Abstract
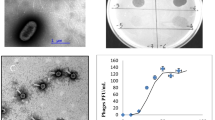
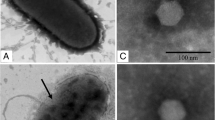
The Nosticoida limicola filamentous morphotype is held responsible for incidents of bulking and foaming in activated sludge. Members of the actinobacterial N. limicola II have been isolated and grown in pure culture and shown to belong to the genus Tetrasphaera, and play an important role in phosphorus removal. This article describes the isolation and genomic characterization of a phage able to lyse Tetrasphaera jenkinsii, TJE1. This lytic phage is a member of the Caudovirales specific for T. jenkinsii. The complete DNA sequence of TJE1 phage revealed it to have a circularly permuted genome (49,219 bp) with 66 putative open reading frames, a single transcriptional terminator, and 6 pairs of inverted repeats within the genome sequence. The TJE1 phage genome is organised into a modular gene structure, but shares only limited sequence identity with other phages so far described.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.H. Nielsen, H. Daims, H. Lemmer, FISH Handbook for Biological Wastewater Treatment (IWA Publishing, London, 2009)
F. Rohwer, Global phage diversity. Cell 18, 113–141 (2003)
L.L. Blackall, E.M. Seviour, D. Bradford, S. Rossetti, V. Tandoi, R.J. Seviour, ‘Candidatus Nostocoida limicola’, a filamentous bacterium from activated sludge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 703–709 (2000)
C.M. McKenzie, E.M. Seviour, P. Schumann, A.M. Maszenan, J.R. Liu, R.I. Webb, P. Monis, C.P. Saint, U. Steiner, R.J. Seviour, Isolation of ‘Candidatus Nostocoida limicola’ Blackall et al. 2000 should be described as three novel species of the genus Tetrasphaera, as Tetrasphaera jenkinsii sp. nov. and Tetrasphaera veronensis sp. nov. Int. J. System. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 2279–2290 (2006)
Y. Kong, J.L. Nielsen, P.H. Nielsen, Identity and ecophysiology of uncultured actinobacterial polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 4076–4085 (2005)
K.D. McMahon, S. He, A. Oehmen, The microbiology of phosphorous removal, in Microbial Ecology of Activated Sludge, ed. by R.J. Seviour, P.H. Nielsen (IWA publishing, London, 2010), pp. 281–320
H.T.T. Nguyen, V.Q. Le, A.A. Hansen, J.L. Nielsen, P.H. Nielsen, High Diversity and abundance of putative polyphosphate- accumulating Tetrasphaera-related bacteria in activated sludge systems. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 76, 256–267 (2011)
S. Chibani-Chennoufi, A. Bruttin, M.L. Dillmann, H. Brussow, Phage–host interaction: an ecological perspective. J. Bacteriol. 186, 3677–3678 (2004)
N.H. Mann, The third age of phage. PLoS Biol. 3, e182 (2005)
E. Jensen, H. Schrader, B. Rieland, T. Thompson, K. Lee, K. Nickerson, T. Kokjohn, Prevalence of broad-host range lytic bacteriophages of Spherotilus natans, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 575–580 (1998)
S.M. Kotay, T. Datta, J. Choi, R. Goel, Biocontrol of biomass bulking caused by Haliscomenobacter hydrossis using a newly isolated lytic bacteriophage. Water Res. 45, 694–704 (2011)
S. Petrovski, R.J. Seviour, D. Tillett, Genome sequence and characterization of the Tsukamurella bacteriophage TPA2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 1389–1398 (2011)
A.J. Drummond, B. Ashton, M. Cheung, J. Heled, M. Kearse, R. Moir, S. Stones-Havas, T. Thierer, A. Wilson, Geneious v5.1. http://www.geneious.com (2010)
S.F. Altschul, W. Gish, W. Miller, E.W. Myers, D.J. Lipman, Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410 (1990)
D. Laslett, B. Canback, ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucl. Acids Res. 32, 11–16 (2004)
E.A. Lesnik, R. Sampath, H.B. Levene, T.J. Henderson, J.A. McNiel, D.J. Ecker, Prediction of rho-independent transcriptional terminators in Escherichia coli. Nucl. Acids Res. 29, 3583–3594 (2007)
S. Petrovski, D. Tillett, R.J. Seviour, Genome sequence and characterization of the related Gordonia phages GTE5 and GRU1 and their use as biocontrol agents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 42–47 (2012)
S. Petrovski, R.J. Seviour, D. Tillett, Characterization of the genome of the polyvalent lytic bacteriophage GTE2, which has potential for biocontrol of Gordonia-, Rhodococcus-, and Nocardia-stabilized foams in activated sludge plants. App. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 3923–3929 (2011)
H. Brüssow, F. Desiere, Comparative phage genomics and the evolution of Siphoviridae: insights from dairy phages. Mol. Microbiol. 39, 213–223 (2001)
M. Borriss, T. Lombardot, F.O. Glöckner, D. Becher, D. Albretcht, T. Schweder, Genome and proteome characterization of psychrophilic Flavobacterium bacteriophage 11b. Extremophiles 11, 95–104 (2007)
F.N. Enikeeva, K.V. Severinov, M.S. Gelfand, Restriction-modification systems and bacteriophage invasion: who wins? J. Theor. Biol. 266, 550–559 (2010)
