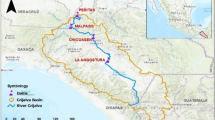
Abstract
Optimal operating policies for hydropower generation in a system of dams were obtained by means of a modified algorithm of stochastic dynamic programming that incorporates the guiding curve concept and other operating requirements defined by the Mexican agency in charge of electricity generation. These operating policies were used to simulate the long term system behavior and to analyze the influence of the guiding curves in the energy generation, the volume spilled and the possible deficit. The results show that by trying different curves it is possible to obtain a range of results that will enable decision makers to choose those that best fit their needs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaya AB, Souissi A, Tarhouni J, Ncib K (2003) Optimization of Nebhana reservoir water allocation by stochastic dynamic programming. Water Resour Manag 17:259–272
Alfieri L, Perona P, Burlando P (2006) Optimal water allocation for an alpine hydropower system under changing scenarios. Water Resour Manag 20:761–778
Ampitiya HK, Bogardi JJ, Nandalal KDW (1996) Derivation of optimal operation policies for the reservoirs of the complex Mahaweli water resources scheme in Sri Lanka via a stochastic dynamic programming based approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Aspects of Conflicts in Reservoirs Development and Management. City University. London, U. K. pp 539–548
Aparicio J, Martínez-Austria P, Güitrón A, Ramírez A (2009) Floods in Tabasco, Mexico: a diagnosis and proposal for courses of action. J Flood Risk Manag 2:132–138
Archibald TWK, McKinnon JM, Thomas LC (1997) An aggregate stochastic dynamic programming model of multireservoir systems. Water Resour Res 33(2):333–340
Arganis JML (2004) Operación óptima de un sistema de presas en cascada para generación hidroeléctrica, tomando en cuenta condiciones reales de operación y el uso de muestras sintéticas para el pronóstico. Ph.D Dissertation. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Postgrado de la Facultad de Ingeniería. México
Arganis JML, Domínguez MR, González VF, Mendoza RR, Carrizosa EE, Alegría DA, Peña DF (2009) Estudio Integral de la Cuenca Alta del Río Grijalva. 3. Manejo óptimo de las presas. Para CFE. Informe final. Noviembre
Babel M, Dinh CN, Mullick MMA, Nanduri UV (2012) Operation of a hydropower system considering environmental flow requirements: a case study in La Nga river basin, Vietnam. J Hydro-Environ Res 6:63–73
Bellman RE (1957) Dynamic programming. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Bogardi JJ, Budhakooncharoen S, Shrestha DL,Nandalal KDW (1988) Effect of state space and inflow discretization on stochastic dynamic programming based reservoir operation rules and system performance. In Proceedings. 6th Congress. Asian and Pacific Regional Division. IAHR. Vol. 1. Kyoto, Japan. pp 429–436
Brass C (2006) Optimising operations of reservoir systems with stochastic dynamic programming (SDP) under consideration of changing objectives and constraints. Ph. D. Dissertation (in German). Ruhr Universitaet Bochum. Germany
Cai X, McKinney DC, Lasdon LS (2001) Solving nonlinear water management models using a combined genetic algorithm and linear programming approach. Adv Water Res 24:667–676
Camac J (1994) Programación dinámica dual determinística en el despacho hidrotérmico. Tesis de Maestria. Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile. Escuela de Ingeniería.137 p
Carrizosa EE, Arganis ML, Domínguez-M R, Osnaya-R J, Esquivel-G G, T. Hollands A, Palacios C, Ramírez S (2009) Estudio Integral de la Cuenca Alta del Río Grjialva. Actualización de Avenidas de Diseño. Para CFE. Informe Final. Noviembre
Chang FJ, Chen L, Chang LC (2005) Optimizing the reservoir operating rule curves by genetic algorithms. Hydrol Process 19:2277–2289
Chen L, McPhee J, Yeh WWG (2007) A diversified multiobjective for optimizing reservoir rule curves. Advances in Water Res 30:1082–1093
Cheng CT, Wang WC, Xu DM, Chau KW (2008) Optimizing hydropower reservoir operation using hybrid genetic algorithm and chaos. Water Resour Manag 22:895–909
Dantzig GB (1998) Linear Programming and Extensions. Princeton University Press, Mathematics, USA, pp 1–31
Dantzig GB (2002) Linear programming. Oper Res 50(1):42–47, INFORMS
