Abstract
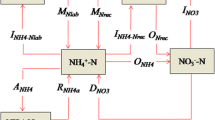
Mn biogeochemistry was studied from 1994 to 2003 in a small forested catchment in the central Czech Republic using the watershed mass balance approach together with measurements of internal stores and fluxes. Mn inputs in bulk deposition were relatively constant during a period of sharply decreasing acidic deposition, suggesting that the Mn source was terrestrial, and not from fossil fuel combustion. Mn inputs in bulk deposition and Mn supplied by weathering each averaged 13 mg m−2 year−1 (26 mg m−2 year−1 total input), whereas Mn export in streamwater and groundwater averaged 43 mg m−2 year−1. Thus an additional Mn source is needed to account for 17 mg m−2 year−1. Internal fluxes and pools of Mn were significantly greater than annual inputs and outputs. Throughfall Mn flux was 70 mg m−2 year−1, litterfall Mn flux was 103 mg m−2 year−1, and Mn net uptake by vegetation was 62 mg m−2 year−1. Large pools of labile or potentially labile Mn were present in biomass and surficial soil horizons. Small leakages from these large pools likely supply the additional Mn needed to close the watershed mass balance. This leakage may reflect an adjustment of the ecosystem to recent changes in atmospheric acidity.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acker, J. G., & Bricker, O. P. (1992). The influence of pH on biotite dissolution and alteration kinetics at low temperature. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 8, 3073–3078.
Atteia, O., & Dambrine, E. (1993). Dynamique d’éléments traces dans les précipitations sous le couvert de 2 pessieres peu polluées de Suisse romande. Annales des Sciences Forestières, 50, 445–459.
Augustin, S., Stephanowitz, H., Wolff, B., Schroder, J., & Hoffmann, E. (2005). Manganese in tree rings of Norway spruce as an indicator for soil chemical changes in the past. European Journal of Forest Research, 124, 313–318.
Berg, T., Royset, O., & Steinnes, E. (1994). Trace elements in atmospheric precipitation at Norwegian background stations (1989–1990) measured by ICP–MS. Atmospheric Environment, 21, 3519–3536.
Blank, L., Roberts, T., & Skeffington, R. (1988). New perspectives on forest decline. Nature, 336, 27–30.
Bondietti, E. A., Momoshima, N., Shortle, W. C., & Smith, K. T. (1990). A historical perspective on divalent-cation trends in red spruce stemwood and the hypothetical relationship to acidic deposition. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 20(12), 1850–1858.
Burianek, V. (2004). Norway spruce—Picea abies (L.) Karst. In H. Uhlirova (Ed.), Damage of the forest vegetation (pp. 288). Lesnická prace, s.r.o.–VÚLHM (in Czech).
Davidson, E. A., Chorover, J., & Dail, D. B. (2003). A mechanism of abiotic immobilization of nitrate in forest ecosystems: the ferrous wheel hypothesis. Global Change Biology, 9, 228–236.
Drever, J. I. (1988). The geochemistry of natural waters (2nd edn.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA: Prentice Hall, 437 pp.
Drever, J. I., & Clow, D. W. (1995). Weathering rates in catchments. In A. F. White & S. L. Brantley (Eds.), Chemical weathering rates of silicate minerals. Reviews in Mineralogy (Vol. 31, pp. 463–483). Washington, DC: Mineralogical Society of America.
Ducic, T., & Polle, A. (2005). Transport and detoxification of manganese and copper in plants. Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology, 17(1), 103–112.
Ewald, J. (2005). Ecological background of crown condition, growth and nutritional status of Picea abies (L.) Karst. in the Bavarian Alps. European Journal of Forest Research, 124, 9–18.
Forget, E., Courchesne, F., Kennedy, G., & Zayed, J. (1994). Response of Blue spruce (Picea pungens) to manganese pollution from MMT. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 73, 319–324.
Heal, K. V. (2001). Manganese and land-use in upland catchments in Scotland. Science of the Total Environment, 265, 169–179.
