Abstract
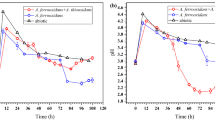
Although two species of chemolithoautotrophic bacteria, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, are widely considered to be the main microorganisms that control the process of bioleaching of heavy metals from sewage sludge, little is known about the effect of dissolved organic matter (DOM) present in sewage sludge on bacterial oxidation of energy substrate. Batch cultures studies showed that sludge DOM significantly inhibited ferrous iron and sulfur oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans LX5 and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans TS6, respectively. The toxicity of sludge DOM appeared when the concentration was higher than 150 mg DOC L−1. Among the organic compounds tested, the monocarboxylic organic acids including formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid exhibited a marked toxicity to Acidithiobacillus species. Of these organic acids, formic acid was the most toxic one as indicating that iron and sulfur oxidation almost were entirely inhibited at a concentration of 1.67 mM. In addition, it was found that A. ferrooxidans LX5 was more sensitive to glucose, starch, and citric acid than A. thiooxidans TS6, while the former seemed to be more acetic, propionic, and butyric acid resistant than the latter. In the selected 150 mg DOC L−1 of DOM derived from Sludge-H, the concentrations of formic acid and acetic acid were 8.94 mM and 2.09 mM, respectively, being a contributing factor causing 95% inhibition of iron oxidation and 70% inhibition of sulfur oxidation. To exploit specific heterotrophic microorganisms to eliminate these toxic organic compounds should be further studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, B., Leach, S. and Ingledew, W. J.: 1987, ‘The relationship between chemiosmotic parameters and sensitivity to anions and organic acids in the acidophile Thiobacillus ferrooxidans’, J. Gen. Microbiol. 133, 1171–1179.
APHA.: 1989, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th ed., Amer. Public Health Assoc., Washington, D.C.
Ashcroft, S. F. and Mortimer, C. T.: 1970, Thermochemistry of Transition Metal Complexes, Academic Press, New York, 196–212 pp.
Bevilaqua, D., Leite, A. L. L. C., Garcia, O., Jr. and Tuovinen, O. H.: 2002, ‘Oxidation of chaocopyrite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans in shake flasks’, Proc. Biochem. 38, 587–592.
Butler, R. D. and Umbreit, W. W.: 1966, ‘Absorption and utilization of organic matter by the strict autotrophy, Thiobacillus thiooxidans, with special reference to aspartic acid’, J. Bacteriol. 91, 661–666.
Cabrera, G., Gömez, J. M. and Cantero, D.: 2005, ‘Influence of heavy metals on growth and ferrous sulphate oxidation by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in pure and mixed cultures’, Proc. Biochem. 40, 2683–2686
Chatain, V., Bayard, R., Sanchez, F., Moszkowicz, P. and Gourdon, R.: 2005, ‘Effect of indigenous bacterial activity on arsenic mobilization under anaerobic conditions’, Environ. Int. 31, 221–226.
Chen, B. Y., Liu, H. L., Chen, Y. W., Cheng and Y. C.: 2004, ‘Dose-response assessment of metal toxicity upon indigenous Thiobacillus thiooxidans BC1’, Proc. Biochem. 39, 735–745.
De, G. C., Oliver, D. J. and Pesic, B. M.: 1997, ‘Effect of heavy metals on the ferrous iron oxidizing ability of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans’, Hydrometallurgy. 44, 53–63.
Deveci, H., Akcil, A. and Alp, I.: 2004, ‘Bioleaching of complex zinc sulphides using mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria: comparative importance of pH and iron’, Hydrometallurgy. 73, 293–303.
Frattini, C. J., Leduc, L. G. and Ferroni, G. D.: 2000, ‘Strain variability and the effects of organic compounds on the growth of the chemolithotrophic bacterium Thiobacillus ferrooxidans’, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 77, 57–64.
Gamache, M., Blais, J. F., Tyagi, R. D. and Meunier, N.: 2001, ‘Microflore hétérotophe impliquée dans le procédé simultané de biolixiviation des métaux et de digwstion des boues dé puration’. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 28, 158–174.
Gu, X. Y. and Wong, J. W. C.: 2004, ‘Identification of inhibitory substances affecting bioleaching of heavy metals from anaerobically digested sewage sludge’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 2934–2939.
Han, Y. and Dague, R. R.: 1997, ‘Laboratory studies on the temperature-phased anaerobic digestion of domestic primary sludge’. Water Environ. Res. 69, 1139–1143.
Harahuc, L., Lizama, H. M. and Suzuki, I.: 2000, ‘Selective inhibition of the oxidation of ferrous iron or sulfur in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans’. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 1031–1037.
Liu, H. L., Teng, C. H. and Cheng, Y.C.: 2004, ‘A semiempirical model for bacterial growth and bioleaching of Acidithiobacillus spp’, Chem. Eng. J. 99, 77–87.
Magnin, J., Baillet, F., Boyer, A., Zlatev, R., Luca, M., Cheruy, A. and Ozil, P.: 1998, ‘Augmentation, par regeneration é lectrochimique du substrat, de la production d'une biomasse (Thiobacillus ferrooxidans DSM 583) pour un procédé biologique de récupération de mé taux’, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 76, 978–984.
Marlina, J. F., Jr.: 1992, In design of anaerobic process for the treatment of industrial and municipal waste, Technomic Publishing, Lancaster, PA. 167 pp.
Mazuelos, A., Iglesias, N. and Carranza, F.: 1999, ‘Inhibition of bioleachig process by organics from solvent extraction’, Proc. Biochem. 35, 425–431.
