Abstract
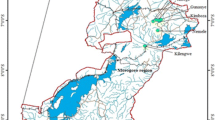
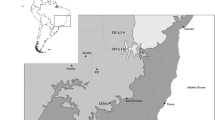
In order to reveal the characteristics of the vegetation affected by monsoons at the northern border of Paleotropics, a tree-by-tree census was conducted in the lowland forests in the southernmost Taiwan (Nanjenshan) and an adjacent islet (Lanyu). The census recorded a total of 109,060 individuals (≥1-cm diameter at breast height) belonging to 255 vascular tree species in 1330 quadrats (10 × 10 m). Two-way Indicator Species Analysis first classified forest types into two groups, Lanyu and Nanjenshan, reflecting biogeographical differences. Five subgroups were further classified, showing correlations with topographic position indices. Forests located on wind-exposed slopes, regardless of elevations, were characterised by low canopy height, high stem density, high proportion of small stems, and high proportion of warm-temperate-related species, compared with the wind-sheltered communities. However, there were no significant differences in basal area and species diversity. In comparison with other tropical forests, our forests are characterised by high stem density, low diversity and a lack of the pan-Paleotropical dominant Dipterocarpaceae. In conclusion, vegetation in the studied regions not only showed a transition characteristic between Paleotropics and Holarctic Kingdoms in terms of composition, but also showed differentiations caused by their biogeographical history and the interaction between topographic positions and wind stress from monsoons.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCA:
-
Detrended Correspondence Analysis
- DBH:
-
Diameter at breast height
- IVI:
-
Importance value index
- TWINSPAN:
-
Two-way Indicator Species Analysis
References
Aiba S, Kitayama K, Takyu M (2004) Habitat associations with topography and canopy structure of tree species in a tropical montane forest on Mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Plant Ecol 174:147–161
Chao K-J (2001) Short-term dynamics of woody floristic community in a lowland rain forest, Nanjenshan, southern Taiwan, National Taiwan University, Taipei. (In Chinese, with English abstract)
Chao W-C, Chao K-J, Song G-ZM, Hsieh C-F (2007) Species composition and structure of the lowland subtropical rainforest at Lanjenchi, Southern Taiwan. Taiwania 52:253–269
Chen Z-S, Hsieh C-F, Jiang F-Y, Hsieh T-H, Sun I-F (1997) Relationship of soil properties to topography and vegetation in a subtropical rain forest in southern Taiwan. Plant Ecol 132:229–241
Chiou C-R, Song G-ZM, Chien J-H, Hsieh C-F, Wang J-C, Chen M-Y, Liu H-Y, Yeh C-R, Yang S-Z, Chen T-Y (in press) The winter monsoon, rather than the Massenerhebung effect, determines the altitudinal distribution patterns of plant species in Taiwan. Bot Stud
Chytrý M, Tichý L (2003) Diagnostic, constant and dominant species of vegetation classes and alliances of the Czech Republic: a statistical revision. Folia Fac Sci Nat Univ Masaryk Brun Biol 108:1–231
Co LL, Lagunzad DA, LaFrankie JV, Bartolome NA, Molina JE, Yap SL, Garcia HG, Bautista JP, Gumpal EG, Arano RR, Davies SJ (2004) Palanan forest dynamics plot, Philippines. In: Losos EC, Leigh EG Jr (eds) Forest diversity and dynamism: findings from a large-scale plot network. Chicago University Press, Chicago, pp 574–584
Condit RS, Leigh EG Jr, de Loo Lao S, CTFS Work Group (2004) Species-area relationships and diversity measures in the Forest Dynamics Plots. In: Losos EC, Leigh EG Jr (eds) Tropical forest diversity and dynamism: findings from a large-scale plot network. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 79–89
Fan S-W, Chao W-C, Hsieh C-F (2005) Woody floristic composition, size class distribution and spatial pattern of a subtropical lowland rainforest at Nanjen lake, southernmost Taiwan. Taiwania 50:307–326
Fisher RA, Corbet AS, Williams CB (1943) The relation between the number of species and the number of individuals in a random sample of an animal population. J Anim Ecol 12:42–58
Heywood VH, Brummitt RK, Culham A, Seberg O (2007) Flowering plant families of the world. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London
Hill MO (1979) TWINSPAN—A FORTRAN program for arranging multivariate data in an ordered two-way data in an ordered two-way table by classification of the individuals and attributes. Cornell University, Ithaca, New York
Hill MO, Gauch HG (1980) Detrended correspondence analysis—An improved ordination technique. Vegetatio 42:47–58
Hsieh C-F (2003) Composition, endemism and phytogeographical affinities of the Taiwan Flora. In: Huang TC (ed) Flora of Taiwan. Department of Botany, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, pp 1–14
Hsieh CF, Chen ZS, Hsu YM, Kang KC, Hsieh TH (1998) Altitudinal zonation of evergreen broad-leaved forest on Mount Lopei, Taiwan. J Veg Sci 9:205–206
Hsieh CF, Sun IF, Yang CC (2000) Species composition and vegetation pattern of a lowland rain forest at Nanjenshan LTER site, Southern Taiwan. Taiwania 45:107–119
Hu Z-Z, Bengtsson L, Arpe K (2000) Impact of global warming on the Asian winter monsoon in a coupled GCM. J Geophys Res 105:4607–4624