Domínguez MR, Arganis JML (2009) Operating rules of Grijalva river dams in Mexico. Memories of the 33 IAHR Congress Water Engineering for a Sustainable Environment. Vancouver, British Columbia, August 10–14
Domínguez MR, Mendoza RR (1993) Operación Integral del Sistema Hidroeléctrico del Río Grijalva. Para CFE. Instituto de Ingeniería. UNAM. México
Domínguez MR, Mendoza RR (2000) Funcionamiento de las presas Angostura, Chicoasén, Malpaso y Peñitas sobre el río Grijalva. Para Comisión Nacional del Agua. Informe final. Instituto de Ingeniería. UNAM. México
Domínguez MR, Mendoza RR, Arganis JML (2001) Revisión de las Políticas de Operación Quincenal de las Presas Angostura y Malpaso, en el Río Grijalva. Para CFE. Informe final. Instituto de Ingeniería. UNAM. México
Domínguez MR, Arganis JML, Carrizosa EE, Fuentes MGE, Echeverri VCA (2006) Determinación de avenidas de diseño y ajuste de los parámetros del modelo de optimización de las Políticas de operación del Sistema de Presas del Río Grijalva. Para CFE Informe Final. Instituto de Ingeniería. UNAM. México
Fayaed SS, El-Shafie A, Jaafar O (2013) Integrated Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SDP) model for optimal release policy. Water Resour Manage 27:3679–3696
Goor Q, Halleux C, Mohamed Y, Tilmant A (2010) Optimal operation of a multipurpose multireservoir system in the Easthern Nile River basin. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 7:4331–4369
Goulter IC, Tai FK (1985) Practical implications in the use of stochastic dynamic programming for reservoir operation. Water Resour Bull 121(1):65–74
Huang WC, Yuan LC, Lee CM (2002) Linking genetic algorithms with stochastic dynamic programming to the long-term operation of a multireservoir system. Water Resour Res 38(12):1304. doi:10.1029/2001WR001122
INEGI (2011) Hidrologia del estado de Tabasco. http://inegi.gob.mx Accessed 09 February 2011
Kumar DN, Ballarsingh F (2003) Folded dynamic programming for optimal operation of multireservoir system. Water Resour Manag 17:337–353
Laabs H, Harboe R (1988) Generation of operating rules with stochastic dynamic programming and multiple objectives. Water Resour Manage 2:221–227
Labadie JW (1997) Reservoir System Optimization Models. Colorado State University, Water Resources Update, University Council of Water Resources, 108
Lee JH, Labadie JW (2007) Stochastic optimization of multireservoirs systems via reinforcement learning. Water Resour Res 43, W11408. doi:10.1029/2006WR005627
Liu P, Guo S, Xu X, Chen J (2010) Derivation of aggregation-based join operation rule curves for cascade hydropower reservoirs. Water Resour Manage 25:3177–3200
Mousavi SJ, Ponnambalam K, Karray F (2005) Reservoir operation using a dynamic programming fuzzy rule–based approach. Water Resour Manage 19:655–672
Nandalal KDW, Bogardi JJ (2007) Dynamic programming based operation of reservoirs: applicability and limits. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ostadrahimi L, Mariño MA, Afshar A (2012) Multi-reservoir operation rules: multi-swarm. pso-based optimization approach. Water Resour Manage 26:407–427
Tospornsampan J, Kita I, Ishii M, Kitamura Y (2005) Optimization of a multiple reservoir system operation using a combination of genetic algorithm and discrete differential dynamic programming: a case study in Mae Klong system, Thailand. Paddy Water Environ 3:29–38
Umamahesh NV, Chandramouli S (2004) Fuzzy dynamic programming model for optimal operation of a multipurpose reservoir. In: Herath S, Pathirana A, Weerakoon SB (eds) Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Water Resources Management in the Changing Environment of the Monsoon Region. Vol. II. November. Sri Lanka. pp 552–557
World News Network. (2010). Available in: http://wn.com/Tropical_Depression_Matthew_Slams_Mexico Accessed 15 January 2013
Yen LH, Hsu YY, Chang BS, Chen KK (1996) A linear programming method for the scheduling of pumped-storage units with oscillatory stability constraints. IEEE Trans Power Syst 11(4):1705–1710
Yoo JH (2009) Maximization of hydropower generation through the application of a linear programming model. J Hydrol 376:182–187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arganis-Juárez, M.L., Mendoza-Ramírez, R., Domínguez-Mora, R. et al. Influence of Guiding Curves in the Optimal Management of a Hydropower System. Water Resour Manage 27, 4989–5001 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0460-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0460-7