Abstract
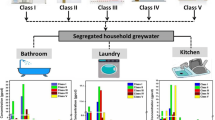
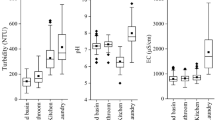
With the emerging crisis of water, greywaters represent a significant resource of water if considering recycling for uses not requiring a drinking water quality. Samples of greywaters were taken from a few households. Their characterization led to results similar to those in literature. However, they showed a lack of phosphorus in C/N/P ratio. Nevertheless, it was shown that, in our study, median was more appropriate than mean. The potential treatment steps studied during this work were sand bed filtration, adsorption onto granular activated carbon (GAC), and sanitation by chlorine. The sand bed which was supplied with sequential feedings led to a very good removal of total suspended solids (TSS; and consequently of turbidity) as well as to a 30% COD decrease. However, the organic matter withdrawal was more efficient by adsorption onto GAC. The chlorination of greywaters was efficient to decrease the microbial population. Therefore, following the reclaimed water quality which would be required treatment might imply all steps or just one or two. This kind of low-cost device could thus be implemented for reuse such as irrigation, agricultural need, or urban use.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agence Française de Sécurité Sanitaire des Aliments (AFSSA). (2008). Réutilisation des eaux usées traitées pour l’arrosage et l’irrigation. http://www.afssa.fr . Accessed 12 June 2009.
Ahmad, A. A., & Hameed, B. H. (2009). Reduction of COD and color of dyeing effluent from a cotton textile mill by adsorption onto bamboo-based activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(2–3), 1538–1543.
Al-Jayyousi, O. (2003). Greywater reuse: Towards sustainable water management. Desalination, 156(1–3), 181–192.
Australian capital Territory. Greywater Use: Guidelines for residential properties in Canberra. (2004). Australian Capital Territory. Australia: Canberra.
Bansode, R. R., Losso, J. N., Marshall, W. E., Rao, R. M., & Portier, R. J. (2004). Pecanshell based granular activated carbon for treatment of chemical oxygen demand (COD) in municipal wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 94(2), 129–135.
Canadian Guidelines for household reclaimed water for use in toilet and urinal flushing. (2007). Draft for consultation. http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/ewh-semt/alt_formats/hecs-sesc/pdf/consult/_2007/reclaim-recycle/reclaim-recycle-eng.pdf. Accessed 20 July 2009.
Centre d’informations de l’eau. (2004). Les usages domestiques dans le monde. http://www.cieau.com/toutpubl/sommaire/texte/6/contenu/6161.htm. Accessed 28 August 2009.
Chabaud, S., Andres, Y., Lakel, A., & Le Cloirec, P. (2006). Bacteria removal in sceptic effluent: Influence of biofilm and protozoa. Water Research, 40, 3109–3114.
Chin, W. H., Roddick, F. A., & Harris, J. L. (2009). Greywater treatment by UVC/H2O2. Water Research, 43(16), 3940–3947.
Decreto 2 maggio. (2006). Norme techniche per il riutilizzo delle acque reflue. Italy: Ministero dell’ambiante della tutela del territorio.
Diaper, C., Dixon, A., Butler, D., Fewkes, A., Parsons, S. A., Strathern, M., et al. (2001). Small scale water recycling systems—Risk assessment and modelling. Water Science and Technology, 43, 83–90.
Elmitwalli, T. A., & Otterpohl, R. (2007). Anaerobic biodegradability and treatment of greywater in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Water Research, 41, 1379–1387.
Eriksson, E., Auffarth, K., Henze, M., & Ledin, A. (2002). Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban Water, 4, 85–104.
Faur-Brasquet, C., Kadirvelu, K., & Le Cloirec, P. (2002). Removal of metal ions from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated carbon cloths: adsorption competition with organic matter. Carbon, 40(13), 2387–2392.
Friedler, E., & Hadari, M. (2006). Economic feasibility of on-site greywater reuse in multi-storey buildings. Desalination, 190(1–3), 221–234.
Gilboa, Y., & Friedler, E. (2008). UV-disinfection of RBC-treated light greywater effluent: Kinetics, survival and regrowth of selected microorganisms. Water Research, 42(4), 1043–1050.
Gray, S., & Becker, N. (2002). Contaminant flows in urban residential water systems. Urban water, 4(4), 331–346.
Gross, A., Kaplan, D., & Baker, K. (2007). Removal of chemical and microbiological contaminants from domestic greywater using recycled vertical flow bioreactor (RVFB). Ecological Engineering, 31(2), 107–114.
Hightower, M., & Pierce, S. (2008). The energy challenge. Nature, 452(7185), 285–286.
Hourlier, F., Massé, A., Jaouen, P., Lakel, A., Gérente, C., Faur, C., et al. (2010). Formulation of a synthetic greywater as an evaluation tool for wastewater recycling technologies. Environmental Technology, 31(2), 215–223.
