Abstract
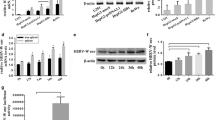
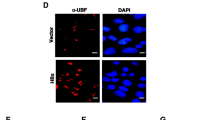
It is well known that telomerase activation and virus infection are strongly associated with human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) plays an important role in HCC pathogenesis. However, the mechanisms of HBx on telomerase activity are not well understood. To determine the potential roles of HBx in telomerase activity, both transfection and antisense assay were designed to examine the effects of HBx on telomerase in this report. Results showed that HBX gene increased telomerase activity and human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) expression in HBx-transfected cells and HBx-positive HCC samples. Co-transfection and luciferase reporter assay showed that HBx could stimulate hTERT promoter in a dose-dependent manner in different cells. Truncated and mutant reporter assays revealed that Sp1 binding sites mapped at −132 to +5 nt in hTERT promote were important for HBx-mediated upregulation of hTERT. Western blot did not show any change of Sp1 expression in HBx-transfected cells, but EMSA showed evidence of that HBx increased binding of Sp1 to its target DNA. These results provide new insights into the role of HBx in liver carcinogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.L. Chan, J.J. Sung, Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. Semin. Liver Dis. P26, 153–161 (2006)
S. Murakami, Hepatitis B virus X protein: a multifunctional viral regulator. J. Gastroenterol. 36, 651–660 (2001)
C. Kim, K. Koike, I. Saito, T. Miyamura, G. Jay, HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 351, 317–320 (1991)
S.G. Lee, H.M. Rho, Transcriptional repression of the human p53 gene by hepatitis B viral X protein. Oncogene 19, 468–471 (2000)
D. Cougot, C. Neuveut, M.A. Buendia, HBV induced carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Virol. 34, S75–S78 (2005)
L. Jia, X.W. Wang, C.C. Harris, Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits nucleotide excision repair. Int. J. Cancer 80, 875–879 (1999)
M.J. Bouchard, R.J. Schneider, The enigmatic X gene of hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 78, 12725–12734 (2004)
N.W. Kim, M.A. Piatyszek, K.R. Prowse, C.B. Harley, M.D. West, P.L. Ho, G.M. Coviello, W.E. Wright, S.L. Weinrich, J.W. Shay, Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 266, 2011–2015 (1994)
I. Horikawa, J.C. Barrett, Transcriptional regulation of the telomerase hTERT gene as a target for cellular and viral oncogenic mechanisms. Carcinogenesis 24, 1167–1176 (2003)
J.C. Poole, L.G. Andrews, T.O. Tollefsbol, Activity, function, and gene regulation of the catalytic subunit of telomerase (hTERT). Gene 269, 1–12 (2001)
H. Liu, F. Luan, Y. Ju, H.Y. Shen, L.F. Gao, X.Y. Wang, S.X. Liu, L.N. Zhang, W.S. Sun, C.H. Ma, In vitro transfection of the hepatitis B virus PreS2 gene into the human hepatocarcinoma cell line HepG2 induces upregulation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 355, 379–384 (2007)
J.T. Kadonaga, R. Tjian, Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 83, 5889–5893 (1986)
R.W. Kriwacki, S.C. Schultz, T.A. Steitz, J.P. Caradonna, Sequence-specific recognition of DNA by zinc-finger peptides derived from the transcription factor Sp1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 9759–9763 (1992)
J. Song, H. Ugai, K. Ogawa, Y. Wang, A. Sarai, Y. Obata, I. Kanazawa, K. Sun, K. Itakura, K.K. Yokoyama, Two consecutive zinc fingers in Sp1 and in MAZ are essential for interactions with cis-elements. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 30429–30434 (2001)
C.L. Parks, T. Shenk, The serotonin 1a receptor gene contains a TATA-less promoter that responds to MAZ and Sp1. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 4417–4430 (1996)
