Abstract
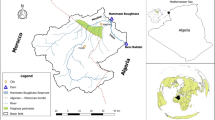
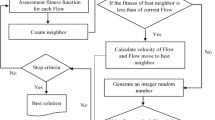
The growing prevalence of droughts and water scarcity have increased the importance of operating dam and reservoir systems efficiently. Several methods based on algorithms have been developed in recent years in a bid to optimize water release operation policy, in order to overcome or minimize the impact of droughts. However, all of these algorithms suffer from some weaknesses or drawbacks – notably early convergence, a low rate of convergence, or trapping in local optimizations – that limit their effectiveness and efficiency in seeking to determine the global optima for the operation of water systems. Against this background, the present study seeks to introduce and test a Hybrid Algorithm (HA) which integrates the Gravitational Search Algorithm (GSA) with the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm (PSOA) with the goal of minimizing irrigation deficiencies in a multi-reservoir system. The proposed algorithm was tested for a specific important multi-reservoir system in Iran: namely the Golestan Dam and Voshmgir Dam system. The results showed that applying the HA could reduce average irrigation deficiencies for the Golestan Dam substantially, to only 2 million cubic meters (MCM), compared to deficiency values for the Genetic Algorithm (GA), PSOA and GSA of 15.1, 6.7 and 5.8 MCM respectively. In addition, the HA performed very efficiently, reducing substantially the computational time needed to achieve the global optimal when compared with the other algorithms tested. Furthermore, the HA showed itself capable of assuring a high volumetric reliability index (VRI) to meet the pattern of water demand downstream from the dams, as well as clearly outperforming the other algorithms on other important indices. In conclusion, the proposed HA seems to offer considerable potential as an optimizer for dam and reservoir operations world-wide.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari-Alashti H, Bozorg Haddad O, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Marino M.A (2014) Multi-reservoir real-time operation rules: A new genetic programming approach. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Water Management 167(10):561–576
Bahrami M, Bozorg-Haddad O, Chu X (2017) Application of cat swarm optimization algorithm for optimal reservoir operation. J Irrig Drain Eng 144(1):04017057
Bai T, Kan YB, Chang JX, Huang Q, Chang FJ (2017) Fusing feasible search space into PSO for multi-objective cascade reservoir optimization. Appl Soft Comput 51:328–340
Bashiri-Atrabi H, Qaderi K, Rheinheimer DE, Sharifi E (2015) Application of harmony search algorithm to reservoir operation optimization. Water Resour Manag 29(15):5729–5748
Bolouri-Yazdeli Y, Haddad OB, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Mariño MA (2014) Evaluation of real-time operation rules in reservoir systems operation. Water Resour Manag 28(3):715–729
Bozorg-Haddad O, Janbaz M, Loáiciga HA (2016) Application of the gravity search algorithm to multi-reservoir operation optimization. Adv Water Resour 98:173–185
Bustince H, Minárová M, Fernandez J, Sesma-Sara M, Marco-Detchart C, Ruiz-Aranguren J (2017) A generalization of the gravitational search algorithm. In: International summer school on aggregation operators. Springer, Cham, pp 162–171
Ehteram M, Karami H, Mousavi SF, El-Shafie A, Amini Z (2017a) Optimizing dam and reservoirs operation based model utilizing shark algorithm approach. Knowl-Based Syst 122:26–38
Ehteram M, Karami H, Mousavi SF, Farzin S, Kisi O (2017b) Optimization of energy management and conversion in the multi-reservoir systems based on evolutionary algorithms. J Clean Prod 168:1132–1142
Feng ZK, Niu WJ, Cheng CT (2017) Multi-objective quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization for economic environmental hydrothermal energy system scheduling. Energy 131:165–178
Gonzalez B, Valdez F, Melin P (2017) A gravitational search algorithm using Type-2 fuzzy logic for parameter adaptation. In: Nature-inspired design of hybrid intelligent systems. Springer International Publishing, pp 127–138
Haddad OB, Moravej M, Loáiciga HA (2014) Application of the water cycle algorithm to the optimal operation of reservoir systems. J Irrig Drain Eng 141(5):04014064
Haddad OB, Hosseini-Moghari SM, Loáiciga HA (2015) Biogeography-based optimization algorithm for optimal operation of reservoir systems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 142(1):04015034
Li Y, Cui Q, Li C, Wang X, Cai Y, Cui G, Yang Z (2017) An improved multi-objective optimization model for supporting reservoir operation of China's south-to-north water diversion project. Sci Total Environ 575:970–981
Li YH, Zeng ZY (2017) Particle swarm optimization-differential evolution algorithm and its application in the optimal reservoir operation. In: New energy and sustainable development: proceedings of 2017 international conference on new energy and sustainable development, pp 688–698
Mansouri A, Aminnejad B, Ahmadi H (2018) Introducing modified version of penguins search optimization algorithm (PeSOA) and its application in optimal operation of reservoir systems. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 18(4):1484–1496
Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH (2017) Chaotic gravitational constants for the gravitational search algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 53:407–419
Peng Y, Peng A, Zhang X, Zhou H, Zhang L, Wang W, Zhang Z (2017) Multi-Core parallel particle swarm optimization for the operation of Inter-Basin water transfer-supply systems. Water Resour Manag 31(1):27–41
Qaderi K, Akbarifard S, Madadi M. R, Bakhtiari B (2017) Optimal operation of multi-reservoirs by water cycle algorithm. In Proceedings of the Institutionof Civil Engineers-Water Management 171(4):179–190
Raso L, Malaterre PO, Bader JC (2017) Effective stream flow process modeling for optimal reservoir operation using stochastic dual dynamic programming. J Water Resour Plan Manag 143(4):04017003
Srinivasan K, Kumar K (2018) Multi-objective simulation-optimization model for long-term reservoir operation using piecewise linear hedging rule. Water Resour Manag 32(5):1901–1911
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all reviewers and the Editor-In-Chief for their insightful comments that have helped to improve the quality of the final manuscript. The authors would also like to express their appreciation for the technical and financial support received from research grant coded GPF082A-2018 funded by the University of Malaya.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors claim that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karami, H., Farzin, S., Jahangiri, A. et al. Multi-Reservoir System Optimization Based on Hybrid Gravitational Algorithm to Minimize Water-Supply Deficiencies. Water Resour Manage 33, 2741–2760 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02238-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02238-3