Abstract
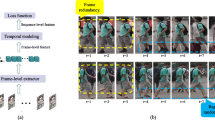
Directly benefiting from the rapid advancement of deep learning methods, person re-identification (Re-ID) applications have been widespread with remarkable successes in recent years. Nevertheless, cross-scene Re-ID is still hindered by large view variation, since it is challenging to effectively exploit and leverage the temporal clues due to heavy computational burden and the difficulty in flexibly incorporating discriminative features. To alleviate, we articulate a long-short temporal–spatial clues excited network (LSTS-NET) for robust person Re-ID across different scenes. In essence, our LSTS-NET comprises a motion appearance model and a motion-refinement aggregating scheme. Of which, the former abstracts temporal clues based on multi-range low-rank analysis both in consecutive frames and in cross-camera videos, which can augment the person-related features with details while suppressing the clutter background across different scenes. In addition, to aggregate the temporal clues with spatial features, the latter is proposed to automatically activate the person-specific features by incorporating personalized motion-refinement layers and several motion-excitation CNN blocks into deep networks, which expedites the extraction and learning of discriminative features from different temporal clues. As a result, our LSTS-NET can robustly distinguish persons across different scenes. To verify the improvement of our LSTS-NET, we conduct extensive experiments and make comprehensive evaluations on 8 widely-recognized public benchmarks. All the experiments confirm that, our LSTS-NET can significantly boost the Re-ID performance of existing deep learning methods, and outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of robustness and accuracy.














Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
06 July 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01497-1
References
Bai, S., Bai, X., & Tian, Q. (2017). Scalable person re-identification on supervised smoothed manifold. In CVPR (pp. 2530–2539).
Bai, S., Tang, P., Torr, P. H., & Latecki, L. J. (2019). Re-ranking via metric fusion for object retrieval and person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 740–749).
Burr, D. C., & Santoro, L. (2001). Temporal integration of optic flow, measured by contrast and coherence thresholds. Vision Research, 41(15), 1891–1899.
Candès, E. J., Li, X., Ma, Y., & Wright, J. (2011). Robust principal component analysis? JACM, 58(3), 11.
Chen, B., Deng, W., & Hu, J. (2019). Mixed high-order attention network for person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 371–381).
Chen, D., Li, H., Xiao, T., Yi, S., & Wang, X. (2018). Video person re-identification with competitive snippet-similarity aggregation and co-attentive snippet embedding. In CVPR (pp. 1169–1178).
Chen, D., Zhang, S., Ouyang, W., Yang, J., & Tai, Y. (2018). Person search via a mask-guided two-stream CNN model. In ECCV (pp. 734–750).
Dai, J., Zhang, P., Wang, D., Lu, H., & Wang, H. (2019). Video person re-identification by temporal residual learning. TIP, 28(3), 1366–1377.
Fu, Y., Wang, X., Wei, Y., & Huang, T. S. (2019). Sta: Spatial–temporal attention for large-scale video-based person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (Vol. 33(01), pp. 8287–8294).
Fu, Y., Wei, Y., Wang, G., Zhou, Y., Shi, H., & Huang, T. S. (2019). Self-similarity grouping: A simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 6112–6121).
Gu, X., Ma, B., Chang, H., Shan, S., & Chen, X. (2019). Temporal knowledge propagation for image-to-video person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 9647–9656).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In CVPR (pp. 770–778).
Hirzer, M., Beleznai, C., Roth, P. M., & Bischof, H. (2011). Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. In SCIA (pp. 91–102).
Hou, R., Ma, B., Chang, H., Gu, X., Shan, S., & Chen, X. (2019). Interaction-and-aggregation network for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 9317–9326).
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K. Q., & van der Maaten, L. (2017). Densely connected convolutional networks. In CVPR (pp. 4700–4708).
Huang, H., Li, D., Zhang, Z., Chen, X., & Huang, K. (2018). Adversarially occluded samples for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 5098–5107).
Kalayeh, M. M., Basaran, E., Gokmen, M., Kamasak, M. E., & Shah, M. (2018). Human semantic parsing for person re-identification. In CVPR.
Karanam, S., Gou, M., Wu, Z., Rates-Borras, A., Camps, O., & Radke, R. J. (2018). A systematic evaluation and benchmark for person re-identification: Features, metrics, and datasets. In TPAMI (p. 1).