Meruane, G. and Vargas, T.: 2003, ‘Bacterial oxidation of ferrous iron by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cin the pH ranges 2.5–7.0’, Hydrometallurgy. 71, 149–158.
Picher, S., Drogui, P., Guay, R. and Blais, J. F.: 2002, ‘Wastewater sludge and pig manure used as culture media for bioleaching of metal sulphides’, Hydrometallurgy. 65, 177–186.
Qureshi, S., Richards, B. K., Hay, A. G., Tsai, C. C., McBride, M. B., Baveye, P. and Steenhuis, T. S.: 2003, ‘Effect of microbial activity on trace element release from sewage sludge’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 37, 3361–3366.
Ryu, H. W., Moon, H. S., Lee, E. Y., Cho, K. S. and Choi, H.: 2003, ‘Leaching characteristics of heavy metals from sewage sludge by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans MET’, J. Environ. Qual. 32, 751–759.
Schrader, J. A. and Holmes, D. S.: 1988, ‘Phenotypic switching Thiobacillus ferrooxidans’, J. Bacteriol. 170, 3915–3923.
Schrenk, M. O., Edwards, K. J., Goodman, R. M., Hamers, R. J. and Banfield, J. F.: 1998, ‘Distribution of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans – implications for generation of acid mine drainage’, Science 279, 1519–1522.
Sharma, P. K., Das, A., Hanumamtha Rao, K. and Forssberg, K. S. E.: 2003, ‘Surface characterization of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cells grown under different conditions’, Hydrometallurgy 71, 285–292.
Shen, S. B., Tyagi, R. D., Blais, J. F. and Surampalli, R. Y.: 2003, ‘Bacterial leaching of metals from tannery sludge by indigenous sulphur-oxidizing bacteria – effect of sludge solids concentration’, J. Environ. Eng. 129, 513–519.
Shi, S. Y. and Fang, Z. H.: 2005, ‘Bioleaching of marmatite flotation concentrate by adapted mixed mesoacidophilic cultures in an air-lift reactor’, Int. J. Miner. Process. 76, 3–12.
Sreekrishnan, T. R., Tyagi, R. D., Blais, J. F., Meunier, N. and Campbell, P. G. C.: 1996, ‘Effect of sulfur concentration on sludge acidification during the SSDML process’, Water Res. 30, 2728–2738.
Suzuki, I., Lee, D., Mackay, B., Harahuc, L. and Oh, J. K.: 1999, ‘Effect of various ions, pH, and osmotic pressure on oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans’, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 5163–5168.
Tuovinen, O. H., Niemela, S. I. and Gyllenberg, H. G.: 1971, ‘Effect of mineral nutrients and organic substances on the development of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans’, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 13, 517-527.
Tuttle, J. H. and Dugan, P. R.: 1976, ‘Inhibition of growth, iron, and sulfur oxidation in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans by simple organic compounds’, Can. J. Microbiol. 22, 719–730.
Tyagi, R. D., Blais, J. F., Auclair, J. C. and Meunier, N.: 1993, ‘Bacterial leaching of toxic metals from municipal sludge: Influence of sludge characteristics’, Water Environ. Res. 65, 196–204.
Tyagi, R. D., Blais, J. F., Meunier, N. and Benmoussa, H.: 1997, ‘Simultaneous sewage sludge digestion and metal leaching-Effect of sludge solids concentration’, Water Res. 31, 105–118.
Tyagi, R. D., Sreekrishnan, T. R., Blais, J. F. and Campbell, P. G. C.: 1994, ‘Kinetics of heavy metal bioleaching from sewage sludge-III. Temperature effects’, Water Res. 28, 2367–2375.
Tyagi, R. D., Sreekrishnan, T. R., Blais, J. F., Surampalli, R. Y. and Campbell, P. G. C.: 1998, ‘Effect of dissolved oxygen on sludge acidification during the SSDML process’, Water Air Soil Pollut. 102, 139–155.
Vogler, K. G., Lepage, G. A. and Umbreit, W.W.: 1942, ‘The respiration of Thiobacillus thiooxidans on sulfur’, J. Gen. Physiol. 26, 89–102.
Wang, S. M., Zhou, L. X., Huang, F. Y., Fang, D.: 2004, ‘Isolation of heterotrophic microorganism and its role in bioleaching of heavy metals from tannery sludge’, Environ. Sci. 25, 153–157.
Yates, J. R. and Holmes, D. S.: 1987, ‘Two families of repeated DNA sequences in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans’, J. Bacteriol. 169, 1861–1870.
Yoshizaki, S. R. and Tomida, T. H.: 2000, ‘Principle and process of heavy metal removal from sewage sludge’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 1572–1575.
Zhou, L. X., Fang, D., Wang, S. M., Wong, J. W. C. and Wang, D. Z.: 2005, ‘Bioleaching of Cr from tannery sludge: The effects of initial acid addition and recycling of acidified bioleached sludge’, Environ. Technol. 26, 277–284.
Zhou, L. X. and Wong, J. W. C.: 2001, ‘Effect of dissolved organic matters derived from sludge and composted sludge on soil Cu sorption’, J. Environ. Qual. 30, 878–883.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, D., Zhou, L.X. Effect of Sludge Dissolved Organic Matter on Oxidation of Ferrous Iron and Sulfur by Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus Thiooxidans. Water Air Soil Pollut 171, 81–94 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9014-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9014-9