Abstract
The effects of two different biological treatments on hydrocarbon degradation and on soil biological activities were determined during a 100-d incubation period. An evaluation of soil biological activities as a monitoring instrument for the decontamination process of diesel-oil contaminated soil was made using measurements of organic carbon content, soil microbial respiration, soil ATP and dehydrogenase, β-glucosidase, lipase enzyme activities. Five samples were used: S (control, uncontaminated soil), CS (contaminated soil), SCS (sterilized contaminated soil), CFS (contaminated soil plus N and P), CCS (contaminated soil plus compost). The relationships between soil parameters and the levels of total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) residues were investigated.
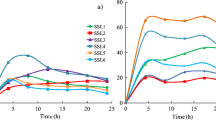
Results showed that inorganic nutrients NP and compost stimulated hydrocarbon biodegradation but not all biological activities to a significant extent. The residual hydrocarbon trend was positively related with that of the organic C content, microbial respiration and with β-glucosydase activity, while both soil lipase and dehydrogenase activities were negatively related with the hydrocarbon trend. Lipase activity was found to be the most useful parameter for testing hydrocarbon degradation in soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alef, K. and Nannipieri, P.: 1995, Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry, Academic Press, London, 576 pp.
Anderson, J. P. E.: 1982, ‘Soil respiration’, in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller and D. R. Keeney (eds.), Agronomy Monograph Number 9: Part 2. Chemical and Biological Properties. Second edition. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp. 831–871.
Casida, L. E. jr, Klein, D. A. and Santoro, T.: 1964, ‘Soil dehydrogenase activity’, Soil Sci. 98, 371–376.
Ceccanti, B., Garcia, C., Masciandaro, G., Macci, C., Carmignani, A. and Filareto, A.: 2003, ‘Il ruolo dei lombrichi (Eisenia foetida) nella bioremediation di un suolo contaminato da idrocarburi’, Convegno SISS Qualità del suolo, impatto antropico e qualità dei prodotti agricoli, Siena 9–12 giugno 2003.
Ciardi, C. and Nannipieri, P.: 1990, ‘A comparison of methods for measuring ATP in soil’, Soil Biol. Biochem. 22, 725–727.
Contin, M., Franco, L. and De Nobili, M.: 2002, ‘Indicatori biochimici di resilienza nell'inquinamento del suolo da petrolio’, Convegno annuale S.I.S.S., 2002.
DIN 38409-18: 1981, Bestimmung von Kohlenwasserstoffen. In Deutsche Einheitsverfahren zur Wasser-, Abwasser-, und Schlammuntersuchung, 9. Lieferung, VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim.
Eiland, F.: 1985, ‘Determination of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenylate energy charge (AEC) in soil and use of adenine nucleotides as measures of soil microbial biomass and activity’, Danish J. Pl. Soil Sci. 1777, 1–193.
Eivazi, F. and Tabatabai, M.A.: 1988, ‘Glucosidases and galactosidases in soils’, Soil Biol. Biochem. 20, 601–606.
Felsot, A. S.: 1998, ‘Landfarming pesticide-contaminated soil’, in Pesticide Remediation in Soil and Water, Hohn Wiley and Sons Ltd, Chichester, U.K., pp 129–160.
Ghazali, F., Zaliha, R., Salleh, A. and Basri, M.: 2004, ‘Biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil by microbial consortium’, International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 54, 61–67.
Howard, P. J. A.: 1972, ‘Problems in the estimation of biological activity in soil’, Oikos. 23, 230–240.
Jaeger, K. E., Randac, S., Dijkstra, B. W., Colson, C., van Heuvel, M. and Missed, O.: 1994, ‘Bacterial Lipases’, FEMS Microbiological Letters. 15, 29–63.
Jackson, A. W., Pardue, J. H. and Araujo, R.: 1996, ‘Monitoring crude oil mineralization in salt marhes: use of stable carbon isotope ratios’, Environ. Sci. Techn. 30, 1139–1144.
Jorgensen, K. S., Puustinen, J. and Suortti, A. M.: 2000, ‘Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil by composting in biopiles’, Environ. Pollut. 107, 245–254.
Levi-Minzi, R., Riffaldi, R. and Saviozzi, A.: 1990, ‘Carbon mineralization in soil amended with different organic material’, Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 31, 325–335.
Margesin, R. and Schinner, F.: 1999, ‘Biological decontamination of oil spills in cold environments’, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 74, 1–9.
Margesin, R., Feller, G., Hammerle, M., Stegner, U. and Schinner, F.: 2002, ‘A colorimetric method for the determination of lipase activity in soil’, Biotechnology Letters 24, 27–33.
Margesin, R., Walder, G. and Schinner, F.: 2000a, ‘The impact of hydrocarbon remediation (diesel oil and polyciclic aromatic hydrocarbon) on enzyme activities and microbial properties of soil’, Acta Biotecnologica. 20, 313–333.
Margesin, R., Zimmerbauer, A. and Schinner, F.: 2000b, ‘Monitoring of bioremediation by soil biological activities’, Chemosphere. 40, 339–346.
Namkoong, W., Hwang, E.-Y., Park, J.-S. and Choi J.-K.: 2002, ‘Bioremediation of diesel contaminated soil with composting’, Environ. Pollut. 119, 23–31.
Platen, H.: 1995, ‘The determination of hydrocarbon content by infrared spectroscopy’, in K. Alef and P. Nannipieri (eds.), Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemestry, Academic Press, Harcourt Brace & Company, San Diego, USA, pp. 506–528.
Skujins, J.: 1976, ‘Enzymes in soil’, in A.D. Mclaren and G.H. Peterson (eds.), Soil Biochemistry, M. Dekker, New York, pp. 371–414.
Snedecor, G. W. and Cochran, W. G.: 1978, Statistical Methods, The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, USA.
Sorkhoh, N. A., Al-Hasan, R. H., Khanafer, M. and Radwan, S. S.: 1995, ‘Establishment of oil-degrading bacteria associated with cyanobacteria in oil-polluted soil’, J. Appl. Bact. 78, 194–199.
Van Gestel, K., Mergaert, J., Swings, J. and Coosemans, J.: 2003, ‘Bioremediation of diesel oil-contaminated soil by composting with biowaste’, Environ. Pollut. 125, 361–368.
Walworth, J. L., Woolard, C. R. and Harris, K. C.: 2003, ‘Nutrient amendments for contaminated peri-glacial soils: use of cod bone meal as a controlled release nutrient source’, Cold Regions Science and Technology 37, 81– 88.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riffaldi, R., Levi-Minzi, R., Cardelli, R. et al. Soil Biological Activities in Monitoring the Bioremediation of Diesel Oil-Contaminated Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 170, 3–15 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-6328-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-6328-1