Khan, F. M., & Bremond, F. (2016). Unsupervised data association for metric learning in the context of multi-shot person re-identification. In AVSS (pp. 256–262).
Kodirov, E., Xiang, T., Fu, Z., & Gong, S. (2016). Person re-identification by unsupervised L1 graph learning. In ECCV (pp. 178–195).
Li, D., Chen, X., Zhang, Z., & Huang, K. (2017). Learning deep context-aware features over body and latent parts for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 384–393).
Li, J., Wang, J., Tian, Q., Gao, W., & Zhang, S. (2019). Global-local temporal representations for video person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 3958–3967).
Li, J., Zhang, S., & Huang, T. (2020). Multi-scale temporal cues learning for video person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 29, 4461–4473.
Li, M., Zhu, X., & Gong, S. (2018). Unsupervised person re-identification by deep learning tracklet association. In ECCV (pp. 737–753).
Li, M., Zhu, X., & Gong, S. (2019). Unsupervised tracklet person re-identification. In TPAMI.
Li, S., Bak, S., Carr, P., & Wang, X. (2018). Diversity regularized spatiotemporal attention for video-based person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 369–378).
Li, S., Shao, M., & Fu, Y. (2017). Person re-identification by cross-view multi-level dictionary learning. In TPAMI (p. 1).
Li, W., Zhu, X., & Gong, S. (2019a). Scalable person re-identification by harmonious attention. In IJCV (pp. 1–19).
Li, W., Zhu, X., & Gong, S. (2019b). Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. IEEE Access, 7, 22457–22470.
Liao, S., Hu, Y., Zhu, X., & Li, S. Z. (2015). Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In CVPR (pp. 2197–2206).
Lin, J., Ren, L., Lu, J., Feng, J., & Zhou, J. (2017). Consistent-aware deep learning for person re-identification in a camera network. In CVPR (pp. 5771–5780).
Liu, H., Feng, J., Jie, Z., Karlekar, J., Zhao, B., Qi, M., et al. (2017). Neural person search machines. In ICCV (pp. 493–501).
Liu, H., Jie, Z., Jayashree, K., Qi, M., Jiang, J., Yan, S., & Feng, J. (2017). Video-based person re-identification with accumulative motion context. TCSVT.
Liu, J., Ni, B., Yan, Y., Zhou, P., Cheng, S., & Hu, J. (2018). Pose transferrable person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 4099–4108).
Liu, K., Ma, B., Zhang, W., & Huang, R. (2015). A spatio-temporal appearance representation for viceo-based pedestrian re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 3810–3818).
Liu, Y., Yan, J., & Ouyang, W. (2017). Quality aware network for set to set recognition. In CVPR (pp. 4694–4703).
Liu, Z., Wang, D., & Lu, H. (2017). Stepwise metric promotion for unsupervised video person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 2448–2457).
Lv, J., Chen, W., Li, Q., & Yang, C. (2018). Unsupervised cross-dataset person re-identification by transfer learning of spatial–temporal patterns. In CVPR (pp. 7948–7956).
Ma, A. J., Li, J., Yuen, P. C., & Li, P. (2015). Cross-domain person reidentification using domain adaptation ranking SVMS. TIP, 24(5), 1599–1613.
Ma, L., Sun, Q., Georgoulis, S., Van Gool, L., Schiele, B., & Fritz, M. (2018). Disentangled person image generation. In CVPR (pp. 99–108).
Ma, X., Zhu, X., Gong, S., Xie, X., Hu, J., Lam, K.-M., et al. (2017). Person re-identification by unsupervised video matching. PR, 65, 197–210.
McLaughlin, N., del Rincon, J. M., & Miller, P. (2016). Recurrent convolutional network for video-based person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 1325–1334).
Miao, J., Wu, Y., Liu, P., Ding, Y., & Yang, Y. (2019). Pose-guided feature alignment for occluded person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 542–551).
Peng, P., Tian, Y., Xiang, T., Wang, Y., Pontil, M., & Huang, T. (2018). Joint semantic and latent attribute modelling for cross-class transfer learning. TPAMI, 40(7), 1625–1638.
Peng, P., Xiang, T., Wang, Y., Pontil, M., Gong, S., Huang, T., & Tian, Y. (2016). Unsupervised cross-dataset transfer learning for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 1306–1315).
