Abstract
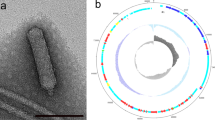
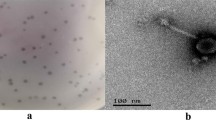
A novel virulent bacteriophage vB_SpuP_Spp16 (hereafter designated Spp16) that infects Salmonella enterica serovar pullorum was isolated. Transmission electron microscopy showed that Spp16 possessed an isometric polyhedral head (60 nm in diameter) and a short tail (10 nm in length) belonging to the family Podoviridae. Its complete genome was determined to be 41,832 bp, with a 39.46% GC content by next-generation sequencing. The genome contains 53 proposed open reading frames that are involved in DNA replication and modification, transcriptional regulation, phage structural and packaging proteins and bacterial lysis. No transfer RNA genes were identified. The termini of genome were determined using our previously proposed termini identification method, which suggests that this phage has redundant termini with 421 bp direct terminal repeats. BLASTn analysis revealed the highest sequence similarity with Yersinia phage phi80-18, with a genome coverage of 33% and highest sequence identity of 69%. The phylogenetic analysis indicated that Spp16 forms a distinct branch of the subfamily Autographivirinae. Comparative genomics analysis showed that the phage Spp16 should be regarded as a new subcluster within the GAP227-like cluster in the Autographivirinae subfamily. The phage Spp16 has an obligate lytic life cycle demonstrated by experimental data and genomic analysis. These results suggest that Spp16 may be a proper candidate to control diseases caused by Salmonella enterica serovar pullorum.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foley SL, Lynne AM, Nayak R (2008) Salmonella challenges: prevalence in swine and poultry and potential pathogenicity of such isolates. J Anim Sci 86(14 Suppl):E149
Galanis E, Dm LFW, Patrick ME, Binsztein N, Cieslik A, Chalermchikit T, Aidarakane A, Ellis A, Angulo FJ, Wegener HC (2006) Web-based surveillance and global Salmonella distribution, 2000-2002. Emerg Infect Dis 12(3):381
Capita R, Alvarezastorga M, Alonsocalleja C, Moreno B, Del CGM (2003) Occurrence of salmonellae in retail chicken carcasses and their products in Spain. Int J Food Microbiol 81(2):169–173
Elsharkawy H, Tahoun A, Elgohary EGA, Elabasy M, Elkhayat F, Gillespie T, Kitade Y, Hafez HM, Neubauer H, Eladawy H (2017) Epidemiological, molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from chicken farms in Egypt. Gut Pathogens 9(1):8
Voetsch AC, Van Gilder TJ, Angulo FJ, Farley MM, Shallow S, Marcus R, Cieslak PR, Deneen VC, Tauxe RV (2004) FoodNet estimate of the burden of illness caused by nontyphoidal Salmonella infections in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 38(Suppl 3):S127
Medina E, Pieper DH (2016) Tackling threats and future problems of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 398:3–33
Hagens S, Loessner MJ (2010) Bacteriophage for biocontrol of foodborne pathogens: calculations and considerations. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 11(1):58
Akhtar M, Viazis S, Diez-Gonzalez F (2014) Isolation, identification and characterization of lytic, wide host range bacteriophages from waste effluents against Salmonella enterica serovars. Food Control 38(1):67–74
Adams MH (1959) Bacteriophages. Intercience Publishers Inc, New York
Ackermann HW (2009) Basic phage electron microscopy. Methods Mol Biol 501:113
Chen M, Xu J, Yao H, Lu C, Zhang W (2016) Isolation, genome sequencing and functional analysis of two T7-like coliphages of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Gene 582(1):47–58
Chen Y, Sun E, Song J, Yang L, Wu B (2018) Complete genome sequence of a novel T7-like bacteriophage from a pasteurella multocida capsular type A isolate. Curr Microbiol 75(5):574–579
Postic B, Finland M (1961) Observations on bacteriophage typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Investig 40(11):2064–2075
Lu S, Le S, Tan Y, Zhu J, Li M, Rao X, Zou L, Li S, Wang J, Jin X (2013) Genomic and proteomic analyses of the terminally redundant genome of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage PaP1: establishment of genus PaP1-like phages. PLoS ONE 8(5):e62933
Li S, Fan H, An X, Fan H, Jiang H, Chen Y, Tong Y (2014) Scrutinizing virus genome termini by high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85806–e85806
Li S, Fan H, An X, Fan H, Jiang H, Chen Y, Tong Y (2014) Scrutinizing virus genome termini by high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85806