Hypes, W., Batten, C., & Wilkins, J. (1975). Processing of combined domestic bath and laundry wastewater for reuse as commode flushing water. NASA technical note TN-D7937. Washington DC: National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Jefferson, B., Laine, A., Parsons, S., Stephenson, T., & Judd, S. (1999). Technologies for domestic wastewater recycling. Urban Water, 1, 285–292.
Jeppesen, B. (1996). Domestic greywater reuse: Australia’s challenge for the future. Desalination, 106(1–3), 311–315.
Kishino, H., Ishida, H., Iwabu, H., & Nakano, I. (1996). Domestic wastewater reuse using a submerged membrane bioreactor. Desalination, 106, 115–119.
Li, F., Whichmann, K., & Otterpohl, R. (2009). Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. The Science of the Total Environment, 407, 3439–3449.
Lim, Y. N., Shaaban, M. G., & Yin, C. Y. (2009). Treatment of landfill leachate using palm shell-activated carbon column: Axial dispersion modeling and treatment profile. Chemical Engineering Journal, 146(1), 86–89.
Merz, C., Scheumann, R., El Hamouri, B., & Kraume, M. (2007). Membrane bioreactor technology for the treatment of greywater from a sports and leisure club. Desalination, 215, 37–43.
Metcalf and Eddy. (1991). Design of facilities for the treatment and disposal of sludge In: wastewater engineering treatment: disposal and reuse. 3rd ed. USA. McGraw-Hill International Editions, New York, USA.
Mohan, D., Singh, K. P., & Singh, V. K. (2008). Wastewater treatment using low cost activated carbon derived from agricultural by-products—A case study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152(3), 1045–1053.
Nolde, E. (1999). Greywater reuse systems for toilet flushing in multi-storey buildings—Over ten years experience in Berlin. Urban Water, 1, 275–284.
Oschmann, N., Nghiem, L. D., & Schäfer, A. I. (2005). Fouling mechanisms of submerged ultrafiltration membranes in greywater recycling. Desalination, 179, 215–223.
Palmquist, H., & Hanaeus, J. (2005). Hazardous substances in separately collected grey- and blackwater from ordinary Swedish households. The Science of the Total Environment, 348, 151–163.
Pidou, M., Avery, L., Stephenson, T., Jeffrey, P., Parsons, S. A., Liu, S., et al. (2008). Chemical solutions for greywater recycling. Chemosphere, 71(1), 147–155.
Ramon, G., Green, M., Semiat, R., & Dosoretz, C. (2004). Low strength graywater characterization and treatment by direct membrane filtration. Desalination, 170, 241–250.
Real decreto 1620/2007 de 7 de deciembre por el que se establece el regimen juridico de la reutilisacion de las aguas depuradas, Spain.
Salomon, T., & Bedel, S. (2001). La maison des [néga]watts-Le guide malin de l’énergie chez soi. Ed. Mens, France: Terre Vivante.
Smith, A. J., Khow, J., Lodge, B., & Bavister, G. (2001). Desalination of poor quality brackish groundwater for non-potable use. Desalination, 139, 207–215.
Sostar-Turk, S., Petrinic, I., & Simonic, M. (2005). Laundry wastewater treatment using coagulation and membrane filtration. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 44(2), 185–196.
Stevik, T. K., Ausland, G., Jenssen, P. D., & Siegrist, R. L. (1999). Removal of E. Coli during intermittent filtration of wastewater effluents as affected by dosing rate. Water Research, 33(9), 2088–2098.
US Environmental Protection Agency. (2004). Guidelines for Water reuse. EPA/625/R-04/108. US. Washington DC: Agency for International Development.
World Heatlh Organization (WHO). (2006). Guidelines for the Safe Use of wastewater, excreta and greywater. Vol IV: Excreta and grey water reuse in agriculture. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Winward, G. P., Avery, L. M., Frazer-Williams, R., Pidou, M., Jeffrey, P., Stephenson, T., et al. (2008). A study of the microbial quality of greywater and an evaluation of treatment technologies for reuse. Ecological Engineering, 32(2), 187–197.
Winward, G. P., Avery, L. M., Stephenson, T., & Jefferson, B. (2008). Chlorine disinfection of greywater for reuse: Effect of organics and particles. Water Research, 42, 483–491.
Acknowledgment
This research has been partially realized within the framework of CYCLEAUX program (France), which is a program approved by the Competitiveness cluster EMC2, Direction Générale des Entreprises (DGE) and Région Bretagne.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaillou, K., Gérente, C., Andrès, Y. et al. Bathroom Greywater Characterization and Potential Treatments for Reuse. Water Air Soil Pollut 215, 31–42 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0454-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0454-5