bacteriology, 172, 4238–4246.
Wariishi, H., Valli, K., & Gold, M. H. (1992). Manganese(II) oxidation by manganese peroxidase from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Kinetic mechanism and role of chelators. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 23688–23695.
Yadav, A., Mukherji, S., & Garg, A. (2013). Removal of chemical oxygen demand and color from simulated textile wastewater using a combination of chemical/physicochemical processes. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 52, 10063–10071.
Yi, X., Kim, E., Jo, H.-J., Schlenk, D., & Jung, J. (2009). A toxicity monitoring study on identification and reduction of toxicants from a wastewater treatment plant. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 1919–1924.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Forest Science & Technology Project (Project No. S121012L110100), provided by the Korea Forest Service of the Korean Government, and by a Korea University Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, YS., Seo, JY., Lee, H. et al. Decolorization and Detoxification of Wastewater Containing Industrial Dyes by Bjerkandera adusta KUC9065. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1801 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1801-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1801-0