Abstract
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) was detected by RT-PCR in 105 out of 391 samples which were collected from five dairy farms in Ningxia, China during 2010–2011. Non-cytopathogenic BVDV was isolated from 13 samples and a 230-bp fragment of the 5′-untranslated region was amplified and sequenced. While the predominant subgenotypes were BVDV-1b and BVDV-1d, a potentially novel subgenotype was identified by phylogenetic analysis, which may have implications for vaccine development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is a ubiquitous pathogen that infects domestic animals such as cattle, goats, sheep, and pigs, as well as many wild and captive animals [1]. To date, the BVDV circulating in the Chinese cattle population is mainly BVDV-1b, -1c, -1m, -1p, and BVDV-2a [2–4]. To investigate the prevalence of BVDV in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region of China, a total of 391 blood samples were collected from five dairy farms, without vaccination history, during 2010–2011, and tested by an RT-PCR method targeting the 5′-untranslated region (5′-UTR).
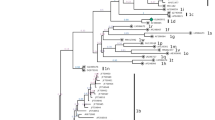
One hundred and five samples were found positive for BVDV infection. Virus isolation was successful in 13 samples and all isolated viruses were of non-cytopathogenic biotype. Comparative analysis of the 230-bp fragment of the 5′-UTR showed that the 13 isolates shared an identity of 85.2–100 % and had an identity of 85.7–99.6 % between the isolates and BVDV-1 reference strains. The newly determined sequences have been deposited in GenBank under accession numbers JX437146-JX437158. Phylogenetic analysis clustered the 13 isolates into three subgenotypes: BVDV-1b, BVDV-1d, and a potentially novel subgenotype, tentatively designated as “BVDV-1*” (Fig. 1). While BVDV normally causes subclinical infection or mild disease, the cattle which were infected with “BVDV-1*” were characterized by fevers and oral lesions. Further studies are required to confirm an association between these clinical signs and BVDV-1*. This is the first report describing the detection of subgenotypes BVDV-1d and BVDV-1* in the Chinese cattle population, which may have important implications for developing effective BVDV vaccines against the newly identified subgenotypes in China.
The phylogenetic tree was generated based on comparison of nucleotide sequences of the 5′-UTR of 13 BVDV isolates with sequences downloaded from the GenBank database. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining (NJ) method and a bootstrap test by means of MEGA version 4.1. The numbers at the phylogenetic branches indicate the bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) in percentage supporting each group. Subgenotype BVDV-1b included three isolates and is indicated in red; subgenotype BVDV-1d included six isolates and is indicated in light blue; subgenotype BVDV-1* included four isolates and is indicated in green (Color figure online)
References
N. Mishra, S. Vlicek, K. Rajukumar, R. Dubey, A. Tiwari, V. Galav, H.K. Pradhan, Res. Vet. Sci. 84(3), 507–510 (2007)
F.G. Zhong, N. Li, X. Huang, Y. Guo, H.X. Chen, X.H. Wang, C.Q. Shi, X.Y. Zhang, Virus Genes 42(2), 204–207 (2011)
F. Xue, Y.M. Zhu, J. Li, L.C. Zhu, X.G. Ren, J.K. Feng, H.F. Shi, Y.R. Gao, Vet. Microbiol. 143(2–4), 379–383 (2010)
Y.Q. Lin, L.Q. Zhu, J. Tao, H.J. Sun, X.S. Meng, J.Y. Wang, G.Q. Zhu, Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 33(1), 23–27 (2011) (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grants from NBCITS, MOA (CARS-38).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X., Cao, X., Zheng, F. et al. Identification and characterization of a novel subgenotype of bovine viral diarrhea virus isolated from dairy cattle in Northwestern China. Virus Genes 46, 375–376 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0861-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0861-3