Abstract
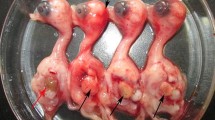
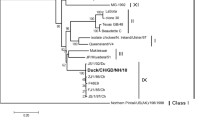
Egg-laying duck flocks in Guangdong province, southern China, have been suffering a widely spreading infectious disease with abrupt egg drops and death since the winter of 2010. However, the causative pathogen was not known. We obtained two independent virus isolates named FS and JM from the diseased layer duck flocks and identified them as duck-origin Tembusu virus by PCR detection, sequencing the entire length of the open reading frames (ORFs). The two isolates FS and JM shared high sequence similarity to the isolates of duck-origin Tembusu virus that was first emerged in eastern China in April 2010. Blast analysis shows that the whole ORF sequences of FS and JM have the highest similarity (>99 %) to BYD-1(the first reported duck-origin Tembusu virus) and JS804 (the first reported goose-origin Tembusu virus), indicating that the full-length genomes were highly conserved in waterfowl-origin Tembusu viruses. The present study suggests that duck-origin Tembusu viruses have spread fast from eastern China to southern China, causing widely spreading infections. The high conservation of duck-origin Tembusu virus strains provides the genomic basis for choosing the strains for vaccine preparation for better protection against this new virus infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Su, S. Li, X.D. Hu, X.L. Yu, Y.Y. Wang, P.P. Liu, X.S. Lu, G.Z. Zhang, X.Y. Hu, D. Liu, X.X. Li, W.L. Su, H. Lu, N.S. Mok, P.Y. Wang, M. Wang, K.G. Tian, G.F. Gao, PLoS ONE 6(3), e18106 (2011)
P.X. Yan, Y.S. Zhao, X. Zhang, D.W. Xu, X.G. Dai, Q.Y. Teng, L.P. Yan, J.W. Zhou, X.W. Ji, S.M. Zhang, G.Q. Liu, Y.J. Zhou, Y. Kawaoka, G.Z. Tong, Z.J. Li, Virology 417(1), 1–8 (2011)
Q.Y. Teng, P.X. Yan, X. Zhang, L.P. Yan, Z.J. Li, Chinese J.Anim. Infect. Dis. (in Chinese) 18(6), 1–4 (2010)
M. Liao, X.D. MOU, Y. Geng, T.L. Bian, X.H. Lu, Q.Y. Chen, Z.Y. Ren, C. Ding, J.Y. Zhou, Chinese J. Anim. Infect. Dis. 19(1), 22–26 (2011). in Chinese
Y. Tang, Y. Diao, X. Gao, C. Yu, L. Chen, D. Zhang. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. doi:10.1111/j.1865-1682.2011.01275.x
M. Liu, C. Liu, G. Li, X. Li, X. Yin, Y. Chen, Y. Zhang, J. Virol. 86(6), 3398–3399 (2012)
Z. Cao, C. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, W. Ye, J. Han, G. Ma, D. Zhang, F. Xu, X. Gao, Y. Tang, S. Shi, C. Wan, C. Zhang, B. He, M. Yang, X. Lu, Y. Huang, Y. Diao, X. Ma, D. Zhang, Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17(10), 1873–1875 (2011)
T. Yun, D. Zhang, X. Ma, Z. Cao, L. Chen, Z. Ni, W. Ye, B. Yu, J. Hua, Y. Zhang, C. Zhang, J. Virol. 86(6), 3406–3407 (2012)
T. Yun, W. Ye, N. Zi, D. Zhang, C. Zhang. Vet Microb. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.01.013
C.M. Rice, E.M. Lenches, S.R. Eddy, S.J. Shin, R.L. Sheets, J.H. Strauss, Science 229, 726–733 (1985)
X.M. Huang, Y. Li, D.M. Zhao, Y.Z. Zhao, J.F. Zhang, K.W. He, J.B. Hou, H.M. Niu, B. Li, L.B. Wen, Y.S. Wang, G.Q. Shao, K.N. Zhang, J.N. Zhu, D.M. Wu, L. Gao, S Jiang. J. Agri. Sci. (in Chinese) 27(2), 354–360 (2011)
S.L. Chen, S.Y. Chen, S. Wang, F.Q. Lin, B. Jiang, X.X. Chen, M.Q. Huang, X.L. Zhu, Z.L. Li, Fujian J Agri. Sci. (in Chinese) 26(2), 170–174 (2011)
S.J. Seligman, D.J. Bucher, Trends Microbio. J. 11(3), 108–110 (2003)
S.L. Hanna, T.C. Pierson, M.D. Sanchez, A.A. Ahmed, M.M. Murtadha, R.W. Doms, J. Virol. 79(21), 13262–13274 (2005)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Guangdong Provincial Scientific and Technological Planning Project (No. 2008B020700001), and by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest, China (No. 201003012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Li and H. An have contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., An, H., Sun, M. et al. Identification and genomic analysis of two duck-origin Tembusu virus strains in southern China. Virus Genes 45, 105–112 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0753-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0753-6