Heal, K. V., Kneale, P. E., & McDonald, A. T. (2002). Manganese in runoff from upland catchments: Temporal patterns and controls on mobilization. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 47, 769–780.
Heinrichs, H., & Mayer, R. (1980). The role of forest vegetation in the biogeochemical cycle of heavy metals. Journal of Environmental Quality, 9, 111–118.
Hiltbrunner, E., & Fluckiger, W. (1996). Manganese deficiency of silver fir trees (Abies alba) at a reforested site in the Jura mountains, Switzerland: Aspects of cause and effect. Tree Physiology, 16, 963–975.
Juice, S. M., Fahey, T. J., Siccama, T. G., Driscoll, C. T., Denny, E. G., & Eagar, C. (2006). Response of sugar maple to calcium addition to Northern Hardwood Forest. Ecology, 87, 1267–1280.
Kogelmann, W. J., & Sharpe, W. E. (2006). Soil acidity and manganese in declining and nondeclining sugar maple stands in Pennsylvania. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 433–441.
Kozlowski, T. T., & Pallardy, S. G. (1997). Physiology of woody plants, Mineral nutrition. San Diego: Academic.
Kreutzer, K. (1972). The effect of Mn deficiency on colour, pigment and gas exchange of Norway spruce needles. Forstwissenschaftliches Centralblatt, 91(2), 80–89.
Likens, G. E., & Bormann, F. H. (1995). Biogeochemistry of a forested ecosystem (2nd edn.). New York: Springer.
Lindberg, S. E. (1989). Behavior of Cd, Mn, and Pb in forest-canopy throughfall. In J. M. Pacyna & B. Ottar (Eds.), Control and fate of atmospheric trace metals (pp. 233–257). Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Ljungstrom, M., & Nihlgard, B. (1995). Effects of lime and phosphate additions on nutrient status and growth of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) seedlings. Forest Ecology and Management, 74(1–3), 133–148.
Lovett, G. M., Likens, G. E., Buso, D. C., Driscoll, C. T., & Bailey, S. W. (2005). The biogeochemistry of chlorine at Hubbard Brook, New Hampshire, USA. Biogeochemistry, 72, 191–232.
May, H. M., Acker, J. G., Smyth, J. R., Bricker, O. P., & Dyar, M. D. (1995). Aqueous dissolution of low-iron chlorite in dilute acid solutions at 25°C. Clay Minerals Society Proceedings, Abstract 32, 88.
Michopoulos, P., & Cresser, M. S. (2002). Effects of simulated acid precipitation on the cycling of manganese under Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis). Biogeochemistry, 61, 323–335.
Minařík, L., Žigová, A., Bendl, J., Skřivan, P., & Št’astný, M. (1998). The behaviour of rare-earth elements and Y during the rock weathering and soil formation in the Říčany granite massif, Central Bohemia. Science of the Total Environment, 215, 101–111.
Momoshima, N., & Bondietti, E. A. (1990). Cation binding in wood: Applications to understanding historical historical changes in divalent cation availability to red spruce. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 20, 1840–1849.
Nagy, K. L. (1995). Dissolution and precipitation kinetics of sheet silicates. In A. F. White & S. L. Brantley (Eds.), Chemical weathering rates of silicate minerals. Reviews in Mineralogy (Vol. 31, pp. 173–273). Washington, DC: Mineralogical Society of America.
Navrátil, T. (2003) Biogeochemistry of the II.A group elements in a forested catchment, Dissertation, Charles University Prague. Retrieved from http://www.gli.cas.cz/lesnipotok/tommy/documents/these.pdf).
Navrátil, T., Vach, M., Norton, S. A., Skřivan, P., Hruška, J., & Maggini, L. (2003). Chemical response of a small stream in a forested catchment (central Czech Republic) to a short-term in-stream acidification. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 7, 411–423.
Neal, C., Smith, C. J., Walls, J., & Dunn, S. (1986). Major, minor and trace element mobility in the acidic upland forested catchment of the upper River Severn, mid-Wales. Journal of the Geological Society (London), 143, 635–648.
