Abstract
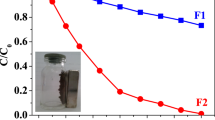
A TiO2 photocatalyst was prepared by depositing silica and titanium dioxide on the surface of black sand that made the photocatalyst recoverable using a magnetic field. The magnetic photocatalyst was used to remove six aqueous dyes from water and the removal was attributed to both adsorption and photocatalytic oxidation. Removal by adsorption was more noticeable with the cationic dyes than with the anionic dyes. The difference was related to the electrostatic interaction between the charged dye molecular and the silica-occupied surface of the photocatalyst. Removal by photocatalytic oxidation occurred with anionic dyes, while it was not appreciable with cationic dyes. It was postulated that photocatalytic oxidation might have happened with cationic dyes as well, but the strong adsorption made the photocatalytic oxidation undetectable.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arslan, İ., Balcioğlu, I. A., & Bahnemann, D. W. (2000). Advanced chemical oxidation of reactive dyes in simulated dyehouse effluents by ferrioxalate-Fenton/UV-A and TiO2/UV-A processes. Dyes and Pigments, 47, 207–218. doi:10.1016/S0143-7208(00)00082-6.
Baran, W., Makowski, A., & Wardas, W. (2008). The effect of UV radiation absorption of cationic and anionic dye solutions on their photocatalytic degradation in the presence TiO2. Dyes and Pigments, 76, 226–230. doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.08.031.
Beydoun, D., Amal, R., Low, G. K. C., & McEvoy, S. (2000). Novel photocatalyst: Titania-coated magnetite. Activity and photodissolution. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 104, 4387–4396. doi:10.1021/jp992088c.
Beydoun, D., Amal, R., Low, G., & McEvoy, S. (2002). Occurrence and prevention of photodissolution at the phase junction of magnetite and titanium dioxide. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A Chemical, 180, 193–200. doi:10.1016/S1381-1169(01)00429-0.
Forgacs, E., Cserháti, T., & Oros, G. (2004). Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: A Review. Environment International, 30, 953–971. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.02.001.
Fu, W., Yang, H., Chang, L., Hari-Bala, Li, M., & Zou, G. (2006). Anatase TiO2 nanolayer coating on strontium ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic photocatalyst.. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 289, 47–52. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.04.013.
Gao, C., Qiu, H., Zeng, W., Sakamoto, Y., Terasaki, O., Sakamoto, K., et al. (2006). Formation mechanism of anionic surfactant-templated mesoporous silica. Chemistry of Materials, 18, 3904–3914. doi:10.1021/cm061107+.
Gupta, V. K., Jain, R., Mittal, A., Mathur, M., & Sikarwar, S. (2007). Photochemical degradation of the hazardous dye Safranin-T using TiO2 catalyst. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 309, 464–469. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.12.010.
Jain, R., Mathur, M., Sikarwar, S., & Mittal, A. (2007). Removal of the hazardous dye rhodamine B through photocatalytic and adsorption treatments. Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 956–964. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.11.002.
Jiang, Z., Wang, H., Huang, H., & Cao, C. (2004). Photocatalysis enhancement by electric field: TiO2 thin film for degradation of dye X-3B. Chemosphere, 56, 503–508. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.02.006.
Kresge, C. T., Leonowicz, M. E., Roth, W. J., Vartuli, J. C., & Beck, J. S. (1992). Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature, 359, 710–712. doi:10.1038/359710a0.
Kurinobu, S., Tsurusaki, K., Natui, Y., Kimata, M., & Hasegawa, M. (2007). Decomposition of pollutants in wastewater using magnetic photocatalyst particles. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 310, 1025–1027. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.11.072.
Lee, S.-W., Drwiega, J., Mazyck, D., Wu, C.-Y., & Sigmund, W. M. (2006). Synthesis and characterization of hard magnetic composite photocatalyst—Barium ferrite/silica/titania. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 96, 483–488. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.07.039.
Li, S. X., Zheng, F. Y., Liu, X. L., Wu, F., Deng, N. S., & Yang, J. H. (2005). Photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol on nanometer size titanium dioxide surface modified with 5-sulfosalicylic acid.. Chemosphere, 61, 589–594. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.054.
Ogawa, M., Shimura, N., & Ayral, A. (2006). Deposition of thin nanoporous silica layers on solid surfaces. Chemistry of Materials, 18, 1715–1718. doi:10.1021/cm0601234.
Qiu, W., Zheng, Y., & Haralampides, K. A. (2007). Study on a novel POM-based magnetic photocatalyst: Photocatalytic degradation and magnetic separation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 125, 165–176. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2006.08.025.
Reutergadh, L. B., & Iangphasuk, M. (1997). Photocatalytic decolourization of reactive azo dye: A comparison between TiO2 and us photocatalysis. Chemosphere, 35, 585–596. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00122-7.
Saleem, M., Pirzada, T., & Qadeer, R. (2007). Sorption of acid violet 17 and direct red 80 dyes on cotton fiber from aqueous solutions. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 292, 246–250. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.06.035.
Shchukin, D. G., Ustinovich, E. A., Sviridov, D. V., & Kulak, A. I. (2004). Titanium and iron oxide-based magnetic photocatalysts for oxidation of organic compounds and sulfur dioxide. High Energy Chemistry, 38, 167–173. doi:10.1023/B:HIEC.0000027654.45001.00.
Wang, W. Y., & Ku, Y. (2007). Effect of solution pH on the adsorption and photocatalytic reaction behaviors of dyes using TiO2 and Nafion-coated TiO2. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 302, 261–268. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.02.037.
Wang, T., Wang, H., Xu, P., Zhao, X., Liu, Y., & Chao, S. (1998). The effect of properties of semiconductor oxide thin films on photocatalytic decomposition of dyeing waste water. Thin Solid Films, 334, 103–108. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(98)01125-0.
Watson, S., Beydoun, D., & Amal, R. (2002). Synthesis of a novel magnetic photocatalyst by direct deposition of nanosized TiO2 crystals onto a magnetic core. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A Chemistry, 148, 303–313. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(02)00057-6.
Watson, S., Scott, J., Beydoun, D., & Amal, R. (2005). Studies on the preparation of magnetic photocatalysts. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 7, 691–705. doi:10.1007/s11051-005-7520-8.
Wu, C. -H. (2004). Comparison of Azo dye degradation efficiency using UV/single semiconductor and UV/coupled semiconductor systems. Chemosphere, 57, 601–608. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.07.008.
Yang, H., Coombs, N., Sokolov, I., & Ozin, G. A. (1996). Free-standing and oriented mesoporous silica films grown at the air–water interface. Nature, 381, 589–592. doi:10.1038/381589a0.
Zainal, Z., Hui, L. K., Hussein, M. Z., Taufiq-Yap, Y. H., Abdullah, A. H., & Ramli, I. (2005). Removal of dyes using immobilized titanium dioxide illuminated by fluorescent lamps. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 125, 113–120. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.05.013.
Acknowledgement
This work was financed by the joint scholarship between University of East Anglia and Chinese Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, M., Bowden, D. & Brimblecombe, P. Removal of Dyes from Water Using a TiO2 Photocatalyst Supported on Black Sand. Water Air Soil Pollut 198, 233–241 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9841-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9841-6