Abstract
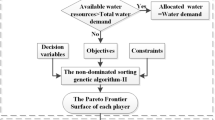
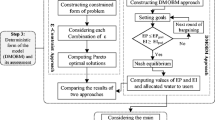
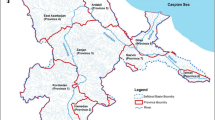
In the present research, a multi-objective model is developed for surface water resource management in the river basin area which is connected to the lake. This model considers different components of sustainable water resource management including economic, social and environmental aspects, and simultaneously tries to resolve conflicts between different stakeholders by means of non-symmetric Nash bargaining, which is linked to the multi-objective optimization method. This study proposes a new methodology to improve Nash Conflict Resolution through finding the optimum degree of the utility function. The proposed model is examined in the Zarrineh River basin in Iran. The results show that the amount of available resources or volume of reservoirs play a significant role in determining the optimal degree of the utility function and efficiency of the proposed method in such a way that the higher amount of resources or the larger reservoirs will result in the higher optimal degree of the utility function. In the proposed multi-objective model, two different amounts of surface water inflow are considered. The first assumed amount is the long-term average flow rate and the second one is equal to 80% of the first mode, which is reduced based on the estimated impacts of climate changes. This multi-objective allocation model could supply 100 and 97.5% of the environmental demand of Lake Urmia in the first and second situations, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour M, Nazaridoust A (2007) Determination of environmental water requirements of Lake Urmia, Iran: an ecological approach. Int J Environ Stud 64:161–169
AghaKouchak A et al (2015) Aral Sea syndrome desiccates Lake Urmia: call for action. J Great Lakes Res 41:307–311
Alizadeh-Choobari O, Ahmadi-Givi F, Mirzaei N, Owlad E (2016) Climate change and anthropogenic impacts on the rapid shrinkage of Lake Urmia. Int J Climatol 36:4276–4286
ASCE (1998) Sustainability Criteria for Water Resource Systems. ASCE, Reston, Virginia, USA
Aumann RJ, Maschler M (1985) Game theoretic analysis of a bankruptcy problem from the Talmud. J Econ Theory 36:195–213
Brooke A, Kendrick D, Meeraus A, Raman R, America U (1998) The general algebraic modeling system GAMS Development Corporation 1050
Cai X, McKinney DC, Lasdon LS (2002) A framework for sustainability analysis in water resources management and application to the Syr Darya basin. Water Resour Res 38(6):1085–1098
Consoli S, Matarazzo B, Pappalardo N (2008) Operating rules of an irrigation purposes reservoir using multi-objective optimization. Water Resour Manag 22:551–564
Davis MD (2007) Integrated water resource management and water sharing. J Water Resour Plan Manag 133:427–445
Degefu DM, He W, Yuan L, Zhao JH (2016) Water allocation in transboundary river basins under water scarcity: a cooperative bargaining approach. Water Resour Manag 12:4451–4466
Fahmi H (1990) Development of Runoff Assessment Model (RAM) for I.R. IRAN. Deputy for Water Affaires, Ministry of Energy, Tehran, Iran
Fattahi P, Fayyaz S (2010) A compromise programming model to integrated urban water management. Water Resour Manag 24:1211–1227
Ganji A, Karamouz M, Khalili D (2007) Development of stochastic dynamic Nash game model for reservoir operation II. The value of players’ information availability and cooperative behaviors. Adv Water Resour 30:157–168
Ganji A, Khalili D, Karamouz M, Ponnambalam K, Javan M (2008) A fuzzy stochastic dynamic Nash game analysis of policies for managing water allocation in a reservoir system. Water Resour Manag 22:51–66
Geng G, Wardlaw R (2013) Application of multi-criterion decision making analysis to integrated water resources management. Water Resour Manag 27:3191
Ghodsi SH, Kerachian R, Estalaki SM, Nikoo MR, Zahmatkesh Z (2016) Developing a stochastic conflict resolution model for urban runoff quality management: application of info-gap and bargaining theories. J Hydrol 533:200–212
Harsanyi J (1959) C.,(1959), A bargaining model for the cooperative n-person games Contributions to the theory of Games IV Princeton University Press, Princeton:325–355
Hassanzadeh E, Zarghami M, Hassanzadeh Y (2012) Determining the main factors in declining the Urmia Lake level by using system dynamics modeling. Water Resour Manag 26:129–145
Hesami A, Amini A (2016) Changes in irrigated land and agricultural water use in the Lake Urmia basin. Lake and Reservoir Management 32:288–296
Homayounfar M, Zomorodian M, Martinez CJ, Lai SH (2015) Two monthly continuous dynamic model based on Nash bargaining theory for conflict resolution in reservoir system. PLoS One 10:e0143198