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., & Sun, J. (2015). Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In NIPS (pp. 91–99).
Ristani, E., Solera, F., Zou, R., Cucchiara, R., & Tomasi, C. (2016). Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In ECCVW.
Sarfraz, M. S., Schumann, A., Eberle, A., & Stiefelhagen, R. (2018). A pose-sensitive embedding for person re-identification with expanded cross neighborhood re-ranking. In CVPR (pp. 420–429).
Si, J., Zhang, H., Li, C.-G., Kuen, J., Kong, X., Kot, A. C., & Wang, G. (2018). Dual attention matching network for context-aware feature sequence based person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 5363–5372).
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In NIPS (pp. 568–576).
Song, C., Huang, Y., Ouyang, W., & Wang, L. (2018). Mask-guided contrastive attention model for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 1179–1188).
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. JMLR, 15(1), 1929–1958.
Su, C., Zhang, S., Xing, J., Gao, W., & Tian, Q. (2016). Deep attributes driven multi-camera person re-identification. In ECCV (pp. 475–491).
Subramaniam, A., Nambiar, A., & Mittal, A. (2019). Co-segmentation inspired attention networks for video-based person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 562–572).
Sun, Y., Xu, Q., Li, Y., Zhang, C., Li, Y., Wang, S., et al. (2019). Perceive where to focus: Learning visibility-aware part-level features for partial person re-identification. CVPR (pp. 393–402).
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Deng, W., & Wang, S. (2017). Svdnet for pedestrian retrieval. In ICCV (pp. 3800–3808).
Tay, C.-P., Roy, S., & Yap, K.-H. (2019). Aanet: Attribute attention network for person re-identifications. In CVPR (pp. 7134–7143).
Tian, M., Yi, S., Li, H., Li, S., Zhang, X., Shi, J., Yan, J., & Wang, X. (2018). Eliminating background-bias for robust person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 5794–5803).
van der Maaten, L. (2014). Accelerating t-sne using tree-based algorithms. JMLR, 15(93), 3221–3245.
Wang, H., Zhu, X., Gong, S., & Xiang, T. (2018). Person re-identification in identity regression space. IJCV, 126(12), 1288–1310.
Wang, J., Zhu, X., Gong, S., & Li, W. (2018). Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 2275–2284).
Wang, T., Gong, S., Zhu, X., & Wang, S. (2014). Person re-identification by video ranking. In ECCV (pp. 688–703).
Wang, T., Gong, S., Zhu, X., & Wang, S. (2016). Person re-identification by discriminative selection in video ranking. TPAMI, 38(12), 2501–2514.
Wei, L., Zhang, S., Gao, W., & Tian, Q. (2018). Person transfer Gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 79–88).
Wu, L., Shen, C., & Hengel, A. V. D. (2016). Deep recurrent convolutional networks for video-based person re-identification: An end-to-end approach. CoRR. arXiv:1606.01609.
Wu, Y., Lin, Y., Dong, X., Yan, Y., Ouyang, W., & Yang, Y. (2018). Exploit the unknown gradually: One-shot video-based person re-identification by stepwise learning. In CVPR (pp. 5177–5186).
Xia, B. N., Gong, Y., Zhang, Y., & Poellabauer, C. (2019). Second-order non-local attention networks for person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 3760–3769).
Xiao, T., Li, S., Wang, B., Lin, L., & Wang, X. (2017). Joint detection and identification feature learning for person search. In CVPR (pp. 3376–3385).
Xiong, F., Gou, M., Camps, O., & Sznaier, M. (2014). Person re-identification using kernel-based metric learning methods. In ECCV (pp. 1–16).
Xu, J., Zhao, R., Zhu, F., Wang, H., & Ouyang, W. (2018). Attention-aware compositional network for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 2119–2128).
Xu, S., Cheng, Y., Gu, K., Yang, Y., Chang, S., & Zhou, P. (2017). Jointly attentive spatial–temporal pooling networks for video-based person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 4733–4742).
Yan, Y., Ni, B., Song, Z., Ma, C., Yan, Y., & Yang, X. (2016). Person re-identification via recurrent feature aggregation. In ECCV (pp. 701–716). Berlin: Springer.
Yan, Y., Zhang, Q., Ni, B., Zhang, W., Xu, M., & Yang, X. (2019). Learning context graph for person search. In CVPR (pp. 2158–2167).