Huang T-C & Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan (1993–2003) Flora of Taiwan. Department of Botany, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
Kawakami T, Sasaki S (1915) List of plants in Lanyu Island, Formosa. Transactions of the Natural History Society Formosa 5:1–23
Lawton RO (1982) Wind stress and elfin stature in a montane rain forest tree: an adaptive explanation. Am J Bot 69:1224–1230
Liao C-C (1995) Altitudinal variation in composition, structure, diversity and distribution pattern of the subtropical rain forest in Nanjenshan. Master Thesis, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan. (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Lichtenthaler HK (1996) Vegetation stress: an introduction to the stress concept in plants. J Plant Physiol 148:4–14
Lin H-Y, Yang K-C, Hsieh T-H, Hsieh C-F (2005) Species composition and structure of a montane rainforest of Mt. Lopei in northern Taiwan. Taiwania 50:234–249
Liu T-S, Lin T-T (1978) Studies on the vegetation and flora of Lanyu. Annu Taiwan Mus 21:1–80
Losos EC, CTFS Work Group (2004) The structure of tropical forests. In: Losos EC, Leigh EG Jr (eds) Tropical forest diversity and dynamism: findings from a large-scale plot network. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 69–78
Mabry CM, Hamburg SP, Lin TC, Horng FW, King HB, Hsia YJ (1998) Typhoon disturbance and stand-level damage patterns at a subtropical forest in Taiwan. Biotropica 30:238–250
Manokaran N, Quah ES, AShton PS, LaFrankie JV, Noor NSM, Ahmad WMSW, Okuda T (2004) Pasoh forest dynamics plot, Peninsular Malaysia. In: Losos EC, Leigh EG Jr (eds) Tropical forest diversity and dynamism: findings from a large-scale plot network. Chicago University Press, Chicago, pp 585–598
McCune B, Mefford MJ (2006) PC-ORD. Multivariate analysis of ecological data, version 5. MjM software. Gleneden Beach, Oregon, USA
Miyake K (1902) A list of ferns found in Lanyu Island, Formosa. Botanical magazine. Tokyo 16:45–52
Ota H (1998) Geographic patterns of endemism and speciation in amphibians and reptiles of the Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan, with special reference to their paleogeographical implications. Res Popul Ecol 40:189–204
Sasaki S (1913) An account of the vegetation of Lanyu Island, Formosa. Trans Nat Hist Soc Formosa 3:35
Su H-J (1984) Studies on the climate and vegetation types of the natural forests in Taiwan (I): analysis of the variations in climate factors. Q J Chin For 17:1–14
Sukumar R, Suresh HS, Dattaraja HS, John R, Joshi NV (2004) Mudumalai forest dynamics plot, India. In: Losos EC, Leigh EG Jr (eds) Tropical forest diversity and dynamism: findings from a large-scale plot network. Chicago University Press, Chicago, pp 551–563
Sun I-F (1993) The species composition and forest structure of a subtropical rain forest at southern Taiwan. PhD Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, USA
Sun I-F, Hsieh CF, Hubbell SP (1998) The structure and species composition of a subtropical monsoon forest in southern Taiwan on a steep wind-stress gradient. In: Dallmeier F, Comiskey JA (eds) Forest Biodiversity Research, monitoring and modeling: conceptual background and old word case studies. Parthenon Publishing Co, Paris, France, pp 565–635
Takhtajan A (1986) Floristic regions of the world. University of California Press, California
Wang C (2004a) Features of monsoon, typhoon and sea waves in the Taiwan Strait. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 22:133–150
Wang W-M (2004b) The impact to vegetation by the Yami in Lanyu. Master Thesis, The National Tainan Teachers College, Tainan. (In Chinese with English Abstract)
White PS, Pickett STA (1985) The ecology of natural disturbance and patch dynamics. Academic Press, Orlando, Florida
Whitmore TC (1998) An introduction to tropical rain forests. Oxford University Press, New York
Yang C-C (1994) Woody floristic composition, structure and distribution pattern of the tropical seasonal forest in Nanjenshan Area. National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
Yasuhiro K, Hirofumi M, Kihachiro K (2004) Effects of topographic heterogeneity on tree species richness and stand dynamics in a subtropical forest in Okinawa Island, southern Japan. J Ecol 92:230–240
Yen M-C, Chen T-C (2000) Seasonal variation of the rainfall over Taiwan. Int J Climatol 20:803–809
Yu F-C, Chen T-C, Lin M-L, Chen C-Y, Yu W-H (2006) Landslides and rainfall characteristics analysis in Taipei City during the Typhoon Nari event. Nat Hazards 37:153–167
Acknowledgements
Valuable contributions were made in the field by numerous volunteers. We thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their crucial comments. We also thank the financial support of Kenting National Park and the National Science Council, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nomenclature source: Huang & Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan (1993–2003).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, WC., Song, GZ.M., Chao, KJ. et al. Lowland rainforests in southern Taiwan and Lanyu, at the northern border of Paleotropics and under the influence of monsoon wind. Plant Ecol 210, 1–17 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9694-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9694-0