Abstract
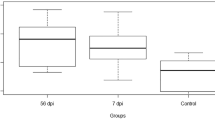
The interactions between gastric microbiota, ovine host, and Haemonchus contortus portray the ovine gastric environment as a complex ecosystem, where all factors play a pertinent role in fine-tuning each other and in haemeostasis. We delineated the impact of early and late Haemonchus infection on abomasal and ruminal microbial community, as well as the ovine host. Twelve, parasite-naive lambs were divided into four groups, 7 days post-infection (dpi) and time-matched uninfected-control groups; 50 dpi and time-matched uninfected control groups were used for the experiment. Six sheep were inoculated with 5000 H. contortus infective larvae and followed for 7 or 50 days with their corresponding uninfected-control ones. Ovine abomasal tissues were collected for histological analysis and gastric fluids were collected for PH value measurements, microbial community isolation and Illumina MiSeq platform and bioinformatic analysis. Our results showed that Haemonchus infection increased the abomasal gastric pH (P = 0.05) and resulted in necrotizing and inflammatory changes that were more severe during acute infection. Furthermore, infection increased the abomasal bacterial load and decreased the ruminal microbiome. A 7-day infection of sheep with H. contortus significantly altered approximately 98% and 94% of genera in the abomasal and ruminal bacterial profile, respectively (P = 0.04–0.05). However, the approximate altered genera 50 days after infection in the ovine abomasal and ruminal microbiome were about 62% and 69%, correspondingly (P = 0.04–0.05) with increase in some bacteria and decrease in others. Overall, these results indicate that Haemonchus infection plays a crucial role in shaping stomach microbial community composition, and diversity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams DB (1993) Systemic responses to challenge infection with Haemonchus contortus in immune merino sheep. Vet Res Commun 17(1):25–35
Alauzet C, Marchandin H, Lozniewski A (2010) New insights into Prevotella diversity and medical microbiology. Future Microbiol 5(11):1695–1718
Berrilli F, Di Cave D, Cavallero S, D'Amelio S (2012) Interactions between parasites and microbial communities in the human gut. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:141
Blitz NM, Gibbs HC (1971) Morphological characterizatioon of the stage of arrested development of Haemonchus contortus in sheep. Can J Zool 47(7):991–995
Bordoloi G, Jas R, Ghosh JD (2012) Changes in the haemato-biochemical pattern due to experimentally induced haemonchosis in Sahabadi sheep. J Parasit Dis : Off Organ Indian Soc Parasitol 36(1):101–105
Cantacessi C, Giacomin P, Croese J, Zakrzewski M, Sotillo J, McCann L, Nolan MJ, Mitreva M, Krause L, Loukas A (2014) Impact of experimental hookworm infection on the human gut microbiota. J Infect Dis 210(9):1431–1434
Christomanou H, Harzer K (1996) Ouchterlony double immunodiffusion method demonstrates absence of ferritin immunoreactivity in visceral organs from nine patients with Niemann-pick disease type C. Biochem Mol Med 58(2):176–183
Coop RL, Field AC (1983) Effect of phosphorus intake on growth rate, food intake and quality of the skeleton of growing lambs infected with the intestinal nematode Trichostrongylus vitrinus. Res Vet Sci 35(2):175–181
Dash KM (1985) Distribution of trichostrongylid nematodes in the abomasum of sheep. Int J Parasitol 15(5):505–510
Ding Y, Zou J, Li Z, Tian J, Abdelalim S, Du F, She R, Wang D, Tan C, Wang H et al (2011) Study of histopathological and molecular changes of rat kidney under simulated weightlessness and resistance training protective effect. PLoS One 6(5):e20008
Douch PG, Morum PE (1993) The effect of age on the response of Romney sheep to gastrointestinal nematodes during grazing. Int J Parasitol 23(5):651–655
Douch PG, Green RS, Morris CA, McEewan JC, Windon RG (1996) Phenotypic markers for selection of nematode-resistant sheep. Int J Parasitol 26(8–9):899–911
El-Ashram S, Suo X (2017) Exploring the microbial community (microflora) associated with ovine Haemonchus contortus (macroflora) field strains. Sci Rep 7(1):70
El-Ashram S, Al Nasr I, Suo X (2016) Nucleic acid protocols: Extraction and optimization. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 12:33–39
El-Ashram S, Al Nasr I, El-Kemary M, Mehmood R, Hu M, Suo X (2017) Early and late gene expression profiles of the ovine mucosa in response to Haemonchus contortus infection employing Illumina RNA-seq technology. Parasitol Int 66(5):681–692
