Abstract
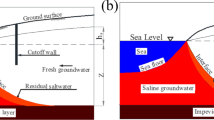
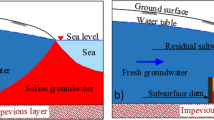
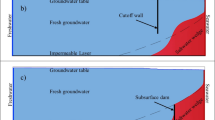
Saltwater intrusion (SWI) has a negative environmental impact on groundwater quality in coastal areas. Therefore, effective management strategies are required to preserve fresh groundwater resources. Historically, vertical barriers have been exclusively considered in both numerical studies and practical applications. The novelty of this study consists in investigating the SWI mitigation effectiveness of inclined physical subsurface barriers (PSBs), and specifically cutoff walls (CWs) and subsurface dams (SDs). An initial benchmark analysis of the Henry problem was performed. Following verification, the proposed model was applied to a real case study - the Biscayne aquifer (Southeastern Florida, USA). The model simulations run for different scenarios considering the vertical placement of the PSB, an inclined placement of the PSB according to different slopes (1/4, 1/2 and 1/1, at sea- and landside) and the combination of the best scenario. The results showed that CWs are more effective in limiting SWI in comparison with SDs. The most positive impact in both cases was achieved for a slope of 1/4, indicating that a moderate vertical inclination of the PSB better preserve coastal groundwater resources. The model presented in this work can be a valuable tool for policy makers in predicting the coastal aquifer response. However, a comprehensive cost–benefit analysis is required to further account for the feasibility and the economic costs related to the construction of inclined PSBs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Data and materials are available upon request.
References
Abiy AZ, Melesse AM, Abtew W, Whitman D (2019) Rainfall trend and variability in Southeast Florida: Implications for freshwater availability in the Everglades. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212008
Abd-Elaty I, Abd-Elhamid HF, Nezhad MM (2019a) Numerical analysis of physical barriers systems efficiency in controlling saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06725-3
Abd-Elaty I, Sallam GAH, Straface S, Scozzari A (2019b) Effects of climate change on the design of subsurface drainage systems in coastal aquifers in arid/semi-arid regions: Case study of the Nile delta. Sci Total Environ J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.483
Abd-Elaty I, Straface S, Kuriqi A (2021) Sustainable saltwater intrusion management in coastal aquifers under climatic changes for humid and hyper-arid regions. Ecol Eng 171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2021.106382
Abd-Elhamid HF, Javadi AA (2011) A cost-effective method to control seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Manage. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9837-7
Abdoulhalik A, Ahmed A, Hamill GA (2017) A new physical barrier system for seawater intrusion control. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.04.005
Allow KA (2011) Seawater intrusion in Syrian coastal aquifers, past, present and future, case study. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0261-8
Armanuos AM, Ibrahim MG, Mahmod WE, Takemura J, Yoshimura C (2019) Analysing the combined effect of barrier wall and freshwater injection countermeasures on controlling saltwater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifer systems. Water Resour Manage. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-2184-9
Basri MH (2001) Two new methods for optimal design of subsurface barrier to control seawater intrusion. Dissertation, University of Manitoba
Bower JW, Motz LH, Durden DW (1999) Analytical solution for determining the critical conditions of saltwater upconing in a leaky artesian aquifer. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00078-5
Chang QP, Zheng TY, Chen YY, Zheng XL, Walther M (2020) Investigation of the elevation of saltwater wedge due to subsurface dams. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13863
Fahs M, Ataie-Ashtiani B, Younes A, Simmons CT, Ackerer P (2016) The Henry problem: New semi-analytical solution for velocity-dependent dispersion. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR019288
Fahs M, Koohbor B, Belfort B, Ataie-Ashtiani B, Simmons CT, Younes A, Ackerer P (2018) A generalized semi-analytical solution for the dispersive Henry problem: Effect of stratification and anisotropy on seawater intrusion. Water. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020230
Galeati G, Gambolati G, Neuman SP (1992) Coupled and partially coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian Model of fresh-water-seawater mixing. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/91WR01927
Gao M, Zheng T, Chang Q, Zheng X, Walther M (2021) Effects of mixed physical barrier on residual saltwater removal and groundwater discharge in coastal aquifers. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.14263
Ghyben BW (1889) Nota in Verband Met de Voorgenomen put Boring Nabij Amsterdam. Van Het Koninkyky Institute Van Ingenieurs, the Netherlands
Henry HR (1959) Saltwater intrusion into fresh-water aquifer. J Geophys Res 64:1911–1919
Henry HR (1964) Effect of dispersion on salt encroachment in coastal aquifers. U.S. Geol Surv Water-Supply Pap 1613-C:70–84
Herbert ER, Boon P, Burgin AJ, Neubauer SC, Franklin RB, Ardón M, Hopfensperger KN, Lamers LPM, Gell P (2015) A global perspective on wetland salinization: Ecological consequences of a growing threat to freshwater wetlands. Ecosphere. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES14-00534.1
Herzberg A (1901) Die wasserversorgung Einnger Nordsecbader. Journal Gasbeleuchtung U. Wasservesurg, Germany
Hubbert MK (1940) The theory of ground water motion. J Geol. https://doi.org/10.1086/624930
Hussain MS, Abd-Elhamid HF, Javadi AA, Sherif MM (2019) Management of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: a review. Water. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122467
