Abstract
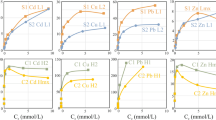
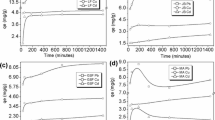
There is evidence in the literature that the ratio of mass of sorbent (M) to volume of solution (V) affects the results of batch tests with soils and sediments. This restricts the use of such data to conditions with the same M/V ratio they were derived with, unless its influence is corrected. To find a correction, we conducted batch tests with soil and zinc solution using four M/V ratios. For each ratio, the experiments produced a different relationship between the mass of zinc sorbed per unit mass of soil (a s) and the zinc concentration in the solution after shaking and removal of the solid phase (C det), which is usually taken as the equilibrium concentration (C eq). A theoretical analysis revealed that the M/V effect can be accounted for by dividing C det by the M/V ratio, if it is caused by the presence of a “third phase”. The relationship between a s and C det×V/M is the same for all ratios then.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. A., Tejedor-Tejedor, M. I., & Stanforth, R. R. (1985). Influence of aggregation on the uptake kinetics of phosphate by goethite. Environmental Science and Technology, 19(7), 632–637.
Aston, S. R., & Duursma, E. K. (1973). Concentration effects on 137Cs, 65Zn, 6°Co and 106Ru sorption by marine sediments, with geochemical implications. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 6(1–2), 225–240.
Bobé, A., Coste, C. M., & Cooper, J.-F. (1997). Factors influencing the adsorption of finopril on soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45(12), 4861–4865.
Bohn, H. L., McNeal, B. L., & O’Connor, G. A. (1979). Soil chemistry. New York: Wiley.
Curl, R. L., & Keoleian, G. A. (1984). Implicit-adsorbate model for apparent anomalies with organic adsorption on natural adsorbents. Environmental Science and Technology, 18(12), 916–922.
DIN 38414, Teil 4. (1984). Deutsche Einheitsverfahren zur Wasser-, Abwasser- und Schlammuntersuchung. Schlamm und Sedimente (Gruppe S). Bestimmung der Eluierbarkeit mit Wasser (S 4). Berlin: Beuth.
Di Toro, D. M. (1985). A particle interaction model of reversible organic chemical sorption. Chemosphere, 14(10), 1503–1538.
Di Toro, D. M., Mahony, J. D., Kirchgraber, P. R., O’Byrne, A. L., Pasquale, L. R., & Piccirilli, D. C. (1986). Effects of nonreversibility, particle concentration, and ionic strength on heavy metal sorption. Environmental Science and Technology, 20(1), 55–61.
Engelmann, F. (1998). Verfahren und Methoden zur Ermittlung von Migrationsparametern. In H. J. Voigt & T. Wippermann (Eds.), Handbuch zur Erkundung des Untergrundes von Deponien und Altlasten, Band 6, Geochemie (pp. 303–316). Berlin: Springer.
Falbe, J., & Regitz, M. (1992). Römpp-Chemie-Lexikon, Band 5. Stuttgart: Thieme.
Fehse, K.-U. (2004). Zur Sorption von Zink-Ionen an natürlichen und technischen Sorbentien unter Berücksichtigung des Feststoff:Lösung-Verhältnisses. Ph.D. thesis. Halle (Saale): Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg.
Geschwend, P. M., & Wu, S. (1985). On the constancy of sediment–water partition coefficients of hydrophobic organic pollutants. Environmental Science and Technology, 19(1), 90–96.
Grover, R., & Hance, R. J. (1970). Effect of the ratio of soil to water on adsorption of linuron and atrazine. Soil Science, 109(2), 136–138.
Hamaker, J. W., & Thompson, J. M. (1972). Adsorption. In C. A. Goring & J. W. Hamaker (Eds.), Organic chemicals in the soil environment (Vol. 1, pp. 49–143). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Horzempa, L. M., & Di Toro, D. M. (1983). PCB partitioning in sediment-water systems: The effect of sediment concentration. Journal of Environmental Quality, 12(3), 373–380.
Jury, W. A., Gardner, W. R., & Gardner, W. H. (1991). Soil physics (5th ed.). New York: Wiley.
Karickhoff, S. W., & Brown, D. S. (1978). Paraquat sorption as a function of particle size in natural sediments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 7(2), 246–252.
Kukowski, H. (1989). Untersuchungen zur Ad- und Desorption ausgewählter Chemikalien in Böden. Ph.D. thesis. Kiel: Christian-Albrechts-Universität.
Lindsay, W. L. (1972). Inorganic phase equilibria of micronutrients in soils. In J. J. Mortvedt, P. M. Giordano & W. L. Lindsay (Eds.), Micronutrients in agriculture (pp. 41–57). Madison: Soil Science Society of America.
Mackay, D., & Powers, B. (1987). Sorption of hydrophobic chemicals from water: A hypothesis for the mechanism of the particle concentration effect. Chemosphere, 16(4), 745–757.
Mayer, R. (1978). Adsorptionsisothermen als Regelgrößen beim Transport von Schwermetallen in Böden. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernährung und Bodenkunde, 141(1), 11–28.
McDonald, L. M., & Evangelou, V. P. (1997). Optimal solid-to-solution ratios for organic chemical sorption experiments. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61(6), 1655–1659.
O’Connor, D. J., & Connolly, J. P. (1980). The effect of concentration of adsorbing solids on the partition coefficient. Water Research, 14(10), 1517–1523.
OECD (1981). Adsorption/Desorption. OECD guideline for testing chemicals, 106.
Rohatgi, N., & Chen, K. Y. (1975). Transport of trace metals by suspended particulates on mixing with seawater. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 47, 2298–2320.
Servos, M. R., & Muir, D. C. G. (1989). Effect of suspended sediment concentration on the sediment to water partition coefficient for 1, 3, 6, 8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Environmental Science and Technology, 23(10), 1302–1306.
Shuman, L. M. (1975). The effect of soil properties on zinc adsorption by soils. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 39(3), 454–458.
Staples, C. A., & Geiselmann, S. J. (1988). Influence of sorbent concentration on sorption of kepone to solids. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 7, 139–142.
Suzuki, M., Yamada, T., Miyazaki, T., & Kawazoe, K. (1979). Sorption and accumulation of cadmium in the sediment of the Tama River. Water Research, 13(1), 57–63.
Syers, J. K., Browman, M. G., Smillie, G. W., & Corey, R. B. (1973). Phosphate sorption by soils evaluated by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 37(3), 358–363.
Voice, T. C., Rice, C. P., & Weber, W. J. (1983). Effect of solids concentration on the sorptive partitioning of hydrophobic pollutants in aquatic systems. Environmental Science and Technology, 17(9), 513–518.
Voice, T. C., & Weber, W. J. (1985). Sorbent concentration effect in liquid/solid partitioning. Environmental Science and Technology, 19(9), 789–796.
Wang, X., & Grady, C. P. L. (1994). Comparison of biosorption isotherms for di-n-butyl phthalate by live and dead bacteria. Water Research, 28(5), 1247–1251.
Wienberg, R. (1998). Adsorption und Desorption. In W. Hiltmann & B. Stribrny (Eds.), Handbuch zur Erkundung des Untergrundes von Deponien und Altlasten, Band 5, Tonmineralogie und Bodenphysik (pp. 209–222). Berlin: Springer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fehse, KU., Borg, H., Sorkau, E. et al. Correcting the Effect of the Sorbent to Solution Ratio on Sorption Isotherms from Batch Tests with Soils and Sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut 210, 211–220 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0243-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0243-1