Abstract
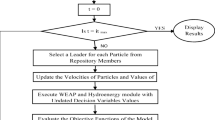
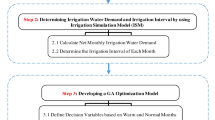
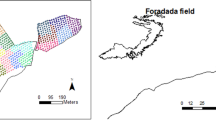
Coupled simulation-optimization models are useful tools for solving optimum water allocation and crop planning problems. In this study, the optimum crops pattern in the Arayez plain in the Karkheh river basin in Iran is determined by integration of a network flow programming (NFP) based simulation model and the shuffle frog leaping optimization algorithm (SFLA) in the form of a simulation-optimization approach. MODSIM applies NFP for finding water allocations which by use of its customization ability, the benefit of water supply for the agricultural crops is calculated based on the agronomic equations. The objective function is to maximize the total net benefit gained from crops production where the decision variables which are the irrigation depths and the cultivation areas are optimized by SFLA. Results show that by use of the coupled SFLA-NFP model, the net benefit increases 12% comparing the present situation in the plain. Also, the sensitivity analyses on effective parameters indicate that the potential maximum yield and the net price of the crops yield in the market have a direct impact on the crops optimum cultivation area.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai X, McKinney DC, Lasdon LS (2003) Integrated hydrologic-agronomic-economic model for river basin management. J Water Res Plan Manag 129(1):4–17
Condon LE, Maxwell RM (2013) Implementation of a linear optimization water allocation algorithm into a fully integrated physical hydrology model. Adv Water Resour 60:135–147
Hipel KW, Fang L, Cullmann J, Bristow M (2015) Conflict resolution in water resources and environmental management. Springer, Heidelberg, 291 pages
Karamouz M, Zahraie B, Kerachian R, Eslami A (2008) Crop pattern and conjunctive use management: A case study. Irrig Drain 59(2):161–173
Khare D, Jat MK, Sunder JD (2007) Assessment of water resources allocation options: Conjunctive use planning in a link canal command. Resour Conserv Recycl 51(2):487–506
Labadie J (2006) MODSIM: decision support system for integrated river basin management. Diss. International environmental modeling and software society
Li YP, Huang GH, Nie SL, Chen X (2011) A robust modeling approach for regional water management under multiple uncertainties. Agric Water Manag 98(10):1577–1588
Lu H, Huang G, He L (2011) An inexact rough-interval fuzzy linear programming method for generating conjunctive water-allocation strategies to agricultural irrigation systems. Appl Math Model 35(9):4330–4340
Md. Azamathulla H, Wu FC, Ghani AA, Narulkar SM, Zakaria NA, Chang CK (2008) Comparison between genetic algorithm and linear programming approach for real time operation. J Hydroenviron Res 2(3):172–181
Montazar A, Riazi H, Behbahani SM (2010) Conjunctive water use planning in an irrigation command area. Water Resour Manag 24(3):577–596
National Water Master Plan (2013) Karkheh Basin reports. Ministry of Energy, Tehran In Persian
Samuel G, Rajan CCA (2014) A modified shuffled frog leaping algorithm for long-term generation maintenance scheduling. In: Pant M et al (eds) Proceedings of the third international conference on soft computing for problem solving. Springer, India, pp 11–24
Shourian M, Mousavi SJ, Tahershamsi A (2008) Basin-wide water resources planning by integrating PSO algorithm and MODSIM. Water Resour Manag 22(10):1347–1366
Singh A (2014) Optimizing the use of land and water resources for maximizing farm income by mitigating the hydrological imbalances. J Hydrol Eng 19(7):1447–1451
Singh A, Panda SN (2013) Optimization and simulation modelling for managing the problems of water resources. Water Resour Manag 27(9):3421–3431
Yang CC, Chang LC, Chen CS, Yeh MS (2009) Multiobjective planning for conjunctive use of surface and subsurface water using genetic algorithm and dynamics programming. Water Resour Manag 23(3):417–437
Acknowledgements
The second author would like to thank and acknowledge Professor S. Jamshid Mousavi from Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran, for supervising his PhD research where a primary version of the present study was proposed and discussed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazlali, A., Shourian, M. A Demand Management Based Crop and Irrigation Planning Using the Simulation-Optimization Approach. Water Resour Manage 32, 67–81 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1791-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1791-6