Abstract
The influence of dredging and land-disposal of a severely polluted river sediment on the release of heavy metals was studied. During the first 20 days of sediment oxidation and ripening, the pH of the sediment decreased from 8.0 to 3.5
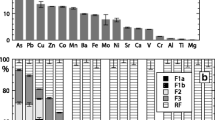
and considerable Zn-(g/L level), Ni-, Cd-, Co-, Cu-, Pb- and Cr-(mg/L level) concentrations were released into the porewater.
In order to be able to make a faster prediction of the evolution of sediment properties upon ripening, the oxidation rate was accelerated by resuspending the sediment in water. During resuspension, a sharp pH-drop (to pH 5.3) after 48 h was accompanied by an important release of Zn and Ni, whereas Cd and Cr were only released after 168 h, when pH decreased below 4 Resuspension of the air-dried sediment also resulted in a considerable release of Zn, Ni, Cd, Co, Cu, Pb and Cr. The results of porewater analysis, resuspension- and leaching tests indicate that this river sediment represents a “chemical time bomb’’ and that the removal of the contaminated sediment is urgent. Additionally, the resuspension experiment applied in this study can be used as a tool for the fast evaluation of the environmental risk of polluted sediments upon oxidation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, J. D., Brown, D. S. and Novogradac, K. J.: 1999, ‘MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, A chemical assessment model for environmental systems: Version 4.02 user's manual’, Environmental Research Laboratory Office of Research and Development. US-EPA, Athens, 81pp.
Baeyens, L.: 1960, ‘Bodemkaart van België. Verklarende tekst bij het kaartblad 26(3–4)’, Centrum voor Bodemkartering en I.W.O.N.L.
Borma, L. S., Ehrlich, M. and Barbosa, M. C.: 2003, ‘Acidification and release of heavy metals in dredged sediments’, Can. Geotech. J. 40, 1154–1163.
Brummer, G. W., Gerth, J. and Herms, U.: 1986, ‘Heavy metal species, mobility and availability in soils’, Z. Planz. Bodenk. 149, 382–398.
Caetano, M., Madureira, M.-J. and Vale, C.: 2003, ‘Metal remobilisation during resuspension of anoxic contaminated sediment: Short-term laboratory study’, Water Air and Soil Pollut. 143, 23–40.
Caille, N., Tiffreau, C., Leyval, C. and Morel, J.-L.: 2003, ‘Solubility of metals in an anoxic sediment during prolonged aeration’, Sci. Total Environ. 301, 239–250.
Calmano, W., Förstner, U. and Kersten, M.: 1986, ‘Metal associations in anoxic sediments under changes following upland disposal’, Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 1, 313–321.
Calmano, W., Hong, J. and Förstner, U.: 1993, ‘Binding and mobilization of heavy metals in contaminated sediments affected by pH and redox potential’, Wat. Sci. Technol. 28(8–9), 223–235.
Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R. and Verhulst, J.: 2004a, ‘Assessment of acid neutralizing capacity and potential mobilisation of trace metals from land-disposed dredged sediments’, Sci. Total Environ. 333(1–3), 233–247.
Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R. and Devivier, A.: 2004b, ‘Influence of ripening on pHstat leaching of heavy metals from dredged sediments’, J. Environ. Monit. 6(9), 774–781.
Chhabra, R., Pleysier, J. and Cremers, A.: 1975, ‘The measurement of the cation exchange capacity and exchangeable cations in soils: A new method’, in Proceedings of the International Clay Conference S.W. Bailey (ed.), Applied Publishing Ltd, Wilmette, IL, pp. 439–449.
Hekstra, G. P.: 1995, ‘Delayed effects of pollutants in soils and sediments: Understanding and handling of chemical time bombs in Europe’, Ecoscript 56. Amsterdam, Sticting Mondiaal Alternatief, 46pp.
Japenga, J. and Salomons, W.: 1993, ‘Dyke-protected floodplains: A possible chemical time bomb?’ Land Degrad. Rehabil. 4, 373–380.
Kosson, D. S., Van der Sloot, H. A. and Eighmy, T. T.: 1996, ‘An approach for estimation of contaminant release during utilization and disposal of municipal waste combustion residues’, J. Hazard. Mat. 47(1–3), 43–75.
