Abstract
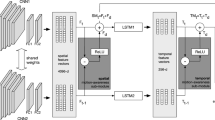
In this paper, we propose the use of a semantic image, an improved representation for video analysis, principally in combination with Inception networks. The semantic image is obtained by applying localized sparse segmentation using global clustering prior to the approximate rank pooling, which summarizes the motion characteristics in single or multiple images. It incorporates the background information by overlaying a static background from the window onto the subsequent segmented frames. The idea is to improve the action–motion dynamics by focusing on the region, which is important for action recognition and encoding the temporal variances using the frame ranking method. We also propose the sequential combination of Inception-ResNetv2 and long–short-term memory network (LSTM) to leverage the temporal variances for improved recognition performance. Extensive analysis has been carried out on UCF101 and HMDB51 datasets, which are widely used in action recognition studies. We show that (1) the semantic image generates better activations and converges faster than its original variant, (2) using segmentation prior to approximate rank pooling yields better recognition performance, (3) the use of LSTM leverages the temporal variance information from approximate rank pooling to model the action behavior better than the base network, (4) the proposed representations are adaptive as they can be used with existing methods such as temporal segment and I3D ImageNet + Kinetics network to improve the recognition performance, and (5) the four-stream network architecture pre-trained on ImageNet + Kinetics and fine-tuned using the proposed representation achieves the state-of-the-art performance, 99.1% and 83.7% recognition accuracy on UCF101 and HMDB51, respectively.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta, R., Shaji, A., Smith, K., Lucchi, A., Fua, P., & Süsstrunk, S. (2012). SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,34(11), 2274–2282. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120.
Ali, S., & Shah, M. (2010). Human action recognition in videos using kinematic features and multiple instance learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,32(2), 288–303. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2008.284.
Allen, G., & Gray, R. M. (2012). Vector quantization and signal compression (Vol. 159). Berlin: Springer.
Bilen, H., Fernando, B., Gavves, E., & Vedaldi, A. (2018). Action recognition with dynamic image networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,40(12), 2799–2813. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2769085.
Bilen, H., Fernando, B., Gavves, E., Vedaldi, A., & Gould, S. (2016). Dynamic image networks for action recognition. In 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 3034–3042). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.331.
Bobick, A. F., & Davis, J. W. (2001). The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,23(3), 257–267. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.910878.
Carreira, J., & Zisserman, A. (2017). Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 4724–4733). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2017.502.
Chen, L.-C., Zhu, Y., Papandreou, G., Schroff, F., & Adam, H. (2018a). Encoder–decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 833–851). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49.
Chen, Y., Kalantidis, Y., Li, J., Yan, S., & Feng, J. (2018b). Multi-fiber networks for video recognition. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 364–380). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01246-5_22.
Chen, Y., Kalantidis, Y., Li, J., Yan, S., & Feng, J. (2018c). A2-nets: Double attention networks. In 32nd Conference on neural information processing systems (NeurIPs) (pp. 352–361).
Cheron, G., Laptev, I., & Schmid, C. (2015). P-CNN: Pose-based CNN features for action recognition. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 3218–3226). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2015.368.
Chopra, S., Hadsell, R., & LeCun, Y. (2005). Learning a similarity metric discriminatively, with application to face verification. In IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’05) (Vol. 1, pp. 539–546). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2005.202.
de Souza, C. R., Gaidon, A., Vig, E., & López, A. M. (2016). Sympathy for the details: Dense trajectories and hybrid classification architectures for action recognition. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 697–716). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46478-7_43.
Diba, A., Fayyaz, M., Sharma, V., Arzani, M. M., Yousefzadeh, R., Gall, J., & Van Gool, L. (2018). Spatio-temporal channel correlation networks for action classification. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 299–315). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_18.
Diba, A., Sharma, V., & Van Gool, L. (2017). Deep temporal linear encoding networks. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 1541–1550). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2017.168.
Donahue, J., Hendricks, L. A., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Guadarrama, S., Saenko, K., et al. (2017). Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,39(4), 677–691. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2599174.
Doretto, G., Chiuso, A., Wu, Y. N., & Soatto, S. (2003). Dynamic textures. International Journal of Computer Vision,51(2), 91–109. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1021669406132.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn, J., & Zisserman, A. (2010). The Pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision,88(2), 303–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4.
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., & Wildes, R. (2016a). Spatiotemporal residual networks for video action recognition. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 3468–3476).
Feichtenhofer, C., Pinz, A., & Zisserman, A. (2016b). Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 1933–1941). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.213.
