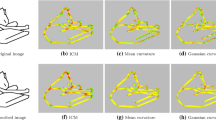
Abstract
We present the first method to handle curvature regularity in region-based image segmentation and inpainting that is independent of initialization.
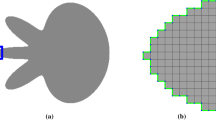
To this end we start from a new formulation of length-based optimization schemes, based on surface continuation constraints, and discuss the connections to existing schemes. The formulation is based on a cell complex and considers basic regions and boundary elements. The corresponding optimization problem is cast as an integer linear program.
We then show how the method can be extended to include curvature regularity, again cast as an integer linear program. Here, we are considering pairs of boundary elements to reflect curvature. Moreover, a constraint set is derived to ensure that the boundary variables indeed reflect the boundary of the regions described by the region variables.
We show that by solving the linear programming relaxation one gets reasonably close to the global optimum, and that curvature regularity is indeed much better suited in the presence of long and thin objects compared to standard length regularity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini, A. A., Weymouth, T. E., & Jain, R. C. (1990). Using dynamic programming for solving variational problems in vision. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 12(9), 855–867.
Bertalmío, M., Sapiro, G., Caselles, V., & Ballester, C. (2001). Image inpainting. In ACM SIGGRAPH, July 2001.
Blake, A., & Zissermann, A. (1987). Visual reconstruction. Cambridge: MIT press.
Bornemann, F., & März, T. (2007). Fast image inpainting based on coherence transport. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 28(3), 259–278.
Boykov, Y., & Jolly, M. P. (2001). Interactive graph cuts for optimal boundary and region segmentation of objects in n-d images. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Vancouver, Canada, July 2001.
Boykov, Y., & Kolmogorov, V. N. (2003). Computing geodesics and minimal surfaces via graph cuts. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Nice, France, October 2003.
Bruckstein, A. M., Netravali, A. N., & Richardson, T. J. (2001). Epi-convergence of discrete elastica. Applicable Analysis, 79, 137–171. Bob Caroll Special Issue.
Cao, F., Gousseau, Y., Masnou, S., & Pérez, P. (2012). Geometrically guided expemplar-based inpainting. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, submitted.
Chan, T. F., Kang, S. H., & Shen, J. (2002). Euler’s elastica and curvature based inpaintings. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2, 564–592.
Chan, T. F., & Vese, L. (2001). Active contours without edges. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 10(2), 266–277.
Dantzig, G. B., & Thapa, M. N. (1997). Linear programming 1: introduction. Springer series in operations research. Berlin: Springer.
El-Zehiry, N. Y., & Grady, L. (2010). Fast global optimization of curvature. In IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, California, June 2010.
Esedoglu, S., & March, R. (2003). Segmentation with depth but without detecting junctions. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 18, 7–15.
Goldlücke, B., & Cremers, D. (2011). Introducing total curvature for image processing. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Barcelona, Spain, November 2011.
Grady, L. (2010). Minimal surfaces extend shortest path segmentation methods to 3d. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 32(2), 321–334.
Greig, D. M., Porteous, B. T., & Seheult, A. H. (1989). Exact maximum a posteriori estimation for binary images. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B Methodological, 51(2), 271–279.
Kanizsa, G. (1971). Contours without gradients or cognitive contours. Giornale Italiano Di Psicologia, 1, 93–112.
Klodt, M., Schoenemann, T., Kolev, K., Schikora, M., & Cremers, D. (2008). An experimental comparison of discrete and continuous shape optimization methods. In European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Marseille, France, October 2008.
Masnou, S. (2002). Disocclusion: A variational approach using level lines. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 11, 68–76.
Masnou, S., & Morel, J. M. (1998). Level-lines based disocclusion. In International conference on image processing (ICIP), Chicago, Michigan, 1998.
Mumford, D., & Shah, J. (1989). Optimal approximations by piecewise smooth functions and associated variational problems. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 42, 577–685.
Nikolova, M., Esedoglu, S., & Chan, T. (2006). Algorithms for finding global minimizers of image segmentation and denoising models. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 66(5), 1632–1648.
Nitzberg, M., Mumford, D., & Shiota, T. (1993). Filtering, segmentation and depth. In LNCS, vol. 662. Berlin: Springer.
Parent, P., & Zucker, S. W. (1989). Trace inference, curvature consistency, and curve detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 11(8), 823–839.
Rudin, W. (1987). Real and complex analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Schoenemann, T., & Cremers, D. (2007). Introducing curvature into globally optimal image segmentation: minimum ratio cycles on product graphs. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, October 2007.
Schoenemann, T., Kahl, F., & Cremers, D. (2009). Curvature regularity for region-based image segmentation and inpainting: A linear programming relaxation. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), Kyoto, Japan, September 2009.
Schoenemann, T., Kuang, Y., & Kahl, F. (2011). Curvature regularity for multi-label problems—standard and customized linear programming. In International workshop on energy minimization methods in computer vision and pattern recognition, St. Petersburg, Russia, July 2011.
Schrijver, A. (1986). Theory of linear and integer programming. Wiley-Interscience series in discrete mathematics and optimization. New York: Wiley.
Strandmark, P., & Kahl, F. (2011). Curvature regularization for curves and surfaces in a global optimization framework. In International workshop on energy minimization methods in computer vision and pattern recognition, St. Petersburg, Russia, July 2011.
Sullivan, J. M. (1992). A crystalline approximation theorem for hypersurfaces. PhD thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey.
Sullivan, J. M. (1994). Computing hypersurfaces which minimize surface energy plus bulk energy. In Motion by mean curvature and related topics (pp. 186–197).
Toshev, A., Taskar, B., & Daniilidis, K. (2010). Object detection via boundary structure segmentation. In IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, California, June 2010.
Tschumperlé, D. (2006). Fast anisotropic smoothing of multi-valued images using curvature-preserving PDE’s. International Journal of Computer Vision, 68(1), 65–82.
Weickert, J. (1998). Anisotropic diffusion in image processing. Stuttgart: Teubner.
Weickert, J. (2003). Coherence-enhancing shock filters. In Pattern recognition (proc. DAGM), Magdeburg, Germany, September 2003.
Ye, Y. (1997). Interior point algorithms: theory and analysis. Wiley-Interscience series in discrete mathematics. New York: Wiley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoenemann, T., Kahl, F., Masnou, S. et al. A Linear Framework for Region-Based Image Segmentation and Inpainting Involving Curvature Penalization. Int J Comput Vis 99, 53–68 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-012-0518-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-012-0518-7