Fausto GC, Pivoto FL, Costa MM, dos Anjos Lopes ST, Franca RT, Molento MB, Minervino AH, da Rocha JB, Leal ML (2014) Protein profile of lambs experimentally infected with Haemonchus contortus and supplemented with selenium and copper. Parasit Vectors 7:355
Forbes JD, Van Domselaar G, Bernstein CN (2016) The gut microbiota in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Front Microbiol 7:1081
Gasso D, Feliu C, Ferrer D, Mentaberre G, Casas-Diaz E, Velarde R, Fernandez-Aguilar X, Colom-Cadena A, Navarro-Gonzalez N, Lopez-Olvera JR et al (2015) Uses and limitations of faecal egg count for assessing worm burden in wild boars. Vet Parasitol 209(1–2):133–137
Gruner L, Aumont G, Getachew T, Brunel JC, Pery C, Cognie Y, Guerin Y (2003) Experimental infection of black belly and INRA 401 straight and crossbred sheep with trichostrongyle nematode parasites. Vet Parasitol 116(3):239–249
Haemonchus contortus and Haemonchosis -- past, present and future trends (2016) [http://public.eblib.com/choice/publicfullrecord.aspx?p=4533856]
Hertzberg H, Guscetti F, Lischer C, Kohler L, Neiger R, Eckert J (2000) Evidence for a parasite-mediated inhibition of abomasal acid secretion in sheep infected with Ostertagia leptospicularis. Vet J (London, England : 1997) 159(3):238–251
Hertzberg H, Huwyler U, Kohler L, Rehbein S, Wanner M (2002) Kinetics of exsheathment of infective ovine and bovine strongylid larvae in vivo and in vitro. Parasitology 125(Pt 1):65–70
Honde C, Bueno L (1982) Haemonchus contortus: egg laying influenced by abomasal pH in lambs. Exp Parasitol 54(3):371–378
Hoste H, Torres-Acosta JF, Aguilar-Caballero AJ (2008) Nutrition-parasite interactions in goats: is immunoregulation involved in the control of gastrointestinal nematodes? Parasite Immunol 30(2):79–88
Idris A, Moors E, Budnick C, Herrmann A, Erhardt G, Gauly M (2011) Is the establishment rate and fecundity of Haemonchus contortus related to body or abomasal measurements in sheep? Anim : An Int J Anim Biosci 5(8):1276–1282
Javanbakht J, Hosseini E, Mousavi S, Hassan MA, Salehzadeh Kazeroni S, Khaki F, Fattahi R, Jani M, Alimohammadi S (2014) Evaluation of two Iranian domestic ovine breeds for their pathological findings to gastrointestinal infection of Haemonchus contortus. J Parasit Dis : Off Organ Indian Soc Parasitol 38(3):311–316
Kringel H, Iburg T, Dawson H, Aasted B, Roepstorff A (2006) A time course study of immunological responses in Trichuris suis infected pigs demonstrates induction of a local type 2 response associated with worm burden. Int J Parasitol 36(8):915–924
Lee YK, Mazmanian SK (2010) Has the microbiota played a critical role in the evolution of the adaptive immune system. Sci (New York, NY) 330(6012):1768–1773
Lee SC, Tang MS, Lim YA, Choy SH, Kurtz ZD, Cox LM, Gundra UM, Cho I, Bonneau R, Blaser MJ et al (2014) Helminth colonization is associated with increased diversity of the gut microbiota. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(5):e2880
Li RW, Wu S, Li W, Huang Y, Gasbarre LC (2011) Metagenome plasticity of the bovine abomasal microbiota in immune animals in response to Ostertagia ostertagi infection. PLoS One 6(9):e24417
Li RW, Wu S, Li W, Navarro K, Couch RD, Hill D, Urban JF Jr (2012) Alterations in the porcine colon microbiota induced by the gastrointestinal nematode Trichuris suis. Infect Immun 80(6):2150–2157
Li RW, Li W, Sun J, Yu P, Baldwin RL, Urban JF (2016) The effect of helminth infection on the microbial composition and structure of the caprine abomasal microbiome. Sci Rep 6:20606
Louvandini H, Veloso CF, Paludo GR, Dell'Porto A, Gennari SM, McManus CM (2006) Influence of protein supplementation on the resistance and resilience on young hair sheep naturally infected with gastrointestinal nematodes during rainy and dry seasons. Vet Parasitol 137(1–2):103–111
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8228–8235
Miller JE, Horohov DW (2006) Immunological aspects of nematode parasite control in sheep. J Anim Sci 84(Suppl):E124–E132
Mizrahi-Man O, Davenport ER, Gilad Y (2013) Taxonomic classification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes using short sequencing reads: evaluation of effective study designs. PLoS One 8(1):e53608
Nicholls CD, Hayes PR, Lee DL (1987) Physiological and microbiological changes in the abomasum of sheep infected with large doses of Haemonchus contortus. J Comp Pathol 97(3):299–308
O'Connor LJ, Walkden-Brown SW, Kahn LP (2006) Ecology of the free-living stages of major trichostrongylid parasites of sheep. Vet Parasitol 142(1–2):1–15
Ondov BD, Bergman NH, Phillippy AM (2011) Interactive metagenomic visualization in a web browser. BMC Bioinf 12:385
