Abstract
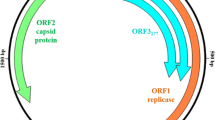
This study reports the molecular characterization of novel caliciviruses, the St-Valérien-like viruses, which were isolated from pig feces in the province of Quebec, Canada between 2005 and 2007. The genomes of St-Valérien-like viruses contain 6409 nucleotides and include two main open reading frames (ORFs). ORF1 encodes the non structural (NS) polyprotein and the major capsid protein (VP1) while ORF2 encodes the putative basic minor capsid protein. Typical conserved amino acid motifs predict a gene order reminiscent of calicivirus genomes. Phylogenetic, pairwise homology, and distance analyses performed on complete genomic sequences and partial amino acid sequences from the NTPase, polymerase, and major capsid protein segregated the St-Valérien-like viruses in a unique cluster sharing a common root with the Tulane virus and the noroviruses. Based on the genomic analyses presented, the St-Valérien-like viruses are members of a new genus of Caliciviridae for which we propose the name Valovirus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.Y. Green, T. Ando, M.S. Balayan, T. Berke, I.N. Clarke, M.K. Estes, D.O. Matson, S. Nakata, J.D. Neill, M.J. Studdert, H.J. Thiel, Taxonomy of the caliciviruses. J. Infect. Dis. 181(Suppl 2), S322–S330 (2000). doi:https://doi.org/10.1086/315591
J.D. Neill, Nucleotide sequence of a region of the feline calicivirus genome which encodes picornavirus-like RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, cysteine protease and 2C polypeptides. Virus Res. 17, 145–160 (1990). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1702(90)90061-F
P.J. Glass, L.J. White, J.M. Ball, I. Leparc-Goffart, M.E. Hardy, M.K. Estes, Norwalk virus open reading frame 3 encodes a minor structural protein. J. Virol. 74, 6581–6591 (2000). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.74.14.6581-6591.2000
S.V. Sosnovtsev, K.Y. Green, Identification and genomic mapping of the ORF3 and VPg proteins in feline calicivirus virions. Virology 277, 193–203 (2000)
M. Koopmans, K.Y. Green, T. Ando, I.N. Clarke, M.K. Estes, D.O. Matson, S. Nakata, J.D. Neil, A.W. Smith, M.J. Studdert, H.J. Theil, in Family Caliciviridae, ed. by C.M. Fauquet, M.A. Mayo, J. Maniloff, U. Desselberger, L.A. Ball. Virus taxonomy, 8th report of the ICTV (Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, 2005), pp. 843–851
T. Farkas, K. Sestak, C. Wei, X. Jiang, Characterization of a rhesus monkey calicivirus representing a new genus of Caliciviridae. J. Virol. 82, 5408–5416 (2008). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00070-08
J.R. Smiley, K.O. Chang, J. Hayes, J. Vinje, L.J. Saif, Characterization of an enteropathogenic bovine calicivirus representing a potentially new calicivirus genus. J. Virol. 76, 10089–10098 (2002). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.76.20.10089-10098.2002
K. Numata, M.E. Hardy, S. Nakata, S. Chiba, M.K. Estes, Molecular characterization of morphologically typical human calicivirus Sapporo. Arch. Virol. 142, 1537–1552 (1997). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050178
I.N. Clarke, P.R. Lambden, Organization and expression of calicivirus genes. J. Infect. Dis. 181(Suppl 2), S309–S316 (2000). doi:https://doi.org/10.1086/315575
B.L. Liu, I.N. Clarke, E.O. Caul, P.R. Lambden, Human enteric caliciviruses have a unique genome structure and are distinct from the Norwalk-like viruses. Arch. Virol. 140, 1345–1356 (1995). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01322662
A.W. Smith, D.E. Skilling, N. Cherry, J.H. Mead, D.O. Matson, Calicivirus emergence from ocean reservoirs: zoonotic and interspecies movements. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 4, 13–20 (1998)
V.F. Ohlinger, B. Haas, H.J. Thiel, Rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD): characterization of the causative calicivirus. Vet. Res. 24, 103–116 (1993)
R.I. Glass, J. Noel, T. Ando, R. Fankhauser, G. Belliot, A. Mounts, U.D. Parashar, J.S. Bresee, S.S. Monroe, The epidemiology of enteric caliciviruses from humans: a reassessment using new diagnostics. J. Infect. Dis. 181(Suppl 2), S254–S261 (2000). doi:https://doi.org/10.1086/315588
X.L. Pang, S. Honma, S. Nakata, T. Vesikari, Human caliciviruses in acute gastroenteritis of young children in the community. J. Infect. Dis. 181(Suppl 2), S288–S294 (2000). doi:https://doi.org/10.1086/315590
J.S. Noel, B.L. Liu, C.D. Humphrey, E.M. Rodriguez, P.R. Lambden, I.N. Clarke, D.M. Dwyer, T. Ando, R.I. Glass, S.S. Monroe, Parkville virus: a novel genetic variant of human calicivirus in the Sapporo virus clade, associated with an outbreak of gastroenteritis in adults. J. Med. Virol. 52, 173–178 (1997). doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199706)52:2<173::AID-JMV10>3.0.CO;2-M
M. Sugieda, H. Nagaoka, Y. Kakishima, T. Ohshita, S. Nakamura, S. Nakajima, Detection of Norwalk-like virus genes in the caecum contents of pigs. Arch. Virol. 143, 1215–1221 (1998). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050369
