Abstract
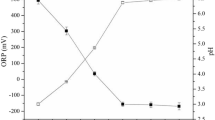
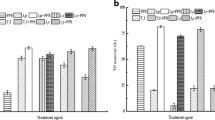
This study has investigated how to simultaneously remove both heavy metals (Cu, Mn, and Zn) and natural organic matters (NOM; humic acid and fulvic acid) from river water using potassium ferrate (K2FeO4), a multipurpose chemical acting as oxidant, disinfectant, and coagulant. In water sample including each 0.1 mM heavy metal, its removal efficiency ranged 28–99% for Cu, 22–73% for Mn, and 18–100% for Zn at the ferrate(VI) doses of 0.03–0.7 mM (as Fe). The removal efficiency of each heavy metal increased with increasing pH, whereas an overall temperature did not make any special effect on the reaction between the heavy metal and ferrate(VI). A high efficiency was achieved on the simultaneous treatment of heavy metals (0.1 mM) and NOM (10 mg/l) at the ferrate(VI) doses of 0.03–0.7 mM (as Fe): 87–100% (Cu), 31–81% (Mn), 11–100% (Zn), and 33–86% (NOM). In the single heavy metal solution, the optimum ferrate dose for treating 0.1 mM Cu or Mn was 0.1 mM (as Fe), while that for treating 0.1 mM Zn was 0.3 mM (as Fe). In the mixture of three heavy metals and NOM, on the other hand, 0.5 mM (as Fe) ferrate(VI) was determined as an optimum dose for removing both 0.1 mM heavy metals (Cu, Mn, and Zn) and 10 mg/l NOM. Prior to the addition of ferrate(VI) into the solution of heavy metals and NOM (HA or FA), complexes were formed by the reaction between divalent cations of heavy metals and negatively charged functional groups of NOM, enhancing the removal of both heavy metals and NOM by ferrate(VI).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia, S. S., & Goyal, D. (2007). Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 98, 2243–2257.
Alsheyab, M. A., & Munoz, A. H. (2006). Reducing the formation of trihalomethanes (THMs) by ozone combined with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2/O3). Desalination, 194, 121–126.
Alsheyab, M., Jiang, J. Q., & Stanford, C. (2009). On-line production of ferrate with an electrochemical method and its potential application for wastewater treatment—A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1350–1356.
Bartzatt, R., Cano, M., Johnson, L., & Nagel, D. (1992). Removal of toxic metals and nonmetals from contaminated water. Journal of Toxicology Environmental Health, Part A, 35(4), 205–210.
Cho, M., Lee, Y. H., Choi, W. Y., Chung, H. M., & Yoon, J. Y. (2006). Study on Fe(VI) species as a disinfectant: Quantitative evaluation and modeling for inactivating Escherichia coli. Water Research, 40, 3580–3586.
Choi, D. J., Park, C. H., & Park, H. K. (1998). A study on formation of aldehydes during ozonation of water containing humic acid. Journal of the Korean Society of Environmental Engineering, 20(3), 385–396.
Delaude, L., & Laszlo, P. (1996). A novel oxidizing reagent based on potassium ferrate(VI). Journal of Organic Chemistry, 61, 6360–6370.
Fan, M. H., Brown, R. C., & Huang, C. P. (2002). Preliminary studies of the oxidation of arsenic(III) by potassium ferrate. International Journal of Environmental Pollution, 18(1), 91–96.
Graham, N., Jiang, C. C., Li, X. Z., & Jiang, J. Q. (2004). The influence of pH on the degradation of phenol and chlorophenols by potassium ferrate. Chemosphere, 55, 949–956.
Jain, A., Sharma, V. K., & Mbuya, O. S. (2009). Removal of arsenic by Fe(VI), Fe(VI)/Fe(III), and Fe(VI)/Al(III) salts: Effect of pH and anions. Journal of Hazardous Material, 169, 339–344.
Jiang, J. Q., & Lloyd, B. (2002). Progress in the development and use of ferrate(VI) salt as an oxidant and coagulant for water and wastewater treatment. Water Research, 36, 1397–1408.
Jiang, J. Q., & Wang, S. (2003). Inactivation of Escherichia coli with ferrate and sodium hypochlorite: A study on the disinfection performance and rate constant. In A. Vogelpohl (Ed.), Oxidation technology water wastewater, CUTEC-Series Publication No 57 (pp. 406–411). Clausthal-Zellerfeld: Papierflieger.
Jiang, J. Q., Lloyd, B., & Grigore, L. (2001). Preparation and evaluation of potassium ferrate as an oxidant and coagulant for potable water treatment. Environmental Engineering Science, 18(5), 323–328.
Jiang, J. Q., Yin, Q., Zhou, J. L., & Pearce, P. (2005). Occurrence and treatment trials of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in wastewaters. Chemosphere, 61(4), 544–550.
Jiang, J. Q., Panagoulopoulos, A., Bauer, M., & Pearce, P. (2006a). The application of potassium ferrate for sewage treatment. Journal of Environmental Management, 79, 215–220.
Jiang, J. Q., Wang, S., & Panagoulopoulos, A. (2006b). The exploration of potassium ferrate(VI) as a disinfectant/coagulant in water and wastewater treatment. Chemosphere, 63, 212–219.