Ouchterlony O (1958) Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy 5:1–78
Plieskatt JL, Deenonpoe R, Mulvenna JP, Krause L, Sripa B, Bethony JM, Brindley PJ (2013) Infection with the carcinogenic liver fluke Opisthorchis Viverrini modifies intestinal and biliary microbiome. FASEB J : Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 27(11):4572–4584
Qi J, Asl HF, Bjorkegren J, Michoel T (2014) kruX: matrix-based non-parametric eQTL discovery. BMC Bioinf 15:11
Rahman WA, Collins GH (1990) The establishment and development of Haemonchus contortus in goats. Vet Parasitol 35(3):189–193
Rahman WA, Collins GH (1991) Infection of goats with Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis: histopathology and pH changes. Br Vet J 147(6):569–574
Roeber F, Jex AR, Gasser RB (2013) Impact of gastrointestinal parasitic nematodes of sheep, and the role of advanced molecular tools for exploring epidemiology and drug resistance - an Australian perspective. Parasit Vectors 6:153
Rutter JM, Beer RJ (1975) Synergism between Trichuris suis and the microbial flora of the large intestine causing dysentery in pigs. Infect Immun 11(2):395–404
Saemann MD, Bohmig GA, Osterreicher CH, Burtscher H, Parolini O, Diakos C, Stockl J, Horl WH, Zlabinger GJ (2000) Anti-inflammatory effects of sodium butyrate on human monocytes: potent inhibition of IL-12 and up-regulation of IL-10 production. FASEB J : Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 14(15):2380–2382
Salman SK, Duncan JL (1984) The abomasal histology of worm-free sheep given primary and challenge infections of Haemonchus contortus. Vet Parasitol 16(1–2):43–54
Shin JL, Gardiner GW, Deitel W, Kandel G (2004) Does whipworm increase the pathogenicity of campylobacter jejuni? A clinical correlate of an experimental observation. Can J Gastroenterol = J Can de Gastroenterol 18(3):175–177
Simcock DC, Joblin KN, Scott I, Burgess DM, Rogers CW, Pomroy WE, Simpson HV (1999) Hypergastrinaemia, abomasal bacterial population densities and pH in sheep infected with Ostertagia circumcincta. Int J Parasitol 29(7):1053–1063
Simpson HV, Lawton DE, Simcock DC, Reynolds GW, Pomroy WE (1997) Effects of adult and larval Haemonchus contortus on abomasal secretion. Int J Parasitol 27(7):825–831
Stear MJ, Bishop SC, Doligalska M, Duncan JL, Holmes PH, Irvine J, McCririe L, McKellar QA, Sinski E, Murray M (1995) Regulation of egg production, worm burden, worm length and worm fecundity by host responses in sheep infected with Ostertagia circumcincta. Parasite Immunol 17(12):643–652
Strain SA, Stear MJ (2001) The influence of protein supplementation on the immune response to Haemonchus contortus. Parasite Immunol 23(10):527–531
Vadlejch J, Petrtyl M, Zaichenko I, Cadkova Z, Jankovska I, Langrova I, Moravec M (2011) Which McMaster egg counting technique is the most reliable? Parasitol Res 109(5):1387–1394
Vazquez-Baeza Y, Pirrung M, Gonzalez A, Knight R (2013) EMPeror: a tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. GigaScience 2(1):16
Watson Tg HBC (1993) Establishment of resistance to Haemonchus contortus by saanen kids, vol 53. Society of Animal Production, New Zealand
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R et al (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Sci (New York, NY) 334(6052):105–108
Wu S, Li RW, Li W, Beshah E, Dawson HD, Urban JF Jr (2012) Worm burden-dependent disruption of the porcine colon microbiota by Trichuris suis infection. PLoS One 7(4):e35470
Wu X, Zhang H, Chen J, Shang S, Wei Q, Yan J, Tu X (2016) Comparison of the fecal microbiota of dholes high-throughput Illumina sequencing of the V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(8):3577–3586
Zaiss MM, Harris NL (2016) Interactions between the intestinal microbiome and helminth parasites. Parasite Immunol 38(1):5–11
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program (973 program) of China (Grant No. 2015CB150300), and the Start-up Research Grant Program provided by Foshan University, Foshan city, Guangdong province for distinguished researchers. Additionally, the funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Revising the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 186 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Ashram, S., Al Nasr, I., Abouhajer, F. et al. Microbial community and ovine host response varies with early and late stages of Haemonchus contortus infection. Vet Res Commun 41, 263–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-017-9698-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-017-9698-5