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, Dejongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. Bmc Genom 9(1):75
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes: implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucl Acids Res 29(12):2607–2618
Marchlerbauer A, Lu S, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Deweesescott C, Fong JH, Geer LY, Geer RC, Gonzales NR (2011) CDD: a conserved domain database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucl Acids Res 39:225–229
Schattner P, Brooks AN, Lowe TM (2005) The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucl Acids Res 33:W686
Krogh A, Larsson B, Heijne GV, Sonnhammer ELL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305:567–580
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, Dejongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. Bmc Genom 9(8):75
Krumsiek J, Arnold R, Rattei T (2007) Gepard: a rapid and sensitive tool for creating dotplots on genome scale. Bioinformatics 23(8):1026–1028
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Lefkowitz EJ, Dempsey DM, Hendrickson RC, Orton RJ, Siddell SG, Smith DB (2018) Virus taxonomy: the database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucl Acids Res 46:D708–D717
Nechaev S, Severinov K (2003) Bacteriophage-induced modifications of host RNA polymerase. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:301–322. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090942
Dh Krüger, Schroeder C (1981) Bacteriophage T3 and bacteriophage T7 virus-host cell interactions. Microbiol Rev 45(1):9
Fujisawa H, Morita M (1997) Phage DNA packaging. Genes Cell 2(9):537
Fischetti VA (2010) Bacteriophage endolysins: a novel anti-infective to control Gram-positive pathogens. Int J Med Microbiol 300(6):357–362
Gründling A, Manson MD, Young R (2001) Holins kill without warning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(16):9348
Shi Y, Yan Y, Ji W, Du B, Meng X, Wang H, Sun J (2012) Characterization and determination of holin protein of Streptococcus suisbacteriophage SMP in heterologous host. Virol J 9(1):70
Yannick B, Lars F, Janine M, Rudi L, Brion D, Loessner MJ (2011) Novel virulent and broad-host-range Erwinia amylovora bacteriophages reveal a high degree of mosaicism and a relationship to Enterobacteriaceae phages. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(17):5945–5954
Inmaculada GH, Francisco RV, Ana-Belen MC (2013) Novel group of podovirus infecting the marine bacterium Alteromonas macleodii. Bacteriophage 3(2):e24766
Daudén MI, Martínbenito J, Sánchezferrero JC, Pulidocid M, Valpuesta JM, Carrascosa JL (2013) Large terminase conformational change induced by connector binding in bacteriophage T7. J Biol Chem 288(23):16998–17007
Benson SD, Bamford JKH, Bamford DH, Burnett RM (1999) Viral evolution revealed by bacteriophage PRD1 and human adenovirus coat protein structures. Cell 98(6):825–833
Grose JH, Casjens SR (2014) Understanding the enormous diversity of bacteriophages: the tailed phages that infect the bacterial family Enterobacteriaceae. Virology 468–470:421–443
Lin DM, Koskella B, Lin HC (2017) Phage therapy: an alternative to antibiotics in the age of multi-drug resistance. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 8(3):162–173
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Guangqian Pei, Yunfei Wang, Yonghuan Wang, and Yibao Chen for their help during this work.
Funding
This study was funded by the Nature Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (grant no. ZR2015CM020), and the State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and biosecurity (SKLPBS1518).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yigang Tong and Huiying Ren conceived and designed the experiments and critically evaluated the manuscript. Feiyang Zhao carried out the data analysis and wrote the manuscript. Guangqin Liu isolated and identified the phage. Huzhi Sun and Xiangying Zhou carried out the experiments. Manli Li analyzed the phage sequences. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Edited by Joachim Jakob Bugert.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, F., Sun, H., Zhou, X. et al. Characterization and genome analysis of a novel bacteriophage vB_SpuP_Spp16 that infects Salmonella enterica serovar pullorum. Virus Genes 55, 532–540 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-019-01664-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-019-01664-0