Jalili S, Kirchner I, Livingstone DM, Morid S (2012) The influence of large-scale atmospheric circulation weather types on variations in the water level of Lake Urmia, Iran. Int J Climatol 32:1990–1996
Karamouz M, Akhbari M, Moridi A, Kerachian R (2006) A system dynamics-based conflict resolution model for river water quality management. Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering 3:147–160
Karamouz M, Nazif S, Sherafat MA, Zahmatkesh Z (2014) Development of an optimal reservoir operation scheme using extended evolutionary computing algorithms based on conflict resolution approach: a case study. Water Resour Manag 28:3539
Karamouz M, Szidarovszky F, Zahraie B (2003) Water resources systems analysis. CRC Press
Kerachian R, Karamouz M (2006) Optimal reservoir operation considering the water quality issue: A deterministic and stochastic conflict resolution approach. Water Resour Res 42(12):1–17
Liu D, Chen X, Lou Z (2010) A model for the optimal allocation of water resources in a saltwater intrusion area: a case study in Pearl River Delta in China. Water Resour Manag 24:63–81
Loucks DP (2000) Sustainable water resources management. Water Int 25:3–10
Loucks DP, Gladwell JS (1999) International hydrological programme, and Unesco/IHP-IV project M-4.3. Sustainablity criteria for water resource systems. Cambridge University Press, New York
Madani K (2010) Game theory and water resources. J Hydrol 381:225–238
Madani K, Lund JR (2011) California’s Sacramento–San Joaquin delta conflict: from cooperation to chicken. J Water Resour Plan Manag 138:90–99
MGC (2012) National Water Master Plan Study: the Lake Urmia Basin 4
Mianabadi H, Mostert E, Zarghami M, van de Giesen N (2014) A new bankruptcy method for conflict resolution in water resources allocation. J Environ Manag 144:152–159
Nash J (1953) Two-person cooperative games Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society:128–140
Parrachino I, Dinar A, Patrone F (2006) Cooperative game theory and its application to natural, environmental, and water resource issues: 3. application to water resources
Read L, Madani K, Inanloo B (2014) Optimality versus stability in water resource allocation. J Environ Manag 133:343–354
Roozbahani R, Schreider S, Abbasi B (2015) Optimal water allocation through a multi-objective compromise between environmental, social, and economic preferences. Environ Model Softw 64:18–30
Safari N, Zarghami M, Szidarovszky F (2014) Nash bargaining and leader–follower models in water allocation: application to the Zarrinehrud River basin, Iran. Appl Math Model 38:1959–1968
Schmeidler D (1969) The nucleolus of a characteristic function game. SIAM J Appl Math 17:1163–1170
Shapley LS (1953) A value for n-person games. Contributions to the Theory of Games 2:307–317
Teasley RL, McKinney DC (2011) Calculating the benefits of transboundary river basin cooperation: Syr Darya Basin. J Water Resour Plan Manag 137:481–490
Torabi Palatkaleh S, Estiri K, Hafez B (2010) The role of environmental requirements in process of water allocation for watersheds in Iran: sustainable development approach. In: 2nd international conference Water, ecosystems and sustainable development in arid and semi-arid zones, Tehran
ULRP (2015) URMIA LAKE RESTORATION PROGRAM, Brief Report and Projects Outline URMIA LAKE RESTORATION PROGRAM
UNDP (2016) Iran third National Communication to United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), Chapter 4 Tehran: National Climate Change Office, Department of Environment
Xuan W, Quan C, Shuyi L (2012) An optimal water allocation model based on water resources security assessment and its application in Zhangjiakou region, northern China. Resour Conserv Recycl 69:57–65
Yang W, Yang Z (2013) Development of a long-term, ecologically oriented dam release plan for the Lake Baiyangdian Sub-basin, Northern China. Water Resour Manag 27(2):485–506.
Zarghami M, Szidarovszky F (2011) Multicriteria analysis: applications to water and environment management. Springer Science & Business Media,
Zarrineh N, Abad MAN (2014) Integrated water resources management in Iran: environmental, socio-economic and political review of drought in Lake Urmia. International Journal of Water Resources and Environmental Engineering 6:40–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarebari, H., Javid, A.H., Mirbagheri, S.A. et al. Multi-Objective Surface Water Resource Management Considering Conflict Resolution and Utility Function Optimization. Water Resour Manage 32, 4487–4509 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2051-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2051-0