Abstract
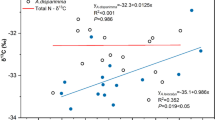
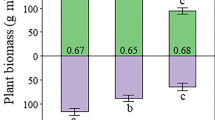
N and P concentrations and their ratios were determined for 132 foliar and 120 below-ground biomass (BGB) samples obtained at 132 sites along the 4500 km Chinese Grassland Transect (CGT) across the Inner Mongolian and Qinghai–Tibet Plateaus. Patterns of foliar and BGB N, P and their ratio (N/P) at the community level were related to altitude, temperature, and precipitation gradients. Also, patterns of relative N and P foliar and BGB concentrations were determined (NF/B, foliar N/BGB N; PF/B, foliar P/BGB P). The relationship between foliar N concentrations and mean annual temperature (MAT) was negative, agreeing with the Temperature-Plant Physiological hypothesis, whereas BGB N decreased with decreasing MAT, supporting the Biogeochemical hypothesis. Patterns of BGB N varying with altitude, MAP and MAT differed from the patterns for leaf N, which may indicate differences in nutrient allocation and utilization by leaves and BGB. NF/B and PF/B may reflect trade-offs by plants for N and P in leaves and BGB. For the entire CGT, NF/B and PF/B increased as altitude increased. NF/B was positively related with MAP but negatively related with MAT, while PF/B showed no correlations with MAP and MAT. Results suggest that ecological stoichiometry at the community level is similar to that at the species level. Strategies of nutrient utilization by leaves and BGB are indicated to be different, and abiotic environmental conditions could influence the stoichiometric characteristics and nutrient allocation to leaves and BGB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Chapin FS (2000) The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and patterns. Adv Ecol Res 30:1–67. doi:10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60016-1
Craine JM, Lee WG (2003) Covariation in leaf and root traits for native and non-native grasses along an altitudinal gradient in New Zealand. Oecologia 134:471–478. doi:10.1007/s00442-002-1155-6
Craine JM, Froehle J, Tilman DG, Wedin DA, Chapin FS (2001) The relationships among root and leaf traits of 76 grassland species and relative abundance along fertility and disturbance gradients. Copenhagen. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0706.2001.930210.x
Craine JM, Lee WG, Bond WJ, Williams RJ, Johnson LC (2005) Environmental constraints on a global relationship among leaf and root traits of grasses. Ecology 86:12–19. doi:10.1890/04-1075
Elser JJ, Fagan WF, Kerkhoff AJ, Swenson NG, Enquist BJ (2010) Biological stoichiometry of plant production: metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol 186:593–608. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03214.x
Fan J, Zhong H, Harris W, Yu G, Wang S, Hu Z, Yue Y (2008) Carbon storage in the grasslands of China based on field measurements of above- and below-ground biomass. Clim Change 86:375–396. doi:10.1007/s10584-007-9316-6
Fan J, Wang K, Harris W, Zhong H, Hu Z, Han B, Zhang W, Wang J (2009) Allocation of vegetation biomass across a climate-related gradient in the grasslands of Inner Mongolia. J Arid Environ 73:521–528. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2008.12.004
Fan J, Harris W, Zhong H (2016) Stoichiometry of leaf nitrogen and phosphorus of grasslands of the Inner Mongolian and Qinghai-Tibet Plateaus in relation to climatic variables and vegetation organization levels. Ecol Res. doi:10.1007/s11284-016-1392-5
Geng Y, Wang L, Jin D, Liu H, He J (2014) Alpine climate alters the relationships between leaf and root morphological traits but not chemical traits. Oecologia 175:445–455. doi:10.1007/s00442-014-2919-5
Gordon WS, Jackson RB (2000) Nutrient concentrations in fine roots. Ecology 81:275–280
Güsewell S (2004) N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: variation and functional significance. New Phytol 164:243–266. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01192.x
Güsewell S, Koerselman M (2002) Variation in nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations of wetland plants. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Syst 5:37–61. doi:10.1078/1433-8319-0000022
Han W, Fang J, Guo D, Zhang Y (2005) Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol 168:377–385. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01530.x
He J, Fang J, Wang Z, Guo D, Flynn DFB, Geng Z (2006) Stoichiometry and large-scale patterns of leaf carbon and nitrogen in the grassland biomes of China. Oecologia 149:115–122. doi:10.1007/s00442-006-0425-0
He J, Wang L, Flynn DFB, Wang X, Ma W, Fang J (2008) Leaf nitrogen:phosphorus stoichiometry across Chinese grassland biomes. Oecologia 155:301–310. doi:10.1007/s00442-007-0912-y
Hobbie SE, Schimel JP, Trumbore SE, Randerson JR (2000) Controls over carbon storage and turnover in high-latitude soils. Glob Change Biol 6:196–210. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.06021.x
Holdaway RJ, Richardson SJ, Dickie IA, Peltzer DA, Coomes DA (2011) Species- and community-level patterns in fine root traits along a 120000-year soil chronosequence in temperate rain forest. J Ecol 99:954–963. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2011.01821.x