Kazama, F. (1994). Inactivation of coliphage QB by potassium ferrate. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 118, 345–350.
Kazama, F. (1995). Viral inactivation by potassium ferrate. Water Science and Technology, 31, 165–168.
Lee, Y., Um, I. H., & Yoon, J. (2003). Arsenic(III) oxidation by iron(VI) (ferrate) and subsequent removal of arsenic(V) by iron(III) coagulation. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 5750–5756.
Li, C., Li, X. Z., & Graham, N. (2005). A study of the preparation and reactivity of potassium ferrate. Chemosphere, 61, 537–543.
Licht, S., Naschitz, V., Halperin, L., Halperin, N., Lin, L., Chen, J., et al. (2001). Analysis of ferrate(VI) compounds and super-iron Fe(VI) battery cathodes: FTIR, ICP, titrimetric, XRD, UV/VIS, and electrochemical characterization. Journal of Power Sources, 101, 167–176.
Lim, M., & Kim, M. J. (2009a). Application of ferrate(VI) to the removal of humic acid and heavy metals (Cu, Mn, and Zn). Journal of the Korean Society of Environmental Engineering (J. of KSEE), 31(6), 454–459.
Lim, M., & Kim, M. J. (2009b). Removal of natural organic matter from river water using potassium ferrate(VI). Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 200(1–4), 181–189.
Lui, W., & Ma, J. (2002). Effects of ferrate(VI) preoxidation on the architecture of algal cells and the mechanism of enhanced coagulation. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 22, 24–28.
Malik, A. (2004). Metal bioremediation through growing cells. Environment International, 30, 261–278.
Nam, S. N., Kim, M. J., Jung, B. S., & Lee, Y. H. (2003). Synthesis of functionalized magnetic-impregnated ion exchange resin and its application for water treatment. Journal of the Korean Society of Environmental Engineering, 25(9), 1078–1084.
Qu, J. H., Liu, H. J., Liu, S. X., & Lei, P. J. (2003). Reduction of fulvic acid in drinking water by ferrate. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 129(1), 17–24.
Rook, J. J. (1974). Formation of haloforms during chlorination of natural waters. Water Treatment Examination, 23, 234–240.
Schreyer, J. M., Thompson, G. W., & Ockerman, L. T. (1950). Oxidation of chromium(III) with potassium ferrate(VI). Analytical Chemistry, 22(11), 691–692.
Seki, H., & Suzuki, A. (1995). Adsorption of heavy metal ions onto insolubilized humic acid. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 171, 490–494.
Sharma, V. K. (2002). Potassium ferrate(VI): An environmentally friendly oxidant. Advance in Environmental Research, 6, 143–156.
Sharma, V. K. (2007). Disinfection performance of Fe(VI) in water and wastewater: A review. Water Science and Technology, 55(1–2), 225–232.
Sharma, V. K. (2008). Oxidation transformations of environmental pharmaceuticals by Cl2, ClO2, O3, and Fe(VI): Kinetics assessment. Chemosphere, 73, 1379–1386.
Sharma, V. K., & Sohn, M. (2009). Aquatic arsenic: Toxicity, speciation, transformation, and remediation. Environment International, 35, 743–759.
Sharma, V. K., Burnett, C. R., & Millero, F. J. (2001). Dissociation constants of the monoprotic ferrate(VI) ion in NaCl media. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 3(11), 2059–2062.
Sharma, V. K., Mishra, S. K., & Nesnas, N. (2006). Oxidation of sulfonamide antimicrobials by ferrate(VI) [FeVIO 2−4 ]. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 7222–7227.
Sharma, V. K., Li, X. Z., Graham, N., & Doong, R. A. (2008). Ferrate(VI) oxidation of endocrine disruptors and antimicrobials in water. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology-AQUA, 57(6), 419–426.
Sharma, V. K., Anquandah, G. A. K., Yngard, R. A., Kim, H., Fekete, J., Bouzek, J., et al. (2009). Nonylphenol, octylphenol, and bisphenol-A in the aquatic environment: A review on occurrence, fate, and treatment. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 44, 423–442.
Stevenson, F. J. (1994). Humus chemistry: genesis, composition, reactions (2nd ed., pp. 378–381). New York: Wiley.
Stupin, D. Y., & Ozernoi, M. I. (2004). Removal of Ni(II) with sodium ferrate(VI) from EDTA-containing aqueous solutions. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 77(8), 1312–1315.
Tomiyasu, H., Fukutomi, H., & Gordon, G. (1985). Kinetic and mechanism of ozone decomposition in basic aqueous solution. Inorganic Chemistry, 24, 2962–2966.
Waite, T. D. (1979). Feasibility of wastewater treatment with ferrate. Journal of the Environmental Engineering Division, 105, 1023–1026.
Wood, R. H. (1958). The heat, free energy and entropy of ferrate(VI) ion. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 80, 2038–2041.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2005-041-D00422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, M., Kim, MJ. Effectiveness of Potassium Ferrate (K2FeO4) for Simultaneous Removal of Heavy Metals and Natural Organic Matters from River Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 211, 313–322 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0302-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0302-7