C. Yang, U. Curth, C. Urbanke, C. Kang, Crystal structure of human mitochondrial single-stranded DNA binding protein at 2.4 Å resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 4, 153–157 (1997)
M.S. Lee, K.J. Marians, Escherichia coli replication factor Y, a component of the primosome, can act as a DNA helicase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 8345–8349 (1987)
E.V. Koonin, K.E. Rudd, A conserved domain in putative bacterial and bacteriophage transglycosylases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 19, 106–107 (1994)
D. Kapitaniov, R.K. Yu, Conserved domains of glycosyltransferases. Glycobiology 9, 961–978 (1999)
J. Fricke, J. Neuhard, R.A. Kelln, S. Pedersen, The cmk gene encoding cytidine monophosphate kinase is located in the rpsa operon and is required for normal replication rate in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 177, 517–523 (1995)
J.B. Thoden, A.D. Hedeman, G. Wesenberg, M.C. Chapeau, P.A. Frey, H.M. Holden, Structural analysis of UDP-sugar binding to UDP-galactose 4-epimerase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 36, 6294–6304 (1997)
N. Kikuchi, H. Narimatsu, Bioinformatics for comprehensive finding and analysis of glycosyltransferases. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1760, 578–583 (2006)
R. Ghai, A.B. Martin-Cuadrado, A.G. Molto, I.G. Heredia, R. Cabrera, J. Martin, M. Verdú, P. Deschamps, D. Moreira, P. López-García, A. Mira, F. Rodriguez-Valera, Metagenome of the Mediterranean deep chlorophyll maximum studied by direct and fosmid library 454 pyrosequencing. ISME J. 4, 1154–1166 (2010)
G.L. Newton, P. Ta, K.P. Bzymek, R.C. Fahey, Biochemistry of the initial steps of mycothiol biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 33910–33920 (2006)
C.E. Catalano, The terminase enzyme from bacteriophage lambda: a DNA-packaging machine. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 57, 128–148 (2000)
G.F. Hatfull, D. Jacobs-Sera, J.G. Lawrence, W.H. Pope, D.A. Russell, C.C. Ko, R.J. Weber, M.C. Patel, K.L. Germane, R.H. Edgar, N.N. Hoyle, C.A. Bowman, A.T. Tantoco, E.C. Paladin, M.S. Myers, A.L. Smith, M.S. Grace, T.T. Pham, M.B. O’Brien, A.M. Vogelsberger, A.J. Hryckowian, J.L. Wynalek, H. Donis-Keller, M.W. Bogel, C.L. Peebles, S.G. Cresawn, R.W. Hendrix, Comparative genomic analysis of 60 mycobacteriophage geneomes: genome clustering, gene acquisition and gene size. J. Mol. Biol. 397, 119–143 (2010)
P.B. Perler, Protein splicing of inteins and hedgehog autoproteolysis: structure, function and evolution. Cell 92, 1–4 (1998)
S. Elleuche, S. Pöggeler, Inteins, valuable genetic elements in molecular biology and biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 87, 479–489 (2010)
C.L. Chen, T.Y. Pan, S.C. Kan, Y.C. Kuan, L.Y. Hong, K.R. Chiu, K.S. Sheu, J.S. Yang, W.H. Hsu, H.Y. Hu, Genome sequence of the lytic bacteriophage P1201 from Corynebacterium glutamicum NCHU 87078: evolutionary relationships to phages from Corynebacterineae. Virology 378, 226–232 (2008)
G.J. Morgan, G.F. Hatfull, S. Casjens, R.W. Hendrix, Bacteriophage Mu genome sequence: analysis and comparison with Mu-like pathogens in Haemophilus, Neisseria and Deinococcus. J. Mol. Biol. 317, 337–359 (2002)
N.M. Luscombe, S.E. Austin, H.M. Berman, J.M. Thornton, An overview of the structures of protein–DNA complexes. Genome Biol. 1:REVIEWS001 (2000)
A. Daniel, P.E. Bonnen, V.A. Fischetti, First complete genome sequence of two Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriophages. J. Bacteriol. 189, 2086–2100 (2007)
M. Sharma, R.L. Ellis, D.M. Hinton, Identification of a family of bacteriophage T4 genes encoding proteins similar to those present in group I introns of fungi and phage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6658–6662 (1992)
L.M. Iyer, E.V. Koonin, L. Aravind, Classification and evolutionary history of the single-strand annealing proteins, RecT, Redbeta, ERF and RAD52. BMC Genomics 3, 8 (2002)
T.S. Vellani, R.S. Myers, Bacteriophage SPP1 Chu is an alkaline exonuclease in the SynExo family of viral two-component recombinases. J. Bacteriol. 185, 2465–2474 (2003)
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Australian Research Council Linkage Grant (LP0774913) together with Melbourne Water and South East Water who are thanked for their financial support. S. Petrovski was funded by the ARC Linkage and La Trobe University grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrovski, S., Tillett, D. & Seviour, R.J. Isolation and complete genome sequence of a bacteriophage lysing Tetrasphaera jenkinsii, a filamentous bacteria responsible for bulking in activated sludge. Virus Genes 45, 380–388 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0771-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0771-4