Hu Z, Yu G, Fan J, Zhong H, Wang S, Li S (2010) Precipitation-use efficiency along a 4500-km grassland transect. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 19:842–851. doi:10.1111/j.1466-8238.2010.00564.x
Kembel SW, Cahill JF (2011) Independent evolution of leaf and root traits within and among temperate grassland plant communities. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019992
Kerkhoff AJ, Enquist BJ, Elser JJ, Fagan WF (2005) Plant allometry, stoichiometry and the temperature-dependence of primary productivity. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 14:585–598. doi:10.1111/j.1466-822x.2005.00187.x
Kerkhoff AJ, Fagan WF, Elser JJ, Enquist BJ (2006) Phylogenetic and growth form variation in the scaling of nitrogen and phosphorus in the seed plants. Am Nat 168:103–122. doi:10.1086/507879
Lambers H, Raven JA, Shaver GR, Smith SE (2008) Plant nutrient-acquisition strategies change with soil age. Trends Ecol Evol 23:95–103. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2007.10.008
Lambers H, Brundrett MC, Raven JA, Hopper SD (2010) Plant mineral nutrition in ancient landscapes: high plant species diversity on infertile soils is linked to functional diversity for nutritional strategies. Plant Soil 334:11–31. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0444-9
Liu G, Freschet G, Pan X, Cornelissen JHC, Li Y, Dong M (2010) Coordinated variation in leaf and root traits across multiple spatial scales in Chinese semi-arid and arid ecosystems. New Phytol 188:543–553. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03388.x
Lu X, Kong D, Pan Q, Simmons ME, Han X (2012) Nitrogen and water availability interact to affect leaf stoichiometry in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia 168:301–310. doi:10.1007/s00442-011-2097-7
McGroddy ME, Daufresne T, Hedin LO (2004) Scaling of C:N: P stoichiometry in forests worldwide implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios. Ecology 85(9):2390–2401. doi:10.1890/03-0351
Pan F, Zhang W, Liu S, Li D, Wang K (2015) Leaf N: P stoichiometry across plant functional groups in the karst region of southwestern China. Trees-Struct Funct 29:883–892. doi:10.1007/s00468-015-1170-y
Reich PB, Oleksyn J (2004) Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11001–11006. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403588101
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Tian H, Wang S, Liu J, Pan S, Chen H, Zhang C, Shi X (2006) Patterns of soil nitrogen storage in China. Global Biogeochem Cycles 20:9. doi:10.1029/2005gb002464
Tjoelker MG, Craine JM, Wedin D, Reich PB, Tilman D (2005) Linking leaf and root trait syndromes among 39 grassland and savannah species. New Phytol 167:493–508. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01428.x
Vitousek PM, Porder S, Houlton BZ, Chadwick OA (2010) Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol Appl 20:5–15. doi:10.1890/08-0127.1
Wright IJ et al (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 428:821–827. doi:10.1038/nature02403
Xu S, Fan X, Wang L, Zhang X, An L (2015) The patterns of nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across communities along altitudinal gradients in Qilian Mountains, China. Biochem Syst Ecol 62:58–65. doi:10.1016/j.bse.2015.07.037
Yuan Z, Chen H (2010) Fine root biomass, production, turnover rates, and nutrient contents in boreal forest ecosystems in relation to species, climate, fertility, and stand age: literature review and meta-analyses. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29:204–221. doi:10.1080/07352689.2010.483579
Yuan Z, Chen H, Reich PB (2011) Global-scale latitudinal patterns of plant fine-root nitrogen and phosphorus. Nat commun 2:344. doi:10.1038/ncomms1346
Zhao N, He N, Wang Q, Zhang X, Wang R, Xu Z, Yu G (2014) The altitudinal patterns of leaf C:N: P stoichiometry are regulated by plant growth form, climate and soil on Changbai mountain. China. Plos One 9:9. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095196
Zhou Y, Fan J, Zhong H, Zhang W (2013) Relationships between altitudinal gradient and plant carbon isotope composition of grassland communities on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sci China-Earth Sci 56:311–320. doi:10.1007/s11430-012-4498-9
Acknowledgements
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 31070427 and Science and Technology Major Project of Qinghai Province (Grant No. 2015-SF-A4-1). We are grateful to Haiyan Zhang for her help in improving the figures, and Huaping Zhong, Yongchun Zhou, Wenyan Zhang, Bin Han, Zhongmin Hu, and Lulu Song for helping with field measurements. We thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions to improve the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Kun-Fang Cao.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Fan, J., Harris, W. et al. Relationships between below-ground biomass and foliar N:P stoichiometry along climatic and altitudinal gradients of the Chinese grassland transect. Plant Ecol 218, 661–671 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-017-0719-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-017-0719-9