Yang, W., Huang, H., Zhang, Z., Chen, X., Huang, K., & Zhang, S. (2019). Towards rich feature discovery with class activation maps augmentation for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 1389–1398).
Ye, M., Lan, X., & Yuen, P. C. (2018). Robust anchor embedding for unsupervised video person re-identification in the wild. In ECCV (pp. 170–186).
Ye, M., Ma, A. J., Zheng, L., Li, J., & Yuen, P. C. (2017). Dynamic label graph matching for unsupervised video re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 5152–5160).
Yu, H.-X., Wu, A., & Zheng, W.-S. (2017). Cross-view asymmetric metric learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 994–1002).
Yu, R., Zhou, Z., Bai, S., & Bai, X. (2017). Divide and fuse: A re-ranking approach for person re-identification. In BMVC.
Zeng, Z., Chan, T.-H., Jia, K., & Xu, D. (2012). Finding correspondence from multiple images via sparse and low-rank decomposition. In ECCV (pp. 325–339). Berlin: Springer.
Zhang, W., Hu, S., & Liu, K. (2017). Learning compact appearance representation for video-based person re-identification. arXiv:1702.06294.
Zhang, R., Li, J., Sun, H., Ge, Y., Luo, P., Wang, X., et al. (2019). Scan: Self-and-collaborative attention network for video person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(10), 4870–4882.
Zhang, W., Yu, X., & He, X. (2018). Learning bidirectional temporal cues for video-based person re-identification. CSVT, 28(10), 2768–2776.
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Lin, M., & Sun, J. (2018). Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In CVPR (pp. 6848–6856).
Zhao, H., Tian, M., Sun, S., Shao, J., Yan, J., Yi, S., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2017). Spindle net: Person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion. In CVPR (pp. 1077–1085).
Zhao, L., Li, X., Zhuang, Y., & Wang, J. (2017a). Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 3219–3228).
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., & Wang, X. (2013). Unsupervised salience learning for person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 3586–3593).
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., & Wang, X. (2017b). Person re-identification by saliency learning. TPAMI, 39(2), 356–370.
Zhao, Y., Shen, X., Jin, Z., Lu, H., & Hua, X.-s. (2019). Attribute-driven feature disentangling and temporal aggregation for video person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 4913–4922).
Zheng, L., Bie, Z., Sun, Y., Wang, J., Su, C., Wang, S., & Tian, Q. (2016). Mars: A video benchmark for large-scale person re-identification. In ECCV (pp. 868–884).
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., & Tian, Q. (2015). Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In ICCV (pp. 1116–1124).
Zheng, L., Zhang, H., Sun, S., Chandraker, M., Yang, Y., & Tian, Q. (2018). Person re-identification in the wild. In ECCV (pp. 176–193).
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., & Yang, Y. (2017). Unlabeled samples generated by Gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In ICCV (pp. 3774–3782).
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Cao, D., & Li, S. (2017a). Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In CVPR (pp. 3652–3661).
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Kang, G., Li, S., & Yang, Y. (2017b). Random erasing data augmentation. In CoRR. arXiv:1708.04896.
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Li, S., & Yang, Y. (2018). Generalizing a person retrieval model hetero-and homogeneously. In ECCV (pp. 172–188).
Zhou, S., Wang, F., Huang, Z., & Wang, J. (2019). Discriminative feature learning with consistent attention regularization for person re-identification. In ICCV (pp. 3760–3769).
Zhou, T., & Tao, D. (2011). Godec: Randomized low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition in noisy case. In ICML (pp. 33–40).
Zhou, Z., Huang, Y., Wang, W., Wang, L., & Tan, T. (2017). See the forest for the trees: Joint spatial and temporal recurrent neural networks for video-based person re-identification. In CVPR (pp. 6776–6785).
Acknowledgements
National Key R & D Program of China (No. 2018YFB1700603), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 61672077 and 61532002), Beijing Natural Science Foundation Haidian Primitive Innovation Joint Fund (L182016), National Science Foundation of USA under Grant IIS-1715985 and IIS-1812606.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Patrick Perez.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mp4 4844 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Song, W., Fang, Z. et al. Long-Short Temporal–Spatial Clues Excited Network for Robust Person Re-identification. Int J Comput Vis 128, 2936–2961 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-020-01349-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-020-01349-4