Abstract
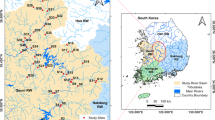
Historical profiles of trace element concentrations were reconstructed from two mangrove sediment cores collected within the Ba Lat Estuary (BLE), Red River, Vietnam. Chronologies of sediment cores were determined by the 210Pb method, which showed that each respective sediment core from the south and north entrances of BLE provided a record of sediment accumulation spanning approximately 100 and 60 years. The profiles of Pb, Zn, Cu, Cr, V, Co, Sb, and Sn concentrations markedly increased from the years of the 1920s–1950s, and leveled out from 1950s–1980s, and then gradually decreased from 1980s to present. The profiles of Cd and Ag concentrations increased from 1920s–1940s, and then decreased from 1940s to present. The profile of Mo concentrations progressively increased from 1920s–1980s, then decreased to present. The Mn concentrations failed to show a clear trend in both sediment cores. Results from contamination factors, Pearson’s correlation, and hierarchical cluster analysis suggest that the trace elements were likely attributed to discharge of untreated effluents from industry, domestic sewage, as well as non-point sources. Pollution Load Index (PLI) revealed levels higher than other mangrove sediment studies, and the long-term variations in PLI matched significant socioeconomic shifts and population growth in Vietnam. Geoaccumulation Index showed that mangrove sediments were moderately polluted by Pb and Ag, and from unpolluted to moderately polluted by Zn, Cu, and Sb. The concentrations of Pb, Zn, Cu, Cr, and Cd exceeded the threshold effect levels and effect range low concentrations of sediment quality guidelines, implying that the sediments may be occasionally associated with adverse biological effects to benthic organisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano, A., Iwamoto, N., Inoue, T., & Inouchi, Y. (2006). Seafloor environmental changes resulting from nineteenth century reclamation in Mishou Bay, Bungo Channel, Southwest Japan. Environmental Geology, 50(7), 989–999.
Amin, B., Ismail, A., Arshad, A., Yap, C., & Kamarudin, M. (2009). Gastropod assemblages as indicators of sediment metal contamination in mangroves of Dumai, Sumatra, Indonesia. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 201, 9–18.
Andersen, T. J., Mikkelsen, O. A., Møller, A. L., & Morten, P. (2000). Deposition and mixing depths on some European intertidal mudflats based on 210Pb and 137Cs activities. Continental Shelf Research, 20(12–13), 1569–1591.
Appleby, P. G., & Oldfield, F. (1978). The calculation of lead-210 dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to the sediment. Catena, 5, 1–8.
Bac, V., & Hien, P. (2009). Regional and local emissions in red river delta, Northern Vietnam. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 2(3), 157–167.
Baskaran, M., & Naidu, A. S. (1995). 210Pb-derived chronology and the fluxes of 210Pb and 137Cs isotopes into continental shelf sediments, East Chukchi Sea, Alaskan Arctic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 4435–4448.
Bernardello, M., Secco, T., Pellizzato, F., Chinellato, M., Sfriso, A., & Pavoni, B. (2006). The changing state of contamination in the Lagoon of Venice. Part 2: Heavy metals. Chemosphere, 64, 1334–1345.
Bjørgesæter, A., & Gray, J. S. (2008). Setting sediment quality guidelines: A simple yet effective method. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57, 221–235.
Bonotto, D., & de Lima, J. (2006). 210Pb-derived chronology in sediment cores evidencing the anthropogenic occupation history at Corumbataí River basin, Brazil. Environmental Geology, 50, 595–611.
Brack, K., & Stevens, R. (2001). Historical pollution trends in a disturbed, estuarine sedimentary environment, SW Sweden. Environmental Geology, 40, 1017–1029.
Callaway, J. C., Delaune, R. D., & Patrick, W. H. (1998). Heavy metal chronologies in selected coastal wetlands from northern Europe. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 36, 82–96.
Cenci, R. M., & Martin, J. M. (2004). Concentration and fate of trace metals in Mekong River Delta. Science of the Total Environment, 332, 167–182.
Chatterjee, M., Massolo, S., Sarkar, S., et al. (2009). An assessment of trace element contamination in intertidal sediment cores of Sunderban mangrove wetland, India for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150, 307–322.
Clark, M. W., McConchie, D., Lewis, D. W., & Saenger, P. (1998). Redox stratification and heavy metal partitioning in Avicennia-dominated mangrove sediments: a geochemical model. Chemical Geology, 149, 147–171.
Farmer, J. G. (1991). The perturbation of historical pollution records in aquatic sediments. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 13(2), 76–83.
Feng, H., Kirk Cochran, J., Lwiza, H., Brownawell, B. J., & Hirschberg, D. J. (1998). Distribution of heavy metal and PCB contaminants in the sediments of an urban estuary: The Hudson River. Marine Environmental Research, 45, 69–88.
Furukawa, K., Wolanski, E., & Mueller, H. (1997). Currents and sediment transport in mangrove forests. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 44, 301–310.
Grant, A., & Middleton, R. (1998). Contaminants in sediments: Using robust regression for grain-size normalization. Estuaries and Coasts, 21, 197–203.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Harbison, P. (1986). Mangrove muds—A sink and a source for trace metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 17, 246–250.
Hornberger, M. I., Luoma, S. N., van Geen, A., Fuller, C., & Anima, R. (1999). Historical trends of metals in the sediments of San Francisco Bay, California. Marine Chemistry, 64, 39–55.