Fei-Fei, L., Johnson, J., & Yeung, S. (2017). Visualizing what ConvNets learn. Retrieved from October 6, 2018, http://cs231n.github.io/understanding-cnn/.
Fernando, B., Gavves, E., Jose Oramas, M., Ghodrati, A., & Tuytelaars, T. (2015). Modeling video evolution for action recognition. In 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 5378–5387). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7299176.
Fischler, M. A., & Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Communications of the ACM,24(6), 381–395. https://doi.org/10.1145/358669.358692.
Geman, S., Bienenstock, E., & Doursat, R. (1992). Neural networks and the bias/variance dilemma. Neural Computation,4(1), 1–58. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1992.4.1.1.
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., & Satoh, Y. (2018). Can spatiotemporal 3D CNNs retrace the history of 2D CNNs and ImageNet. In IEEE international conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 6546–6555).
He, K., & Sun, J. (2015). Convolutional neural networks at constrained time cost. In 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 5353–5360). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7299173.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 770–778). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.90.
Jain, M., Jegou, H., & Bouthemy, P. (2013). Better exploiting motion for better action recognition. In 2013 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2555–2562). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2013.330.
Jain, M., van Gemert, J. C., & Snoek, C. G. M. (2015). What do 15,000 object categories tell us about classifying and localizing actions? In 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 46–55). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298599.
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., & Yu, K. (2013). 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,35(1), 221–231. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59.
Jia, Y., Shelhamer, E., Donahue, J., Karayev, S., Long, J., Girshick, R., et al. (2014). Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the ACM international conference on multimedia—MM’14 (pp. 675–678). New York, NY: ACM Press. https://doi.org/10.1145/2647868.2654889.
Ke, Y., Sukthankar, R., & Hebert, M. (2005). Efficient visual event detection using volumetric features. In Tenth IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV’05) (pp. 166–173). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2005.85.
Kellokumpu, V., Zhao, G., & Pietikainen, M. (2008). Human activity recognition using a dynamic texture based method. In Proceedings of the British machine vision conference (pp. 88.1–88.10). British Machine Vision Association. https://doi.org/10.5244/c.22.88.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2012). ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS) (pp. 1–9).
Laptev, I. (2005). On space–time interest points. International Journal of Computer Vision,64(2–3), 107–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-005-1838-7.
Le, Q. V., Zou, W. Y., Yeung, S. Y., & Ng, A. Y. (2011). Learning hierarchical invariant spatio-temporal features for action recognition with independent subspace analysis. In IEEE International conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3361–3368). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2011.5995496.
Li, C., Chen, C., Carlson, D., & Carin, L. (2016). Preconditioned stochastic gradient langevin dynamics for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the thirtieth association for the advancement of artificial intelligence (AAAI) conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 1788–1794).
Likas, A., Vlassis, N., & Verbeek, J. (2003). The global k-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognition,36(2), 451–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(02)00060-2.
Ma, C.-Y., Chen, M.-H., Kira, Z., & AlRegib, G. (2018). TS-LSTM and temporal-inception: Exploiting spatiotemporal dynamics for activity recognition. Signal Processing: Image Communication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2018.09.003.
Ojala, T., Pietikainen, M., & Maenpaa, T. (2002). Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,24(7), 971–987. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017623.
Olah, C., Mordvintsev, A., & Schubert, L. (2017). Feature visualization. Distill. https://doi.org/10.23915/distill.00007.
Pascanu, R., Mikolov, T., & Bengio, Y. (2013). On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 30th international conference on machine learning (pp. 1310–1318).
Peng, X., Zou, C., Qiao, Y., & Peng, Q. (2014). Action recognition with stacked fisher vectors. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 581–595). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_38.
Perronnin, F., Sánchez, J., & Mensink, T. (2010). Improving the fisher kernel for large-scale image classification. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 143–156). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15561-1_11.
Pirsiavash, H., Ramanan, D., & Fowlkes, C. C. (2009). Bilinear classifiers for visual recognition. In Neural information processing systems (NIPS) (pp. 1482–1490).
Rodriguez, M. D., Ahmed, J., & Shah, M. (2008). Action MACH a spatio-temporal maximum average correlation height filter for action recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1–8). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2008.4587727.
Shechtman, E., & Irani, M. (2005). Space–time behavior based correlation. In IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’05) (Vol. 1, pp. 405–412). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2005.328.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 1–9).