Kuyper, R.: 1996, ‘Ruimtelijke ordening en bodemverontreiniging in het landelijke gebied. Chemische tijdbommen onder Nederland’, Bodem 2, 68–70.
Lors, C., Tiffreau, C. and Laboudigue, A.: 2004, ‘Effects of bacterial activities on the release of heavy metals from contaminated dredged sediments’, Chemosphere 56, 619–630.
Nelson, D. W. and Sommers, L. E.: 1982, ‘Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter’, in: A. L. Page, R. H., Miller, and D. R., Keeney (eds), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. 2nd ed. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp. 516–593.
NEN 7349: 1995, ‘Leaching characteristics of solid earthy and stony building and waste materials. Leaching tests. Determination of the leaching of inorganic components from granular materials with the cascade test’, 1st edition, February 1995, Delft, 10pp.
OVAM: 1995, ‘Vlaams reglement betreffende de bodemsanering – VLAREBO’, Openbare afval-stoffenmaatschappij voor het Vlaamse Gewest., Publicatienummer D/1995/5024/5, 63pp.
OVAM: 2003, ‘Ontwerp uitvoeringsplan Bagger- en Ruimingsspecie’, Beleidsdocumenten afvalstoffen D/2003/5024/11, 2003, 206pp.
Petersen, W., Willer, E. and Williamowski, C.: 1997, ‘Remobilization of trace elements from polluted anoxic sediments after resuspension in oxic water’, Water Air and Soil Pollut. 99, 515–522.
Prokop, Z., Vangeheluwe, M. L., Van Sprang, P. A., Janssen, C. R. and Holoubek, I.: 2003, ‘Mobility and toxicity in sandy sediments deposited on land’, Ecotox. Environ. Safety 34, 65–73.
SedNet: 2003, ‘The SedNet strategy paper. The opinion of SedNet on environmentally, socially and economically viable sediment management’, TNO and Cranfield University (eds), 2003, 22pp.
Simpson, S., Apte, S. C. and Batley, G. E.: 1998, ‘Effect of short-term resuspension events on trace metal speciation in polluted anoxic sediments’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 620–625.
Singh, S. P., Ma, L. Q., Tack, F. M. G. and Verloo, M. G.: 2000, ‘Trace metal leachability of land-disposed dredged sediments’, J. Environ. Qual. 29, 1124–1132.
Stephens, S. R., Alloway, B. J., Cater, J. E. and Parker, A.: 2001, ‘Towards the characterisation of heavy metals in dredged canal sediments and an appreciation of ‘availability’: Two examples from the UK’, Env. Poll. 113, 395–401.
Stigliani, W. M., Doelman, P., Salomons, W., Schulin, R., Smidt, G. R. B. and Van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.: 1991, ‘Chemical time bombs. Predicting the unpredictable’, Environment 33(4), 5–9, 26–30.
Tichy, R, Rulkens, W. H., Grotenhuis, J. T. C., Nydl, V., Cuypers, C. and Fajtl, J.: 1998, ‘Bioleaching of metals from soils or sediments’, Wat. Sci. Technol. 37(8), 119–127.
Van der Sloot, H. A., Rietra, R. and Mulder, E.: 2000, ‘Evaluatie van de gevolgen van de aanpassing van de pH van de uitloogvloeistof in de uitloognormen NEN 7343, 7345 en 7349’, ECN-C-00-081, August 2002.
Van Herreweghe, S., Swennen, R., Cappuyns, V. and Vandecasteele, C.: 2002, ‘Speciation of heavy metals and metalloids in soils: an integrated study near former ore treatment plants with emphasis on pHstat-leaching’, J. Geoch. Expl. 76, 113–138.
Van Thuyne, G. and Breine, J.: 2003, ‘Visbestanden in enkele beken van het Maasbekken’, Instituut voor Bosbouw and Wildbeheer. IBW.Wb.V.IR.2003.147, 12pp.
Vlaamse Milieumaatschappij: 2003, ‘Waterbodemkwaliteit 2002’, VMM, Aalst.
Vogel, A. I.: 1961, ‘Nephelometric determination of sulfate’, in: Longman (ed), A Text-Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, 3rd edn, London, pp. 850–851.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R. & Devivier, A. Dredged River Sediments: Potential Chemical Time Bombs? a Case Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 171, 49–66 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9012-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9012-y