Huong, N. T. L., Masami, O., Li, L., & Takahiro, H. (2007). Heavy metal pollution of the To-Lich and Kim-Nguu River in Hanoi City and the industrial source of the pollutants. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, 52, 141–146.
Ip, C. C. M., Li, X.-D., Zhang, G., Wai, O. W. H., & Li, Y.-S. (2007). Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China. Environmental Pollution, 147, 311–323.
Jara-Marini, M. E., Soto-Jiménez, M. F., & Páez-Osuna, F. (2009). Trophic relationships and transference of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in a subtropical coastal lagoon food web from SE Gulf of California. Chemosphere, 77, 1366–1373.
Lacerda, L. D., Rezende, C. E., Aragon, G. T., & Ovalle, A. R. (1991). Iron and chromium transport and accumulation in a mangrove ecosystem. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 57–58, 513–520.
Le, T. P. Q., Garnier, J., Gilles, B., Sylvain, T., & Minh, C. V. (2007). The changing flow regime and sediment load of the Red River, Viet Nam. Journal of Hydrology, 334, 199–214.
Liang, Y., & Wong, M. H. (2003). Spatial and temporal organic and heavy metal pollution at Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Chemosphere, 52, 1647–1658.
Long, E., Macdonald, D., Smith, S., & Calder, F. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
Lu, X. (2007). A note on removal of the compaction effect for the 210Pb method. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 65, 142–146.
Macdonald, D. D., Carr, R. S., Calder, F. D., Long, E. R., & Ingersoll, C. G. (1996). Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 5, 253–278.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 20–31.
MacFarlane, G. R., Pulkownik, A., & Burchett, M. D. (2003). Accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh.: Biological indication potential. Environmental Pollution, 123, 139–151.
Mackey, A. P., & Hodgkinson, M. C. (1995). Concentrations and spatial distribution of trace metals in mangrove sediments from the Brisbane River, Australia. Environmental Pollution, 90, 181–186.
Marcussen, H., Dalsgaard, A., & Holm, P. E. (2008). Content, distribution and fate of 33 elements in sediments of rivers receiving wastewater in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environmental Pollution, 155, 41–51.
Muller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veranderungen seitt 1971. Umschan, 79, 778–783.
Owen, R. B., & Lee, R. (2004). Human impacts on organic matter sedimentation in a proximal shelf setting, Hong Kong. Continental Shelf Research, 24, 583–602.
Phuong, N., Kang, Y., Sakurai, K., et al. (2010). Levels and chemical forms of heavy metals in soils from Red River Delta, Vietnam. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 207, 319–332.
Praveena, S., Ahmed, A., Radojevic, M., Abdullah, M., & Aris, A. (2008). Multivariate and Geoaccumulation Index Evaluation in mangrove surface sediment of Mengkabong Lagoon, Sabah. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 81, 52–56.
Ray, A. K., Tripathy, S. C., Patra, S., & Sarma, V. V. (2006). Assessment of Godavari estuarine mangrove ecosystem through trace metal studies. Environment International, 32, 219–223.
Saha, M., Sarkar, S. K., & Bhattacharya, B. (2006). Interspecific variation in heavy metal body concentrations in biota of Sunderban mangrove wetland, northeast India. Environment International, 32, 203–207.
Sanders, C. J., Smoak, J. M., Naidu, A. S., Sanders, L. M., & Patchineelam, S. R. (2010). Organic carbon burial in a mangrove forest, margin and intertidal mud flat. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 90, 168–172.
Smoak, J. M., & Patchineelam, S. R. (1999). Sediment mixing and accumulation in a mangrove ecosystem: Evidence from 210Pb, 234Th and 7Be. Mangroves and Salt Marshes, 3(1), 17–27.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (1995). Mangrove soils as sinks for wastewater-borne pollutants. Hydrobiologia, 295, 231–241.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (2000). Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environmental Pollution, 110, 195–205.
Tanabe, S., Hori, K., Saito, Y., Haruyama, S., Vu, V. P., & Kitamura, A. (2003). Song Hong (Red River) delta evolution related to millennium-scale Holocene sea-level changes. Quaternary Science Reviews, 22, 2345–2361.
Thuy, H., Vy, N., & Loan, T. (2007). Anthropogenic input of selected heavy metals (Cu, Cr, Pb, Zn and Cd) in the aquatic sediments of Hochiminh City, Vietnam. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 182, 73–81.
Tomlinson, D., Wilson, J., Harris, C., & Jeffrey, D. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoland Marine Research, 33, 566–575.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–192.
van Maren, D. S. (2007). Water and sediment dynamics in the Red River mouth and adjacent coastal zone. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29, 508–522.
Van Santen, P., Augustinus, P. G. E. F., Janssen-Stelder, B. M., Quartel, S., & Tri, N. H. (2007). Sedimentation in an estuarine mangrove system. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29, 566–575.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the staff of Xuan Thuy National Park, Vietnam for their help with sampling. We express our sincere thanks to Dr. Todd W. Miller and anonymous reviewers for their critical reviews and comments which significantly improved this manuscript. This work was supported by the “Global COE Program” from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tue, N.T., Quy, T.D., Amano, A. et al. Historical Profiles of Trace Element Concentrations in Mangrove Sediments from the Ba Lat Estuary, Red River, Vietnam. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 1315–1330 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0947-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0947-x