Smola, A. J., & Schölkopf, B. (2004). A tutorial on support vector regression. Statistics and Computing,14(3), 199–222. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88.
Srivastava, N., Mansimov, E., & Slakhudinov, R. (2015). Unsupervised learning of video representations using LSTMs. In Proceedings of the 32nd international conference on machine learning (pp. 843–852).
Storath, M., & Weinmann, A. (2014). Fast partitioning of vector-valued images. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences,7(3), 1826–1852. https://doi.org/10.1137/130950367.
Sun, L., Jia, K., Yeung, D.-Y., & Shi, B. E. (2015). Human action recognition using factorized spatio-temporal convolutional networks. In 2015 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 4597–4605). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2015.522.
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., & Alemi, A. A. (2017). Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Thirty-first association for the advancement of artificial intelligence (AAAI) (pp. 4278–4284).
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., & Wojna, Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2818–2826). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.308.
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., & Paluri, M. (2015). Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In 2015 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV) (pp. 4489–4497). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2015.510.
Tran, D., Wang, H., Torresani, L., Ray, J., LeCun, Y., & Paluri, M. (2018). A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 6450–6459). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2018.00675.
Varol, G., Laptev, I., & Schmid, C. (2018). Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,40(6), 1510–1517. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2712608.
Vese, L. A., & Chan, T. F. (2002). A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and Shah model. International Journal of Computer Vision,50(3), 271–293. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020874308076.
Wang, H., Kläser, A., Schmid, C., & Liu, C.-L. (2013). Dense trajectories and motion boundary descriptors for action recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision,103(1), 60–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-012-0594-8.
Wang, H., & Schmid, C. (2013). Action recognition with improved trajectories. In 2013 IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 3551–3558). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2013.441.
Wang, L., Li, W., & Van Gool, L. (2018a). Appearance- and-relation networks for video classification. In IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1430–1439). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2018.00155.
Wang, L., Qiao, Y., & Tang, X. (2015). Action recognition with trajectory-pooled deep-convolutional descriptors. In 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 4305–4314). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7299059.
Wang, L., Qiao, Y., & Tang, X. (2016a). MoFAP: A multi-level representation for action recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision,119(3), 254–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0859-0.
Wang L., Xiong Y., Wang Z., Qiao Y., Lin D., Tang X., & Van Gool L. (2016c). Temporal segment networks: towards good practices for deep action recognition. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 20–36). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2.
Wang, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Y., Lin, D., Tang, X., et al. (2018b). Temporal segment networks for action recognition in videos. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2868668.
Wang, Y., Long, M., Wang, J., & Yu, P. S. (2017). Spatiotemporal pyramid network for video action recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 2097–2106). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2017.226.
Wang Y., Song J., Wang L., Gool L., & Hilliges O. (2016b). Two-stream SR-CNNs for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the British machine vision conference 2016 (pp. 108.1–108.12). British Machine Vision Association. https://doi.org/10.5244/c.30.108.
Willems, G., Tuytelaars, T., & Van Gool, L. (2008). An efficient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal interest point detector. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 650–663). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88688-4_48.
Xie, S., Girshick, R., Dollar, P., Tu, Z., & He, K. (2017). Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 5987–5995). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2017.634.
Xie, S., Sun, C., Huang, J., Tu, Z., & Murphy, K. (2018). Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning: Speed–accuracy trade-offs in video classification. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 318–335). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_19.
Yatziv, L., & Sapiro, G. (2006). Fast image and video colorization using chrominance blending. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,15(5), 1120–1129. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2005.864231.
Yue-Hei Ng, J., Hausknecht, M., Vijayanarasimhan, S., Vinyals, O., Monga, R., & Toderici, G. (2015). Beyond short snippets: Deep networks for video classification. In 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 4694–4702). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7299101.
Zha, S., Luisier, F., Andrews, W., Srivastava, N., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2015). Exploiting image-trained CNN architectures for unconstrained video classification. http://arxiv.org/abs/1503.04144.
Zhao, G., & Pietikainen, M. (2007). Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,29(6), 915–928. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1110.
Zhu, W., Hu, J., Sun, G., Cao, X., & Qiao, Y. (2016). A key volume mining deep framework for action recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR) (pp. 1991–1999). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.219.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Hankuk University of Foreign Studies Research Fund (Grant No. 2019), and also supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2018R1D1A1B07049113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Karteek Alahari.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khowaja, S.A., Lee, SL. Semantic Image Networks for Human Action Recognition. Int J Comput Vis 128, 393–419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01248-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01248-3