Nebe, W. (1967). Zur Manganernahrung der Fichte. Archiv fur Forstwesen, 16, 109–118.
Nriagu, J. O. (1990). Global metal pollution. Environment, 32(7), 7–33.
Ostrofsky, A., Jellison, J., Smith, K. T., & Shortle, W. C. (1997). Changes in cation concentration in red spruce wood decayed by brown rot and white rot fungi. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 27, 567–571.
Pačes, T. (1985). Sources of acidification in Central Europe estimated from elemental budgets in small basins. Nature, 315, 31–36.
Pansu, M., & Gautheyreu, J. (2006). Soil organic and total C, N (H, O, S) analysis. In M. Pansu & J. Gautheyreu (Eds.), Handbook of soil analysis (pp. 327–367). Heidelberg: Springer.
Peters, N. E. (1991) Chloride cycling in 2 forested lake watersheds in the West-Central Adirondack Mountains, New York, USA. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 59(3–4), 841–846.
Scott, N. A., Likens, G. E., Eaton, J. S., & Siccama, T. G. (2001). Trace metal loss following whole-tree harvest of northeastern deciduous forest, USA. Biogeochemistry, 54, 157–217.
Sequens, J. (1998). Revision of mensurational and natural conditions in an experimental catchment Lesní potok located in the National Protected Landscape—Voděradské Beechstands (in Czech). Summary of results of two master theses for the Final Report of the Research Project FRVS no. 0081/1998.
Shanley, J. B. (1986). Manganese biogeochemistry in a small Adirondack forested lake watershed. Water Resources Research, 22, 1647–1656.
Skřivan, P., Fottová, D., Martínek, J., Minařík, L., Kvídová, O., & Burian, M. (1997). Biogeochemical fluxes of manganese in a Central-Bohemian forested catchment on granite bedrock. Biogeomon–Villanova University. Journal of Conference Abstracts, 2, 300.
Skřivan, P., Minařík, L., Burian, M., Martínek, J., Žigová, A., Kvídová, O., et al. (2000). Biogeochemistry of beryllium in an experimental forested landscape of the “Lesni potok” watershed in Central Bohemia, Czech Republic. GeoLines, 12, 41–62.
Skřivan, P., Rusek, J., Fottová, D., Burian, M., & Minařík, L. (1995). Factors affecting the content of heavy metals in bulk atmospheric precipitation, throughfall and stemflow in central Bohemia, Czech Republic. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 85, 841–846.
Stubblefield, W. A., Brinkman, S. F., Davies, P. H., Garrison, T. D., Hockett, J. R., & McIntyre, M. W. (1997). Effects of water hardness on the toxicity of manganese to developing brown trout (Salmo trutta). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 16, 2082–2089.
Vach, M., Fišák, J., Navrátil, T., Fottová, D., Špičková, J., & Skřivan, P. (2004). The precipitation chemistry over central Bohemia, sources and pathways. Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica, 48, 791–809.
Veselý, J. (1994) Effects of acidification on trace metal transport in fresh waters. In C. E. W. Steinberg & R. F. Wright (Eds.), The effects of pH and Acidification of freshwater ecosystems: implications for the future (pp. 141–151). New York: Wiley.
Veselý, J., & Majer, V. (1997). The effects of pH and atmospheric deposition on concentrations of trace elements in acidified freshwaters: A statistical approach. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 88, 227–246.
White, A. F., & Blum, A. (1995). Effect of climate on chemical weathering in watersheds, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 1729–1747.
Acknowledgement
The study was supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic, grant no. 205/04/0060. Long-term financial support for the project was provided by the Geological Institute of the Czech Academy of Science (GLI AS CR), project no. AV0Z30130516. We are grateful to Jan Rohovec (GLI CAS CR) for work on missing Mn data. For more information about the Lesni Potok catchment, visit http://www.gli.cas.cz/lesnipotok/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navrátil, T., Shanley, J.B., Skřivan, P. et al. Manganese Biogeochemistry in a Central Czech Republic Catchment. Water Air Soil Pollut 186, 149–165 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9474-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9474-1