Abstract
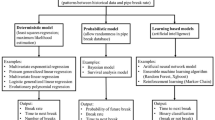
Sustainable management of urban water distribution networks should include not only new methods for monitoring, repairing or replacing aging infrastructure, but also (and more importantly) expanded methods for modelling deteriorating infrastructure, for pro-actively assessing the risk of failure and for devising replace or repair strategies. The study presented herein describes a framework for proactive risk-based integrity monitoring of urban water distribution networks and the results obtained from a case-study based on a 5-year data sample. A combination of artificial neural network and statistical modelling techniques stemming from parametric and nonparametric survival analysis (Kaplan–Meier survival curves with Epanechnikov’s kernel) are utilized in the investigation of identified risk factors and for estimation of the forecasted time to failure metric. The data is stratified for different pipe groups for a more targeted analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreou SA, Marks DH, Clark RM (1987) New methodology for modelling break failure patterns in deteriorating water distribution systems: applications. Adv Water Resour AWREDI 10:2–10
Aslani P (2003) Hazard rate modeling and risk analysis of water mains. MSc. thesis, Polytechnic University
Charalambous B (2005) Experiences in DMA redesign at the water board of Lemesos, Cyprus. International water association’s specialized conference on Leakage, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, pp 403–413
Christodoulou S, Deligianni A (2009) A neurofuzzy decision framework for the management of water distribution networks. J Water Resour Manage 24(1):139–156
Christodoulou S, Aslani P, Vanrenterghem A (2003) A risk analysis framework for evaluating structural degradation of water mains in urban settings, using neurofuzzy systems and statistical modeling techniques. World water and environmental resources congress 2003 and related symposia, Pennsylvania, USA
Christodoulou S, Charalambous B, Adamou A (2007) Managing the ‘repair or replace’ dilemma on water leakages. International water association’s (IWA) third specialty conference on water loss reduction (Water Loss 2007), Bucharest, Romania
Clark RM, Stafford CL, Goodrich JA (1982) Water distribution systems: a spatial and cost evaluation. J Water Resour Plan Manage Div 108:243–256
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc B 34(2):187–220
Epanechnikov VA (1969) Nonparametric estimation of a multidimensional probability density. Theory Appl Probab Appl 14:153–158
Goulter IC, Kazemi A (1988) Spatial and temporal groupings of water main pipe breakage in Winnipeg. Can J Civ Eng 15:91–97
Hintze J (2006) NCSS, PASS and GESS. NCSS, Kaysville
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S, May S (2008) Applied survival analysis: regression modeling of time to event data. Wiley, New York
Kanakoudis VK, Tolikas DK (2004) Assessing the performance level of a water system. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. Focus 4(4):307–318
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Klein JP, Moeschberger ML (1997) Survival analysis techniques for censored and truncated data. Springer, New York
Kleiner Y, Rajani B (1999) Using limited data to assess future needs. J Am Water Works Assoc 91:47–61
Lee ET, Wang JW (2003) Statistical methods for survival data analysis. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Park S (2004) Identifying the hazard characteristics of pipes in water distribution systems by using the proportional hazards model: theory. KSCE J Civ Eng 8(6):663–668
Prasad TD, Hong S-H, Park N (2003) Reliability based design of water distribution networks using multi-objective genetic algorithms. KSCE J Civ Eng 7(3):351–361
Shamir U, Howard C (1979) An analytical approach to scheduling pipe replacement. J Am Water Works Assoc 71:248–258
Tsitsifli S, Kanakoudis V (2007) Predicting the behavior of a pipe network using the “critical Z-score” as its performance indicator. International conference on environmental management, engineering, planning and economics (CEMEPE), Skiathos, Greece
Tuhovcak L, Rucka J, Juhanak T (2006) Risk analysis of water distribution systems. In: Pollert J, Dedus B (eds) Security of water supply systems: from source to tap. NATO science for peace and security series C: environmental security, vol 8. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 169–182
Vanrenterghem-Raven A, Eisenbeis P, Juran I, Christodoulou S (2004) Statistical modeling of the structural degradation of an urban water distribution system: case study of New York City. World Water and Environmental Resources Congress 2003 and Related Symposia, Pennsylvania
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christodoulou, S., Agathokleous, A., Charalambous, B. et al. Proactive Risk-Based Integrity Assessment of Water Distribution Networks. Water Resour Manage 24, 3715–3730 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9629-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9629-5