S. Kyo, M. Takakura, T. Takahiro, T. Kanaya, H. Itoh, M. Yutsudo, H. Ariga, M. Inoue, Sp1 cooperates with c-Myc to activate transcription of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene (hTERT). Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 669–677 (2000)
O.H. ST, S. Kyo, L. Laimins, Telomerase activation by human papillomavirus type 16 E6 protein: induction of human telomerase reverse transcriptase expression through Myc and GC-rich Sp1 binding sites. J. Virol. 75, 5559–5566 (2001)
D. Lee, H.Z. Kim, K.W. Jeong, Y.S. Shim, I. Horikawa, J.C. Barrett, J. Choe, Human papillomavirus E2 down-regulates the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 27748–27756 (2002)
S.C. Verma, S. Borah, E.S. Robertson, Latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus up-regulates transcription of human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter through interaction with transcription factor Sp1. J. Virol. 78, 10348–10359 (2004)
H.A. Edmondson, P.E. Steiner, Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer 7, 462–503 (1954)
F. Luan, H. Liu, L. Gao, J. Liu, Z. Sun, Y. Ju, N. Hou, C. Guo, X. Liang, L. Zhang, W. Sun, C. Ma, Hepatitis B virus protein preS2 potentially promotes HCC development via its transcriptional activation of hTERT. Gut 58(11), 1528–1537 (2009)
R. Higuchi, M.A. Innis, D.H. Gelfand, J.J. Sninsky, T.J. White, PCR Protocols (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1990), pp. 177–183
E. Schreiber, P. Matthias, M.M. Muller, W. Schaffner, Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with ‘mini-extracts’, prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 17(15), 6419 (1989)
X. Zhang, H. Zhang, L. Ye, Effects of hepatitis B virus X protein on the development of liver cancer. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 147, 58–66 (2006)
X.H. Liang, Y.G. Liu, Q. Zhang, L.F. Gao, L.H. Han, C.H. Ma, L.N. Zhang, Y.H. Chen, W.S. Sun, Hepatitis B virus sensitizes hepatocytes to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through Bax. J. Immunol. 178, 503–510 (2007)
J.M. Su, X.M. Lai, K.H. Lan, C.P. Li, Y. Chao, S.H. Yen, F.Y. Chang, S.D. Lee, W.P. Lee, X protein of hepatitis B virus functions as a transcriptional corepressor on the human telomerase promoter. Hepatology 46, 402–413 (2007)
H. Zhang, C.L. Shan, N. Li, X. Zhang, X.Z. Zhang, F.Q. Xu, S. Zhang, L.Y. Qiu, L.H. Ye, X.D. Zhang, Identification of a natural mutant of HBV X protein truncated 27 amino acids at the COOH terminal and its effect on liver cell proliferation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 29, 473–480 (2008)
A.R. Black, D. Jensen, S. Lin, J.C. Azizkhan, Growth/cell cycle regulation of Sp1 phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1207–1215 (1999)
S. Ammanamanchi, J.W. Freeman, M.G. Brattain, Acetylated Sp3 is a transcriptional activator. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 35775–35780 (2003)
Y.I. Lee, S. Lee, Y. Lee, Y.S. Bong, S.W. Hyun, Y.D. Yoo, S.J. Kim, Y.W. Kim, H.R. Poo, The human hepatitis B virus transactivator X gene product regulates Sp1 mediated transcription of an insulin-like growth factor II promoter 4. Oncogene 16, 2367–2380 (1998)
Acknowledgments
We thank the Institute of Genetics, Shandong University School of Medicine for assistance with the Luciferase assays. This work was supported by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 30972753 and No. 30670966), the National Basic Research Program (973), No. 2009CB521900, Shandong Provincial Nature Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (JQ200907), and Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Shi, W., Luan, F. et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates transcriptional activation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase. Virus Genes 40, 174–182 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-009-0441-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-009-0441-3