Jung B, Kim J, Chang H (2002) Finite element modeling of density-dependent groundwater flow and solute transport in the unsaturated layered coastal aquifer system. Proceeding of the 17th Saltwater Intrusion Meeting, Delft, the Netherlands
Kaleris VK, Ziogas AI (2013) The effect of cutoff walls on saltwater intrusion and groundwater extraction in coastal aquifers. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.007
Klassen J, Allen DM (2017) Assessing the risk of saltwater intrusion in coastal aquifers. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.02.044
Kopsiaftis G, Christelis V, Mantoglou A (2019) Comparison of sharp interface to variable density models in pumping optimisation of coastal aquifers. Water Resour Manage. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-2194-7
Langevin CD (2001) Simulation of ground-water discharge to Biscayne Bay, Southeastern Florida. U.S. geological survey, water-resources investigations report 00-4251. Tallahassee, Florida
Langevin CD (2003) Simulation of submarine ground water discharge to a marine estuary: Biscayne Bay, Florida. Ground Water. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2003.tb02417.x
Langevin CD, Panday S, Provost AM (2020) Hydraulic-head formulation for density-dependent flow and transport. Groundwater. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12967
Mirzavand M, Ghasemieh H, Sadatinejad SJ, Bagheri R (2020) An overview on source, mechanism and investigation approaches in groundwater salinization studies. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02647-7
Motevalli A, Moradi HR, Javadi S (2018) A Comprehensive evaluation of groundwater vulnerability to saltwater up-coning and sea water intrusion in a coastal aquifer (case study: Ghaemshahr-juybar aquifer). J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.12.047
Nishikawa T, Siade AJ, Reichard EG, Ponti DJ, Canales AG, Johnson TA (2009) Stratigraphic controls on seawater intrusion and implications for groundwater management, Dominguez Gap area of Los Angeles, California, USA. Hydrogeol J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-009-0481-8
Obeysekera J, Browder JA, Hornung L, Harwell MA (1999) The natural South Florida system I: Climate, geology, and hydrology. Urban Ecosyst. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009552500448
Rachid G, Alameddine I, El-Fadel M (2021) Management of saltwater intrusion in data-scarce coastal aquifers: Impacts of seasonality, water deficit, and land use. Water Resour Manage. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02991-4
Safi A, Rachid G, El-Fadel M, Doummar J, Abou Najm M, Alameddine I (2018) Synergy of climate change and local pressures on saltwater intrusion in coastal urban areas: Effective adaptation for policy planning. Water Int. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060.2018.1434957
Sherif MM, Singh VP, Amer AM (1988) A two-dimensional finite-element model for dispersion (2d-fed) in coastal aquifers. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(88)90003-0
Stoeckl L, Walther M, Morgan LK (2019) Physical and numerical modelling of post-pumping seawater intrusion. Geofluids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7191370
Sugio S, Nakada K, Urish DW (1987) Subsurface seawater intrusion barrier analysis. J Hydraul Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1987)113:6(767)
Tully K, Gedan K, Epanchin-Niell R, Strong A, Bernhardt ES, Bendor T, Mitchell M, Kominoski J, Jordan TE, Neubauer SC, Weston NB (2019) The invisible flood: the chemistry, ecology, and social implications of coastal saltwater intrusion. Bioscience. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biz027
Webb MD, Howard KWF (2011) Modeling the transient response of saline intrusion to rising sea-levels. Ground Water. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00758.x
Wu HQ, Lu CH, Kong J, Werner AD (2020) Preventing seawater intrusion and enhancing safe extraction using finite-length, impermeable subsurface barriers: 3D analysis. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020WR027792
Yingwei L, Zhang Z, Zhang Y (2020) Two-dimensional numerical analysis of differential concentration corrosion in seawater pipeline. Anti-Corros Methods Mater. https://doi.org/10.1108/ACMM-11-2019-2211
Younes A, Fahs M (2014) A semi-analytical solution for saltwater intrusion with very narrow transition zone. Hydrogeol J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-014-1102-8
Zhao M, Zhang G, Wang P, Du X, Zhang X (2020) An accurate frequency-domain model for seismic responses of breakwater-seawater-seabed-bedrock system. Ocean Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106843
Zidane A, Younes A, Huggenberger P, Zechner E (2012) The Henry semianalytical solution for saltwater intrusion with reduced dispersion. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR011157
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ismail Abd-Elaty and Salvatore Straface contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Ismail Abd-Elaty, Lorenzo Pugliese and Salvatore Straface. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ismail Abd-Elaty and Lorenzo Pugliese. All the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Ethical responsibilities are fulfilled and approved by the authors.
Consent to Participate
All authors agreed with the content and gave explicit consent to submit the manuscript.
Consent to Publish
All authors approve to publish this work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare to not have financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd-Elaty, I., Pugliese, L. & Straface, S. Inclined Physical Subsurface Barriers for Saltwater Intrusion Management in Coastal Aquifers. Water Resour Manage 36, 2973–2987 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03156-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03156-7