W.H. Van Der Poel, J. Vinje, H.R. van Der, M.I. Herrera, A. Vivo, M.P. Koopmans, Norwalk-like calicivirus genes in farm animals. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 6, 36–41 (2000)
Q.H. Wang, M. Souza, J.A. Funk, W. Zhang, L.J. Saif, Prevalence of noroviruses and sapoviruses in swine of various ages determined by reverse transcription-PCR and microwell hybridization assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44, 2057–2062 (2006). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02634-05
Q.H. Wang, M.G. Han, S. Cheetham, M. Souza, J.A. Funk, L.J. Saif, Porcine noroviruses related to human noroviruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 11, 1874–1881 (2005)
S.L. Oliver, A.M. Dastjerdi, S. Wong, L. El-Attar, C. Gallimore, D.W. Brown, J. Green, J.C. Bridger, Molecular characterization of bovine enteric caliciviruses: a distinct third genogroup of noroviruses (Norwalk-like viruses) unlikely to be of risk to humans. J. Virol. 77, 2789–2798 (2003). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.77.4.2789-2798.2003
Y. L’Homme, R. Sansregret, É. Plante-Fortier, A.-M. Lamontagne, G. Lacroix, M. Ouardani, J. Deschamps, G. Simard, C. Simard, Genetic diversity of porcine Norovirus and Sapovirus: Canada, 2005–2007. Arch. Virol. 154(4), 581–593 (2009)
V. Martella, E. Lorusso, K. Banyai, N. Decaro, M. Corrente, G. Elia, A. Cavalli, A. Radogna, V. Costantini, L.J. Saif, A. Lavazza, T.L. Di, C. Buonavoglia, Identification of a porcine calicivirus related genetically to human sapoviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46, 1907–1913 (2008). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00341-08
X. Jiang, P.W. Huang, W.M. Zhong, T. Farkas, D.W. Cubitt, D.O. Matson, Design and evaluation of a primer pair that detects both Norwalk- and Sapporo-like caliciviruses by RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 83, 145–154 (1999). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-0934(99)00114-7
E. Scotto-Lavino, G. Du, M.A. Frohman, 3′ end cDNA amplification using classic RACE. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2742–2745 (2006). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.481
G. Belliot, S.V. Sosnovtsev, T. Mitra, C. Hammer, M. Garfield, K.Y. Green, In vitro proteolytic processing of the MD145 norovirus ORF1 nonstructural polyprotein yields stable precursors and products similar to those detected in calicivirus-infected cells. J. Virol. 77, 10957–10974 (2003). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.77.20.10957-10974.2003
B.L. Liu, G.J. Viljoen, I.N. Clarke, P.R. Lambden, Identification of further proteolytic cleavage sites in the Southampton calicivirus polyprotein by expression of the viral protease in E. coli. J. Gen. Virol. 80(Pt 2), 291–296 (1999)
G. Meyers, C. Wirblich, H.J. Thiel, J.O. Thumfart, Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus: genome organization and polyprotein processing of a calicivirus studied after transient expression of cDNA constructs. Virology 276, 349–363 (2000)
S.V. Sosnovtsev, G. Belliot, K.O. Chang, V.G. Prikhodko, L.B. Thackray, C.E. Wobus, S.M. Karst, H.W. Virgin, K.Y. Green, Cleavage map and proteolytic processing of the murine norovirus nonstructural polyprotein in infected cells. J. Virol. 80, 7816–7831 (2006). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00532-06
S.V. Sosnovtsev, M. Garfield, K.Y. Green, Processing map and essential cleavage sites of the nonstructural polyprotein encoded by ORF1 of the feline calicivirus genome. J. Virol. 76, 7060–7072 (2002). doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.76.14.7060-7072.2002
S. Kumar, K. Tamura, M. Nei, MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief. Bioinform. 5, 150–163 (2004). doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/5.2.150
M. Guo, J.F. Evermann, L.J. Saif, Detection and molecular characterization of cultivable caliciviruses from clinically normal mink and enteric caliciviruses associated with diarrhea in mink. Arch. Virol. 146, 479–493 (2001). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050170157
V. Martella, M. Campolo, E. Lorusso, P. Cavicchio, M. Camero, A.L. Bellacicco, N. Decaro, G. Elia, G. Greco, M. Corrente, C. Desario, S. Arista, K. Banyai, M. Koopmans, C. Buonavoglia, Norovirus in captive lion cub (Panthera leo). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 13, 1071–1073 (2007)
M. Kozak, Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 19867–19870 (1991)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Marion Koopmans, Harry Vennema, and Kim Green for helpful discussions and critical review of the manuscript. Special thanks to Denis L’Homme for enlightening discussions on phylogenies. This work was supported by the science division of the CFIA/ACIA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
L’Homme, Y., Sansregret, R., Plante-Fortier, É. et al. Genomic characterization of swine caliciviruses representing a new genus of Caliciviridae . Virus Genes 39, 66–75 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-009-0360-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-009-0360-3