Abstract
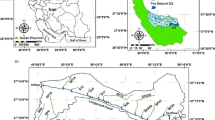
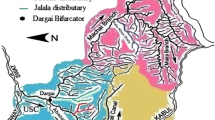
Operation of a secondary canal was recently transferred to the farmers’ organization (FO) under irrigation management transfer (IMT) programme. After modernization of Upper Swat Canal (USC) irrigation system, the water allowance was increased to operate the irrigation system more in demand responsive mode. The study of the existing operation of the canal revealed that most of the time the irrigation supplies exceed the demand and the farmers either over irrigate their fields or waste precious irrigation water. Operation and management aspect of the irrigation system play a pivotal role in overall water management practices. SIC hydrodynamic model was employed to evaluate the operational performance of the distributary. Different operational scenarios were investigated and quantified based on fixed frequency operation. Based on these results it is suggested to operate the distributary at 80–90% of the design discharge during May to July, and 75–90% of the design discharge from August to April to reduce water losses due to high water allowance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankum P (2004) Flow control in irrigation systems. International Institute for Infrastructural, Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering (IHE), Delft
ASCE (1993) Criteria for evaluation of watershed models. J Irrig Drain Eng 119(3):429–442
Baume JP, Malaterre PO, Benoit GB (2005) SIC: a 1D hydrodynamic model for river and irrigation canal modeling and regulation. CEMAGREF, agricultural and environmental engineering research, Montpellier, France, pp 1–81
Bievre BD, Alvarado A, Timbe L, Celleri R, Feyen J (2003) Night irrigation reduction for water saving in medium-sized system. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 129(2):108–116
Bottrall A (1981) Issue in main system management. Workshop on investment decision to further develop and make use of South–East Asia’s irrigation resources. Kasetsart University, Bangkok
Chamber R (1988) Managing canal irrigation: practical analysis from South Asia. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Chaudhry HM (2007) Open channel flow, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Chow VT (1959) Open-channel hydraulics. McGraw-Hill, New York
Cunge JA, Holly FM, Verwey A (1980) Practical aspects of computational river hydraulics. Pitman, London
de Vries TT, Arif A (2006) Irrigation scheduling with travel times. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE 132(2):220–207
Ghumman AR, Khan Z, Turral H (2009) Study of feasibility of night-closure of irrigation canals for water saving. Agric Water Manag 96(3):457–464
Godaliyadda GGA, Ranault D, Hemakumara HM, Makin IW (1999) Strategies to improve manual operation of irrigation system in Sri Lanka. Irrig Drain Syst 13:33–54
Habib Z, Pongput K, Skogerboe GV (1996) Unsteady flow simulation of the designed Pehure High Level Canal and proposed remodeling of Machi and Maira Branch canals, North West Frontier Province, Pakistan. IMMI, Pakistan R-20:125–147
Habib Z, Shah SK, Kaleemullah M, Vabre A, Ahmad MD, Sophyani A (1999) Hydraulic simulation to evaluate and predict design and operation of the Chashma Right Bank Canal. IMMI, Pakistan R-79:119–121
Kumar P, Mishra A, Raghuwanshi NB, Singh R (2002) Application of unsteady flow hydraulic model to a large and complex irrigation system. Agric Water Manag 54:49–66
Latif M, Tariq JA (2008) Performance assessment of irrigation management transfer from government managed to farmers managed irrigation system: a case study. Irrig Drain 58:275–286
Loof R, Das B, Paudyal GN (1994) Improved operation of large irrigation canal systems in Southeast Asia. Int J Water Resour Dev 10(4):393–415
Lozano D, Arranja C, Rijo M, Mateos L (2010) Simulation of automatic control of an irrigation canal. Agric Water Manag 97(1):91–100
Mainuddin M, Loof R, Abernathy C (2000) Operational plans and performance in the Phitsanulok irrigation system in Thailand. Int J Water Resour Dev 16(3):321–343
Malaterre PO, Baume LP (1997) SIC 3.0 a simulation model for canal automation design. In: Proceeding of the international workshop on regulation of irrigation canals. State of the art research and application. University of Semlalia, Marrakech, Morocco, pp 3–12
Mishra A, Anand A, Singh R, Raghuwanshi NS (2001) Hydraulic modeling of Kangsabati main canal for performance assessment. J Irrig Drain Eng ASCE, 127(1):27–34
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50(3):885–900
Plusquellec H (2002) How design, management and policy affect the performance of irrigation projects: emerging modernization procedures and design standards. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok, p 174
Renault D, Makin IW (1998) Modernization of irrigation systems operation: a desegregated approach of the demand. In: Proceedings of the fifth international meeting of ITIS network
Schuurmans W, Maherani M (1991) Operational performance of canal control systems. Water Resour Manage 2(5):149–159
Shahrokhnia MA, Javan JV (2005) Performance assessment of Doroodzan irrigation network by steady state hydraulic modeling. Irrig Drain Syst 19:189–206
Svendsen M, Merry D, Fitgerald W (1983) Meeting the challenges of better irrigation management. Horizon (USA) 2(3):17–25
Turral H, Malano HM, Chien NV (2002) Development and specification of a service agreement and rules for La Khe irrigation system, Ha Dong, Vietnam. Irrig Drain 51:29–140
Wade R, Chambers R (1980) Managing the main system: canal irrigation’s blind spot. Econ Polit Wkly 15(39):A107–A112
Waijjen EG, Hart WW, Kuper W, Brower R (1997) Using hydrodynamic flow model to plan maintenance activities and improving irrigation water: application to Fordwah distributary in Punjab, Pakistan. Irrig Drain Syst 11(4):367–386
Zimbelman DD (1987) Planning, operation, rehabilitation and automation of irrigation water delivery systems. Proceedings of the Symposium Sponsored by the Irrigation and Drainage Division of ASCE, Portland, Oregon, p 381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tariq, J.A., Latif, M. Improving Operational Performance of Farmers Managed Distributary Canal using SIC Hydraulic Model. Water Resour Manage 24, 3085–3099 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9596-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9596-x